Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (34): 5478-5485.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2323
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical efficacy of calcium sulphate/demineralized bone matrix versus bone allograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
Li Yongtao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen, Liang Kaiheng, Zhang Kaixi, Liu Changfeng
Department of Spine Surgery, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-20Revised:2019-12-25Accepted:2020-02-14Online:2020-11-08Published:2020-09-11 -
Contact:Song Wenhui, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Yongtao, Master candidate, Department of Spine Surgery, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Applied Basic Research Project of Shanxi Province, No. 201801D121324
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yongtao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen, Liang Kaiheng, Zhang Kaixi, Liu Changfeng. Clinical efficacy of calcium sulphate/demineralized bone matrix versus bone allograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5478-5485.
share this article
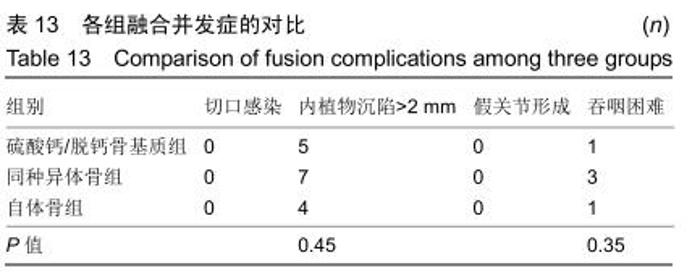
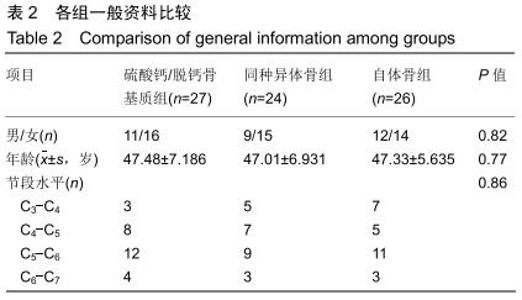
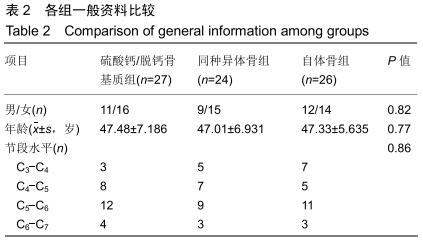
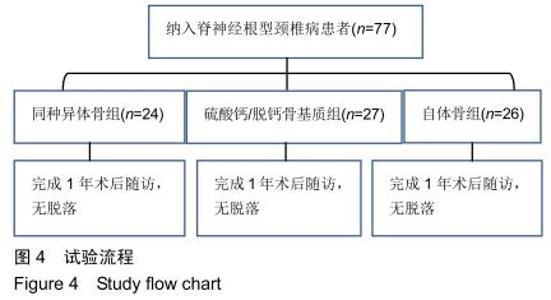
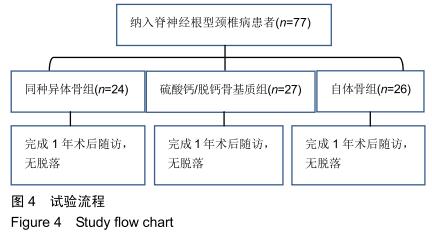
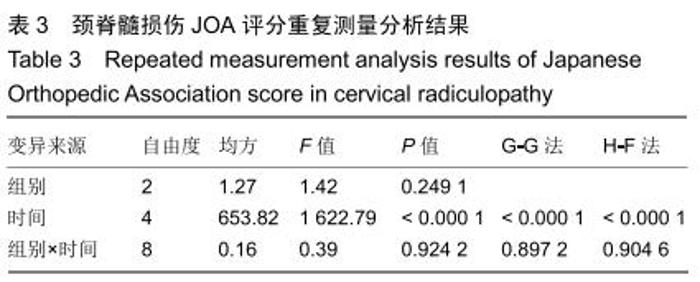
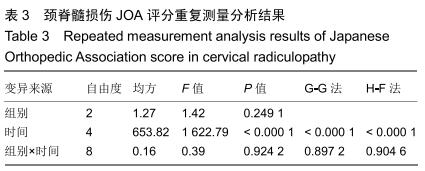
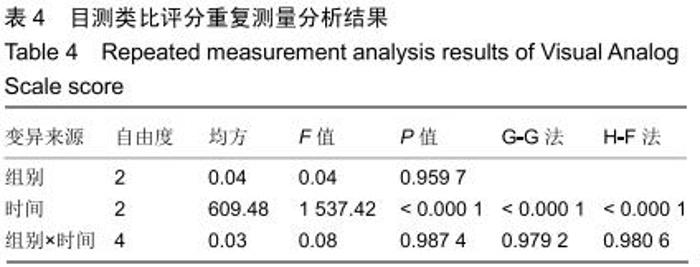
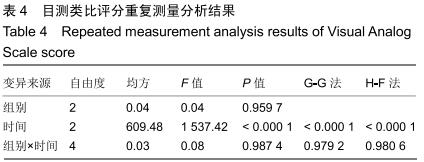
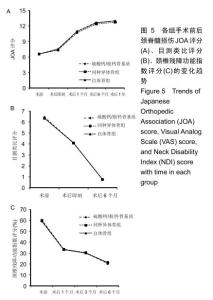
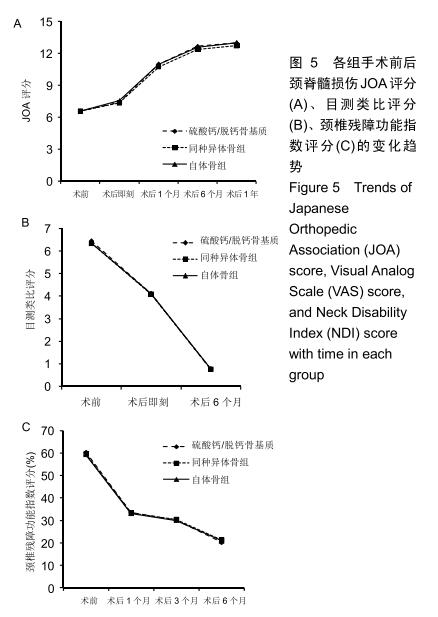
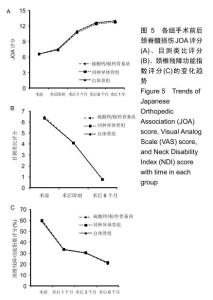
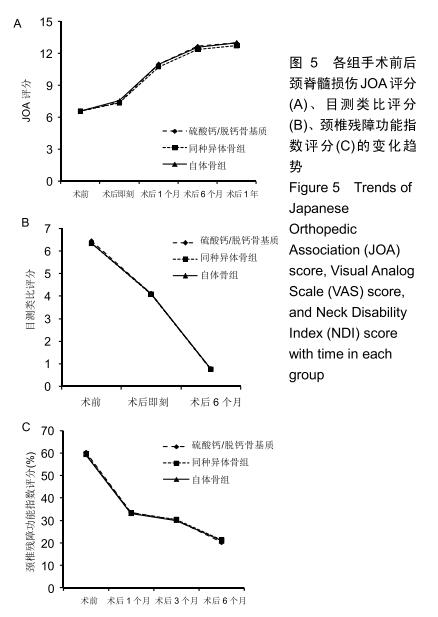
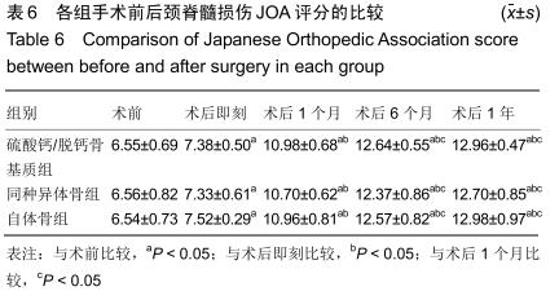
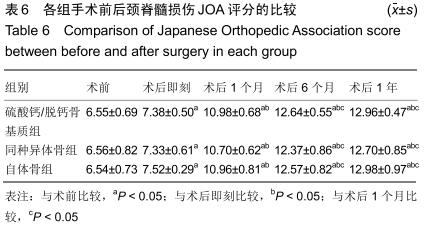
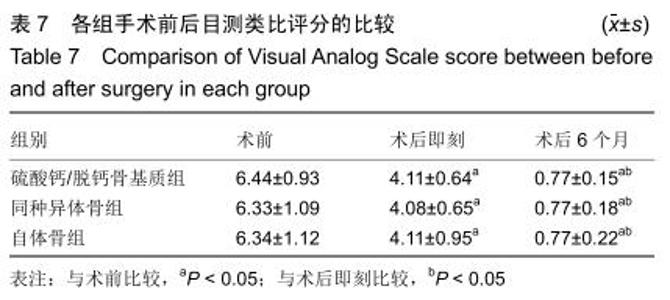
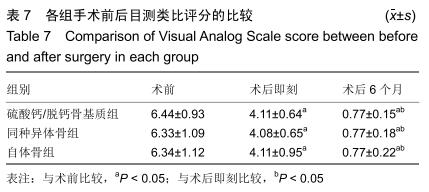
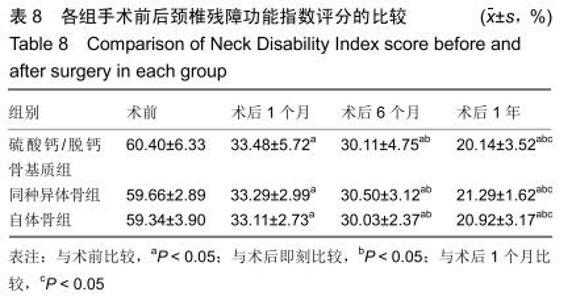
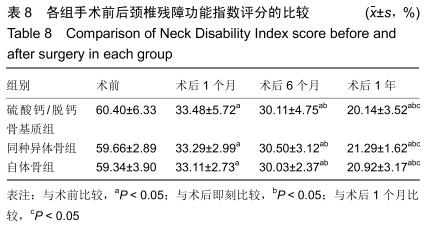
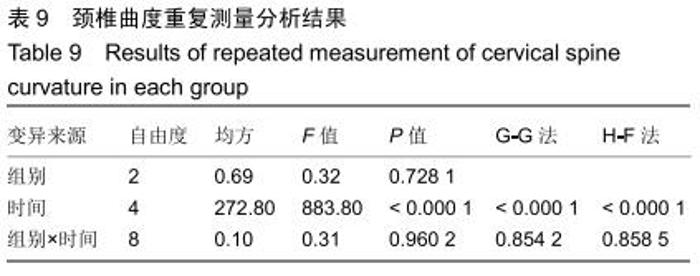
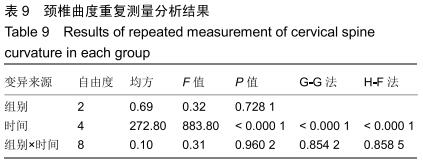
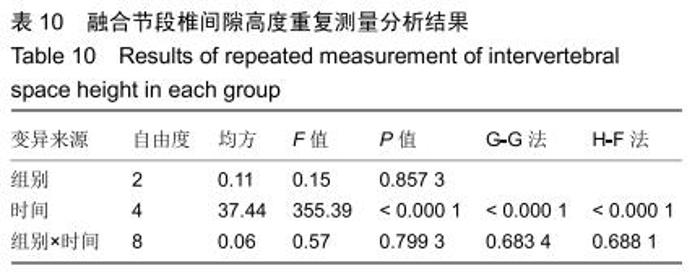
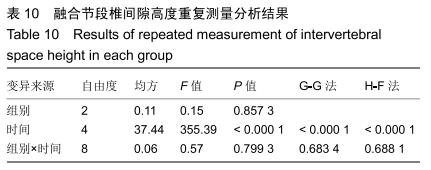
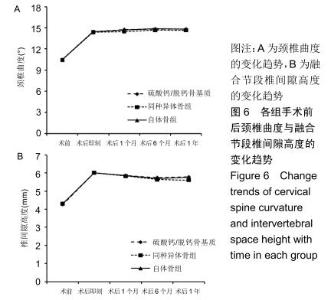
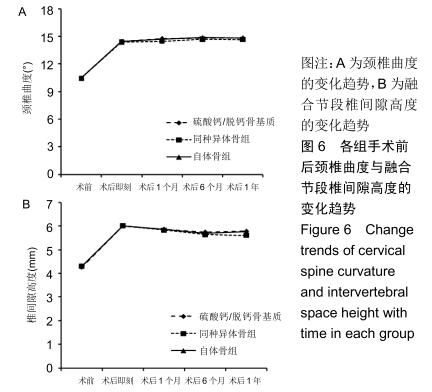
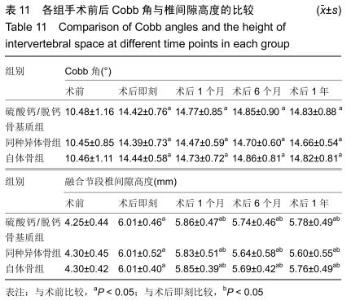
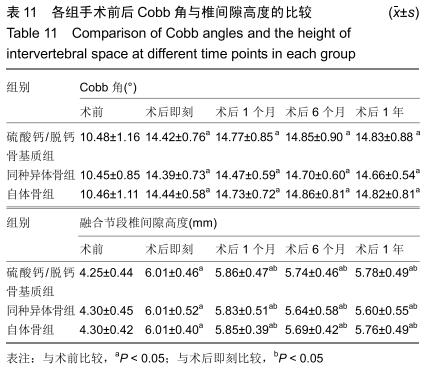
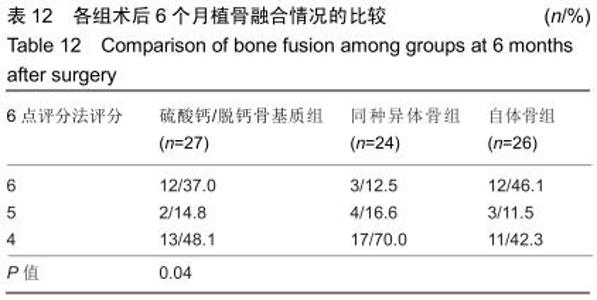
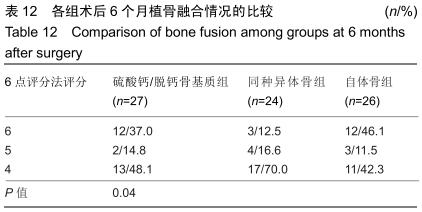
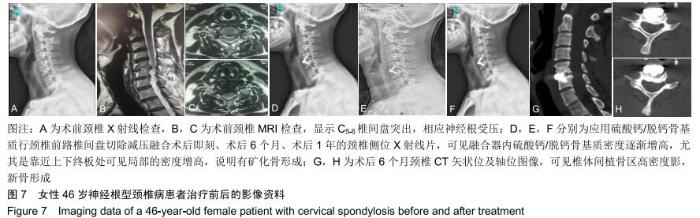
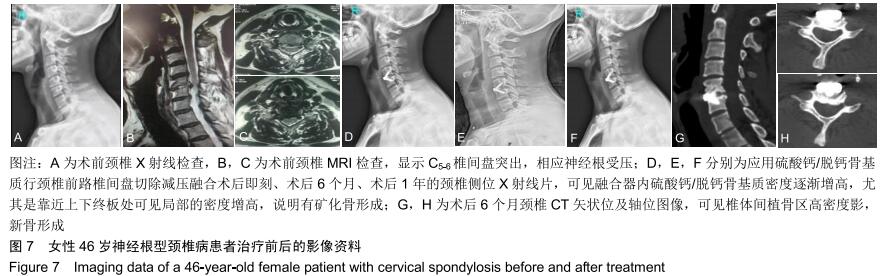
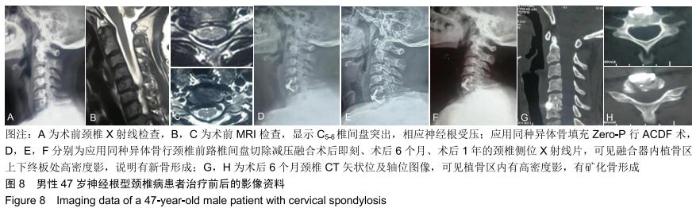
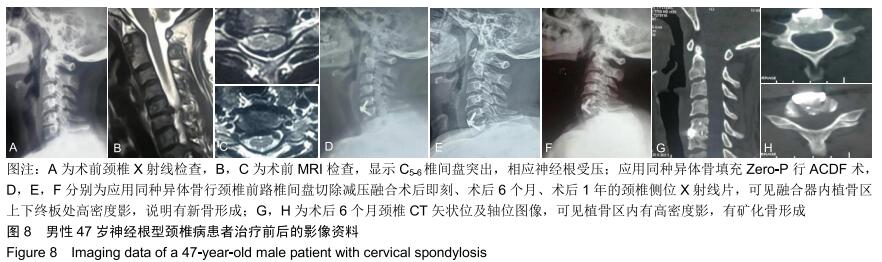
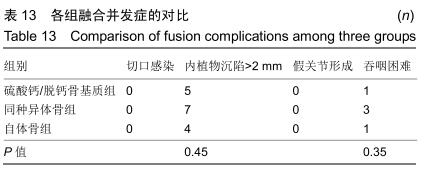
2.5.3 融合过程中相关并发症与植入物生物相容性 在Zero-P融合器中使用硫酸钙/脱钙骨基质行ACDF术后会出现相关并发症,其中最为常见的并发症为吞咽困难、切口感染、植入物沉陷及假关节形成。硫酸钙/脱钙骨基质组、自体骨组各有1例出现了吞咽困难症状,同种异体骨组有3例出现了吞咽困难症状,在随访结束时吞咽困难都获得完全缓解;3组均未出现切口感染症状,术后均达到满意愈合;硫酸钙/脱钙骨基质组有5例(18.5%)内植物沉陷>2 mm,自体骨组有4例(15.3%)内植物沉陷>2 mm,而同种异体骨组有7例(29.1%)内植物沉陷>2 mm,3组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);3组末次随访均获得骨性融合,未见假关节形成,见表13。3组均未发生与植入物相关的不良反应。 "
|
[1] 孙佳佳,杨惠林,周军,等.同种异体骨与自体骨填充椎间融合修复脊髓型颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3): 329-334.
[2] LANDRIEL FA, HEM S, GOLDSCHMIDT E, et al. Polyetheretherketone Interbody Cages Versus Autogenous Iliac Crest Bone Grafts With Anterior Fixation for Cervical Disc Disease.J Spinal Disord Tech.2013;26(2):61-67.
[3] BUTSCHEIDT S, MENARD M, THORSTEN G, et al. Incorporation and remodeling of structural allografts in acetabular reconstruction: multiscale, micro-morphological analysis of 13 pelvic explants.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018; 100(16):1406-1415.
[4] GABRIEL FG, LAETITIA K, YSIA IG, et al. Bone substitutes: a review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9: 1-18.
[5] TILKERIDIS K, TOUZOPOULOS P, VERVERIDIS A, et al. Use of demineralized bone matrix in spinal fusion.World J Orthop. 2014;5(1):30-37. [6] 李忠海,刘谟震,赵彦涛,等.三种植骨材料在腰椎后路椎间融合中的应用比较[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(3):230-235.
[7] PLUM AW, TATUM SA. A comparison between autograft alone, bone cement, and demineralized bone matrix in cranioplasty. Laryngoscope.2015;125(6):1322-1327.
[8] PITZEN TR, CHROBOK J, STULIK J, et al. Implant complications, fusion,loss of lordosis, and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dy-namic or rigid plates: two-year results of a multicentric, randomized,controlled study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(7):641-646.
[9] 冯仕明.同种异体骨移植的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 19(21):1797-1799.
[10] LEE FY, HAZAN EJ, GEBHARDT MC, et al. Experimental model for allograft incorporation and allograft fracture repair.J Orthop Res.2000;18(2):303-306.
[11] HAWKER GA, GIGNAC MA, BADLEY E, et al. A longitudinal study to explain the pain-depression link in older adults with osteoarthritis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).2011;63(10): 1382-1390.
[12] YUE WM, BRODNER W, HIGHLAND TR. Long-Term Results After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion With Allograft and Plating: A 5- to 11-Year Radiologic and Clinical Follow-up Study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(19):2138-2144.
[13] Senn on the Healing of Aseptic Bone Cavities by Implantation of Antiseptic Decalcified Bone.Ann Surg.1889;10(5):352-368.
[14] URIST MR, SILVERMAN BF, BÜRING K, et al. The bone induction principle.Clin Orthop Relat R.1967;53(1):243.
[15] FALDINI C, MISCIONE MT, ACRI F, et al. Single level cervical fusion by an anterior approach using autologous bone graft influences the adjacent levels degenerative changes: clinical and radiographic results at 10-year minimum follow-up.Eur Spine J.2012;21 Suppl 1:S90-93.
[16] BIALY IE, JISKOOT W, NEJADNIK MR. Formulation, delivery and stability of bone morphogenetic proteins for effective bone regeneration.Pharm Res.2017;34:1152-1170.
[17] 赵廷宝,范清宇,周勇,等.组织工程化骨替代材料的评价及其在修复骨肿瘤性骨缺损中的应用[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(10): 1419-1420.
[18] 王军,时宁文,邱阳,等.载万古霉素硫酸钙复合BMP-2治疗创伤性骨髓炎[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2017,9(3):133-139.
[19] 杨诚,彭建强,张旗.脱钙骨基质的临床应用与研究进展[J].社区医学杂志,2007,5(23):39-41.
[20] 孟红亚,张长春,朱坤,等.rhBMP-2在脊柱融合术中应用安全性研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2015,52(1):26-29.
[21] CHEN Z, BA G, SHEN T, et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion: a meta-analysis of ten randomized controlled trials.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(12): 1725-1740.
[22] 龚宗明,张雷,孙晓亮,等.脊髓型颈椎病术后神经功能恢复时间模式研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(34):24-26.
[23] MATSUDA Y, SHIBATA T, OKI S, et al. Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in Patients More Than 75 Years of Age.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(6):529-534. [24] CHUNG HJ, HUR J W, RYU KS, et al. Surgical Outcomes of Anterior Cervical Fusion Using Deminaralized Bone Matrix as Stand-Alone Graft Material: Single Arm, Pilot Study. Korean J Spine. 2016;13(3):114-119. |
| [1] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [2] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [3] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [5] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [6] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [7] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [8] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [9] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [10] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [13] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Wang Xinting, Xu Dandi, Zhang Junxia, Su Hailong Wang Qi. Stability of load-bearing cross barrier of different arch structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3838-3843. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||