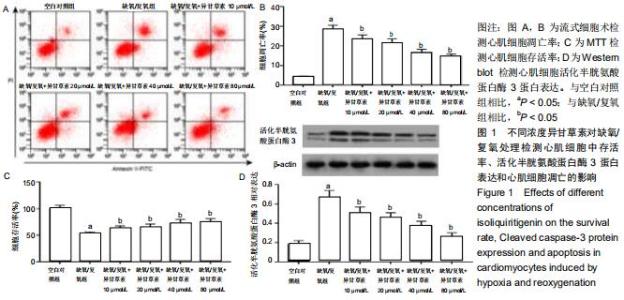
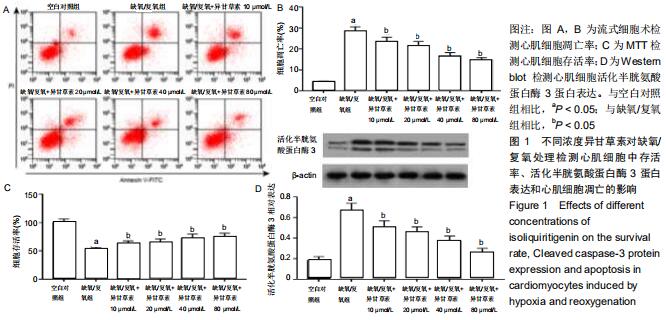
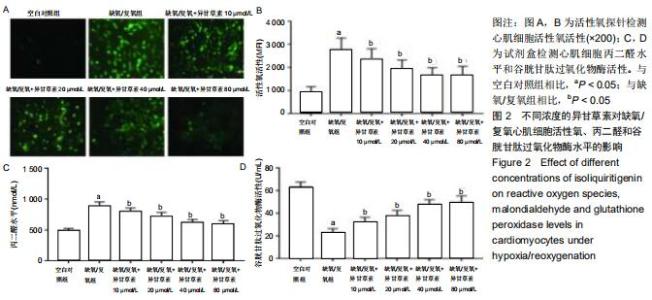
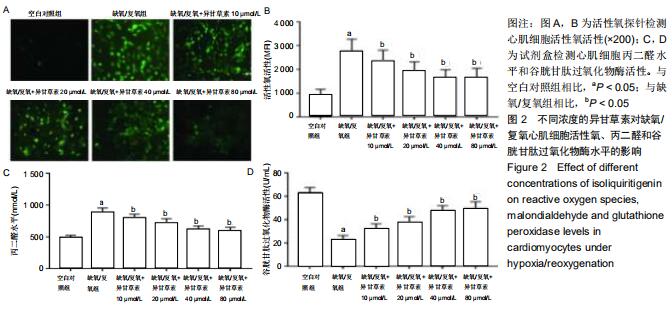
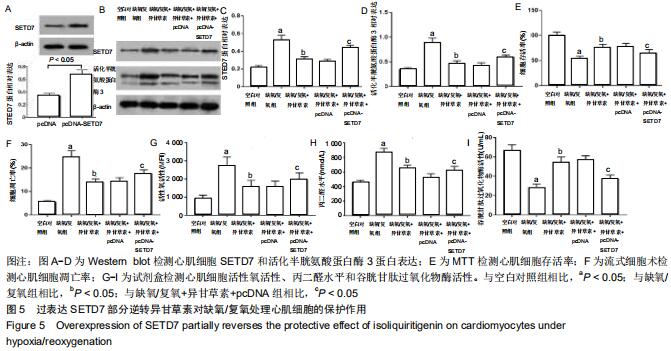
|
[1] SUN L, FAN H, YANG L, et al. Tyrosol prevents ischemia/ reperfusion- induced cardiac injury in H9c2 cells: involvement of ROS, Hsp70, JNK and ERK, and apoptosis. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):3758-3775.
[2] 李利娟,马彦卓,孔令锋,等.载脂蛋白J对缺氧/复氧诱导的乳鼠心肌细胞损伤的影响[J].重庆医学, 2016, 45(33):4612-4615.
[3] CHANG G, ZHANG D, YU H, et al. Cardioprotective effects of exenatide against oxidative stress-induced injury. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 32(5):1011-1020.
[4] 任欢欢,韩吉春,卢宁,等.异甘草素对心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 34(3):343-348.
[5] 郑梅,郝小龙,阴英,等.异甘草素减轻重症急性胰腺炎小鼠心肌损伤机制[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2019, 21(2):71-74.
[6] ZHANG M, WU Y, XIE L, et al. Isoliquiritigenin protects against bloodgainst oxidative stress-induced injuryinvolvement f pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice after traumatic brain injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018; 65(1): 64-75.
[7] DANG Y, MA X, LI Y, et al. Inhibition of SETD7 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury through regulating Keap1/Nrf2 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 106(1):842-849.
[8] 陈赵玲,马建群,夏雪艳,等.MicroRNA-181a调控缺氧/复氧诱导下心肌细胞的凋亡[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2015, 31(6):664-669.
[9] 章道华,叶岚岚,程昊,等.异甘草素对醋氨酚诱导的急性肝细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2008,13(3):293-298.
[10] 彭辉,张华龙.地黄多糖对乳鼠心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤后氧化应激和细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016, 22(23):155-160.
[11] 蒋有琴,刘剑,张冬颖.京尼平对缺氧/复氧心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的影响[J].中国药学杂志,2016,51(1):28-34.
[12] 杜烨湘,罗敏,冯敏.甘草素通过抗炎发挥对阿尔茨海默病的保护作用[J]. 免疫学杂志,2019,35(4):327-333.
[13] 张岩,冯超,韩吉春,等.甘草素减轻大鼠离体心肌缺血再灌注损伤作用研究[J].天然产物研究与开发,2017,29(9):41-46.
[14] ZHANG X, ZHU P, ZHANG X, et al. Natural antioxidant-isoliquiritigenin ameliorates contractile dysfunction of hypoxic cardiomyocytes via AMPK signaling pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2013; 2013(1):390890-390900.
[15] 王秀云,吴新荣,余金十.黄连素对缺氧/复氧诱导的心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2018,17(1):1826-1829.
[16] ZHOU X, CHANG B, GU Y. MicroRNA-21 abrogates palmitate-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through caspase-3/NF-κB signal pathways. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018;20(6): 336-346.
[17] GAO Z, GAO Q, LV X. MicroRNA-668-3p Protects Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in a Rat H9c2 Cardiomyocyte Model of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Targeting the Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2020; 26(1): e919601-e919611.
[18] WEN Z, MAI Z, ZHU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in hypoxic conditions through microRNA144 by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1): 36-46.
[19] 韩学超,徐菁蔓,徐森,等.线粒体通透性转换孔在天麻素抗心肌细胞氧化应激损伤中的作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2018,38(11):1306-1311.
[20] 应婷婷,周纲,郭小琴,等.丙泊酚联合槲皮素对氧化应激条件下心肌细胞凋亡影响研究[J].中国药师,2019,22(2):201-205.
[21] GUO W, LIU X, LI J, et al. Prdx1 alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis through ROS-activated MAPK pathway during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;112(1): 608-615.
[22] KUO CY, CHIU YC, LEE AY, et al. Mitochondrial Lon protease controls ROS-dependent apoptosis in cardiomyocyte under hypoxia. Mitochondrion. 2015;23(1): 7-16.
[23] FARIDVAND Y, HADDADI P, VAHEDIAN V, et al. Human Amnion Membrane Proteins Prevent Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress Injury and Apoptosis in Rat H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020; 21(1): 1-12.
[24] XIA K, ZHANG Y, SUN D. miR‑217 and miR‑543 downregulation mitigates inflammatory response and myocardial injury in children with viral myocarditis by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK/NF‑κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(2): 634-646.
[25] AGBO E, LI MX, WANG YQ, et al. Hexarelin protects cardiac H9C2 cells from angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy via the regulation of autophagy. Pharmazie. 2019; 74(8): 485-491.
[26] WANG Z, BU L, YANG P, et al. Alleviation of sepsis‑induced cardiac dysfunction by overexpression of Sestrin2 is associated with inhibition of p‑S6K and activation of the p‑AMPK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 20(3): 2511-2518.
[27] CHEN Y, WU S, ZHANG XS, et al. MicroRNA-489 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting SPIN1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(15): 6683-6690.
[28] ZHANG X, RUI L, LV B, et al. Adiponectin relieves human adult cardiac myocytes injury induced by intermittent hypoxia. Med Sci Monit. 2019; 25(1): 786-793.
[29] GUO S, YAO Q, KE Z, et al. Resveratrol attenuates high glucose- induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 412(1): 85-94.
[30] SONG H, FENG X, ZHANG M, et al. Crosstalk between lysine methylation and phosphorylation of ATG16L1 dictates the apoptosis of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocytes. Autophagy. 2018; 14(5):825-844.
[31] HE S, OWEN DR, JELINSKY SA, et al. Lysine Methyltransferase SETD7 (SET7/9) Regulates ROS Signaling through mitochondria and NFE2L2/ARE pathway. Sci Rep. 2015; 5(1):14368-14378.
|