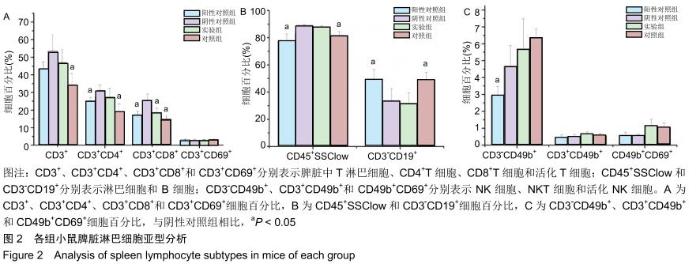
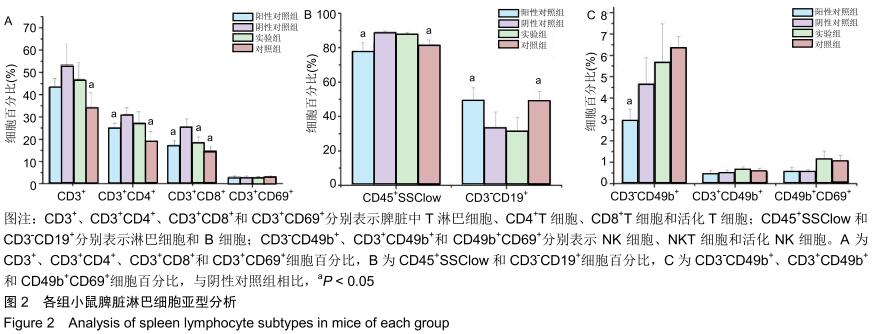
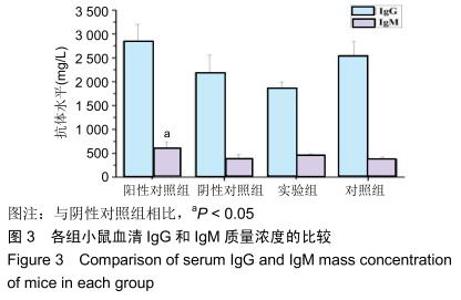
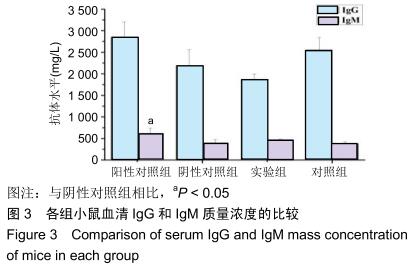
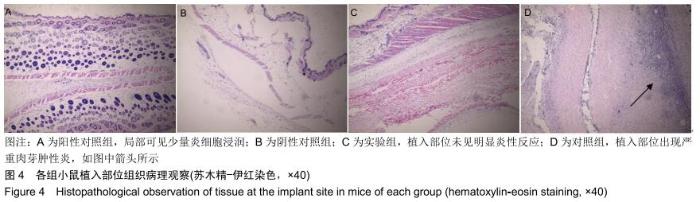
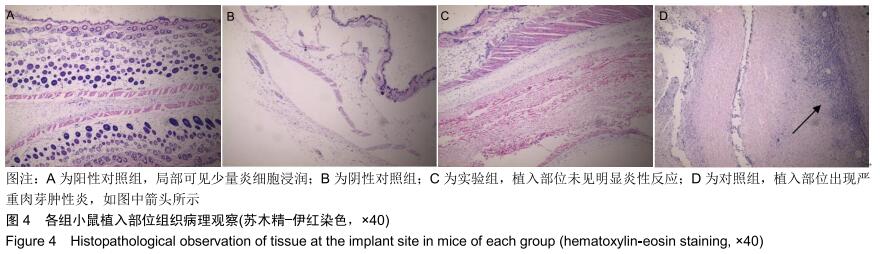
|
[1] LIU VW, HUANG PL. Cardiovascular roles of nitric oxide: a review of insights from nitric oxide synthase gene disrupted mice. Cardiovasc Res.2008;77(1):19-29.
[2] HIRSCH EM, DUMANIAN GA. Discussion: AlloDerm and Strattice in breast reconstruction: a comparison and techniques for optimizing outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg.2012; 129(6):1234-1235.
[3] SARAY A. Porcine dermal collagen (Permacol) for facial contour augmentation: preliminary report.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2003; 27(5):368-375.
[4] 罗晓.不同来源细胞外基质外科补片的生物学性质研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2013.
[5] 祖丽皮也•阿不力克木,古丽加玛丽,朱庆丰,等.巴沙鱼脱细胞鱼皮基质制备与生物相容性评价[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2019, 20(1):37-43.
[6] SMITH MJ, PARAN TS, QUINN F, et al. The SIS extracellular matrix scaffold-preliminary results of use in congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) repair.Pediatr Surg Int.2004; 20(11-12):859-862.
[7] 阴洪,任先军,蒋涛.脱细胞技术在同种异体组织工程支架中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(11):1010-1012.
[8] 殷猛,刘锦纷,藤里俊哉,等.超高压脱细胞技术制备组织工程带瓣血管支架[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19): 3605-3608.
[9] RAHMANI B, MCGREGOR C, BYRNE G, et al. A Durable Porcine Pericardial Surgical Bioprosthetic Heart Valve: a Proof of Concept.J Cardiovasc Transl Res.2019;12(4): 331-337.
[10] PRIVAT-MALDONADO A, BENGTSON C, RAZZOKOV J, et al. Modifying the Tumour Microenvironment: Challenges and Future Perspectives for Anticancer Plasma Treatments. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(12).pii: E1920.
[11] KIM GE, KWON TW, CHO YP, et al. Carotid endarterectomy with bovine patch angioplasty: a preliminary report. Cardiovasc Surg. 2001;9(5):458-462.
[12] 李鑫. Ephrin-B2和CD34阳性细胞参与血管成形术后心包补片愈合的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.
[13] MUSILKOVA J, FILOVA E, PALA J, et al. Human decellularized and crosslinked pericardium coated with bioactive molecular assemblies.Biomed Mater.2019;15(1):15008.
[14] 肖宏涛,田社民,查新建,等.不同交联剂对脱细胞牛心包膜生物材料改性的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(10): 1301-1306.
[15] LEON-TAKAHASHI AM, GOMEZ-PEDRAZA A, CRUZ-RODRIGUEZ A, et al.Use of glutaraldehyde-preserved bovine pericardium patch in vascular repair of portal vein in a patient with pancreatic cancer. Indian J Surg.2013;75(Suppl 1): 247-249.
[16] BARROS JA, FILIPPIN-MONTEIRO FB, DE OLIVEIRA EM, et al. Cytotoxicity of PVPAC-treated bovine pericardium: a potential replacement for glutaraldehyde in biological heart valves.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2014;102(3): 574-582.
[17] MATSAGAS MI, BALI C, ARNAOUTOGLOU E, et al. Carotid endarterectomy with bovine pericardium patch angioplasty: mid-term results.Ann Vasc Surg.2006;20(5):614-619.
[18] FROST P, KERBEL RS. Immunology of metastasis. Can the immune response cope with disseminated tumor? Cancer Metastasis Rev.1983;2(3):239-256.
[19] 张看,赵彦涛,白玉龙,等.不同脱脂方法对异种松质骨脱脂效果及免疫原性的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(6): 585-587.
[20] DOWD KA, PIERSON TC. The Many Faces of a Dynamic Virion: Implications of Viral Breathing on Flavivirus Biology and Immunogenicity.Annu Rev Virol.2018;5(1):185-207.
[21] LU Y, SHAO A, SHAN Y, et al. A standardized quantitative method for detecting remnant alpha-Gal antigen in animal tissues or animal tissue-derived biomaterials and its application. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15424.
[22] 刘成虎,吴平,施燕平,等.医疗器械免疫原性评价与试验策略[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2012,36(1):56-58.
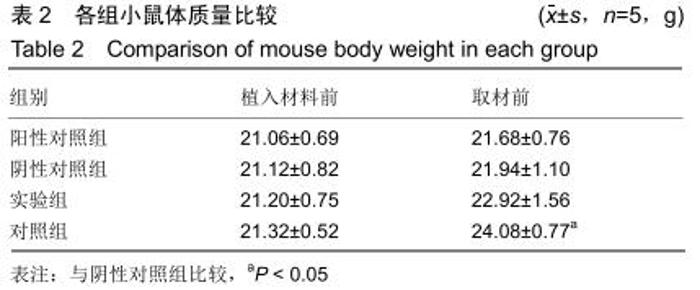
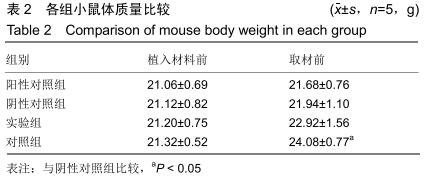
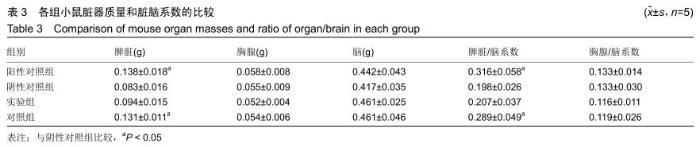
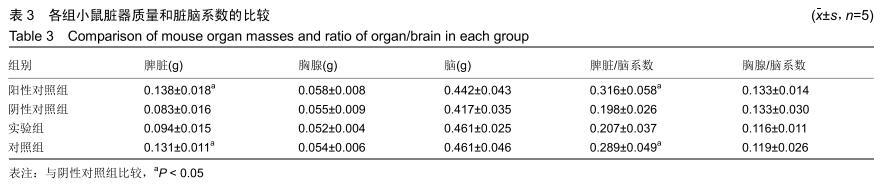
[23] 戴丽军,叶炳飞,黄月玲.Fmr1基因敲除小鼠脏器重量和脏器系数的比较分析[J].中国比较医学杂志,2009,19(6):59-61.
[24] SEO KH, ZHOU L, MENG D, et al. Loss of microRNAs in thymus perturbs invariant NKT cell development and function. Cell Mol Immunol.2010;7(6):447-453.
[25] 李海玲.沥青烟对小鼠中枢神经系统损伤机制的实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2006.
[26] 杨晓芳,奚廷斐.组织工程细胞支架的免疫原性研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(31):6262-6264.
[27] CHOI HJ, KIM MK, LEE HJ, et al. Effect of alphaGal on corneal xenotransplantation in a mouse model. Xenotransplantation. 2011;18(3):176-182.
[28] DELLABONA P, ABRIGNANI S, CASORATI G. iNKT-cell help to B cells: a cooperative job between innate and adaptive immune responses.Eur J Immunol.2014;44(8):2230-2237.
[29] PEREZ N, LASARTE P, BIBILONI N, et al. T and B lymphocytes and NK cells in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Medicina (B Aires). 1991;51(3):233-237.
[30] 蔡帆,张彦,臧林泉.白扁豆多糖对免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志,2018,34(5):407-411.
[31] 张志军,冯霞,蒋娟,等.茯苓多糖对小鼠血清IgA、IgG和IgM生物合成水平的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2013,29(11):1213-1215.
[32] TAHA R, HAMID Q, CAMERON L, et al. T helper type 2 cytokine receptors and associated transcription factors GATA-3, c-MAF, and signal transducer and activator of transcription factor-6 in induced sputum of atopic asthmatic patients.Chest. 2003;123(6):2074-2082.
[33] 安方玉,颜春鲁,刘永琦,等.小补肾汤对镉染毒模型鼠免疫细胞增殖及凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(2):438-441.
[34] SHAO A, XU L, WU X, et al. Gal Epitope Expression and Immunological Properties in iGb3S Deficient Mice.Sci Rep. 2018;8:15433.
[35] 邵安良,魏利娜,范昌发,等.Gal抗原缺失小鼠的应用示范:动物源性硬脑膜补片的免疫原性反应评价[J].药物分析杂志,2018, 38(8):1296-1303.
[36] 魏利娜,邵安良,黄立静,等.去细胞异种角膜基质与去细胞异种结膜基质的免疫原性研究[J].药物分析杂志,2019,39(8): 1362-1369.
[37] 陈亮,邵安良,魏利娜,等.应用Gal抗原缺失小鼠评价可降解异种脱细胞真皮基质的免疫原性[J].药物分析杂志,2019,39(8): 1370-1378.
[38] 徐丽明,邵安良,陈亮,等.动物源性医疗器械精准风险评价的关键技术研究[J].中国药事,2019,33(12):1348-1355.
[39] 田佳鑫.对动物源性医疗器械免疫原性评价的思考[J].生物技术通讯, 2016,27(6):845-847.
|