Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (22): 3602-3608.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2271
Effect of soft silicone silver ion dressing applied in burn wounds
Zhong Shuxian, Shi Yuqing, Yang Yalan, Li Chun
- School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-10-08Revised:2019-10-11Accepted:2019-11-15Online:2020-08-08Published:2020-04-26 -
Contact:Li Chun, Master, Associate professor, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhong Shuxian, Master candidate, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Shuxian, Shi Yuqing, Yang Yalan, Li Chun. Effect of soft silicone silver ion dressing applied in burn wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3602-3608.
share this article
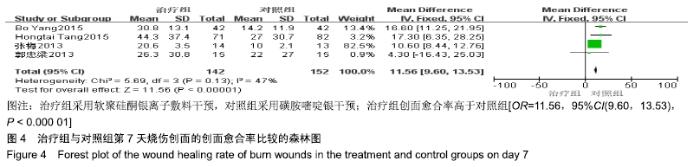
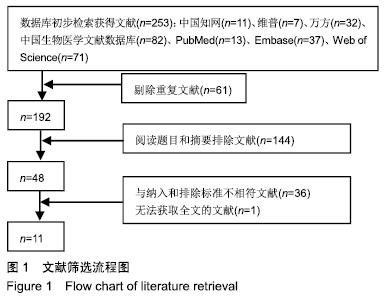
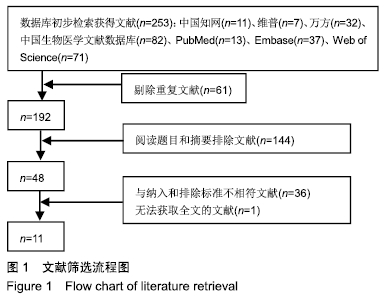
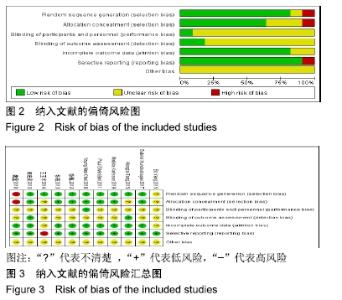
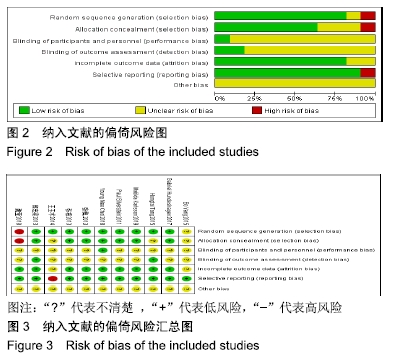
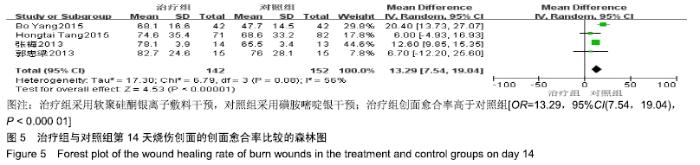
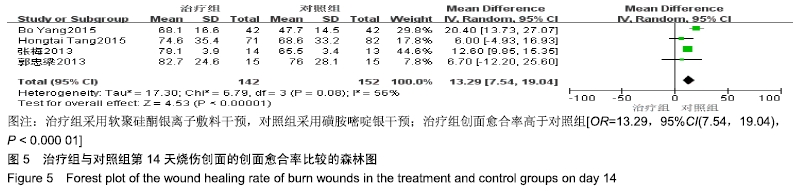
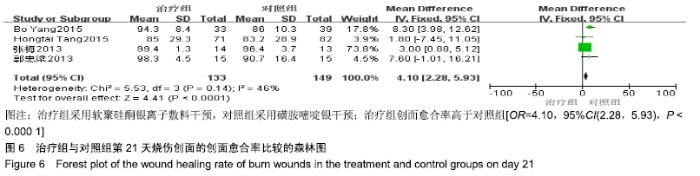
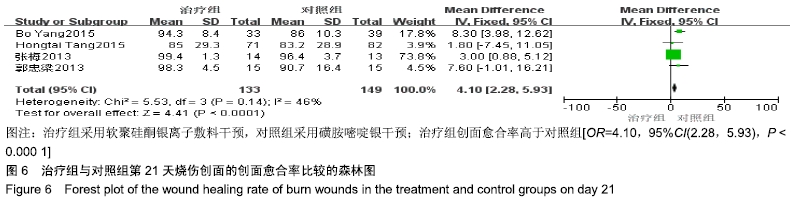
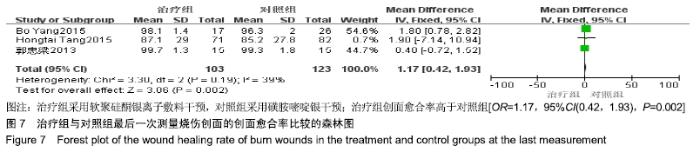
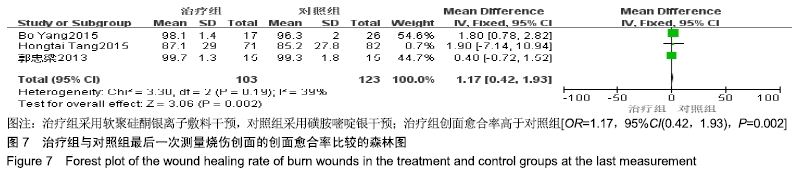
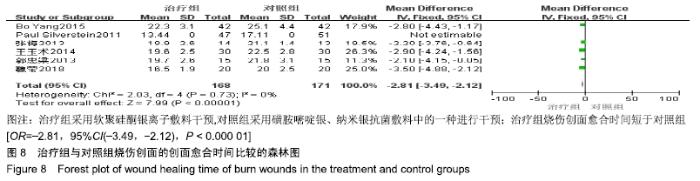
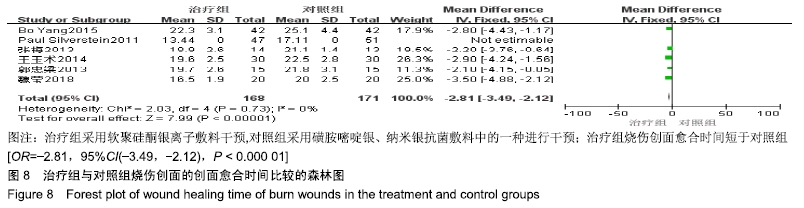
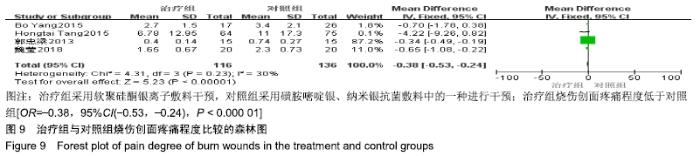
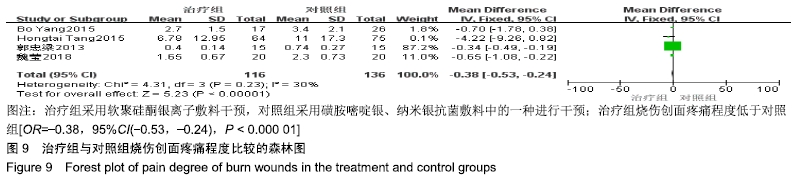
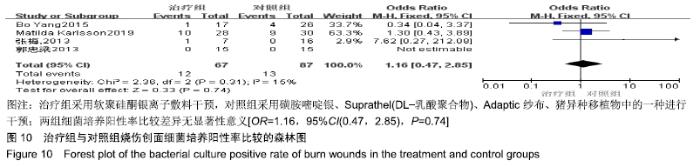
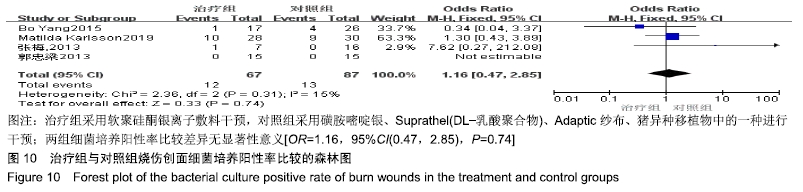
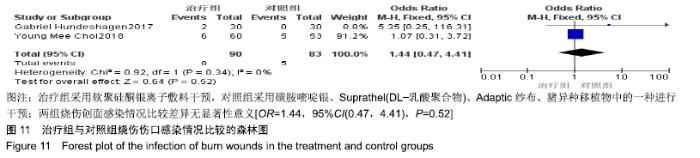
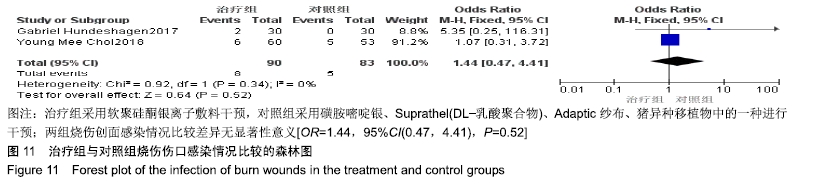
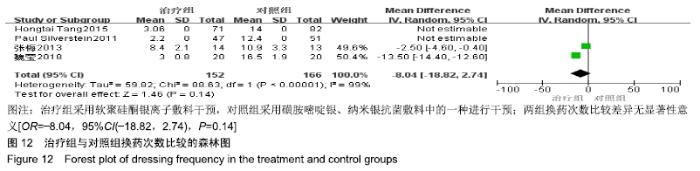
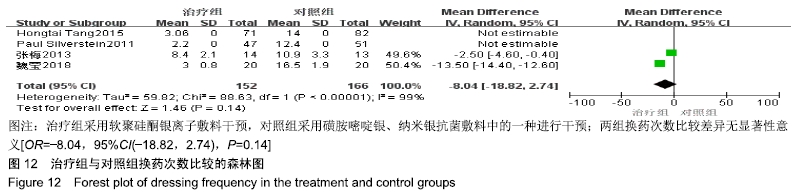
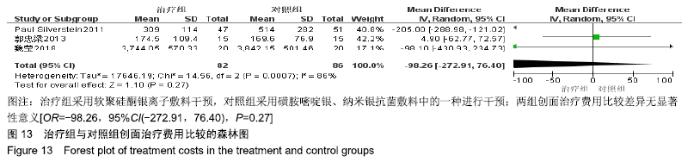
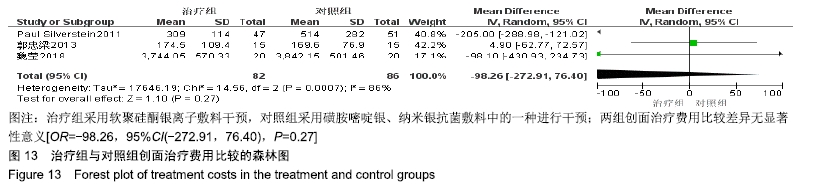
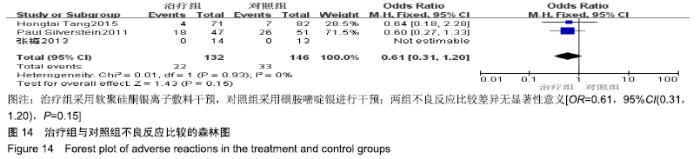
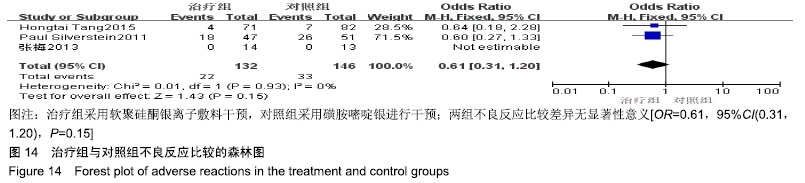
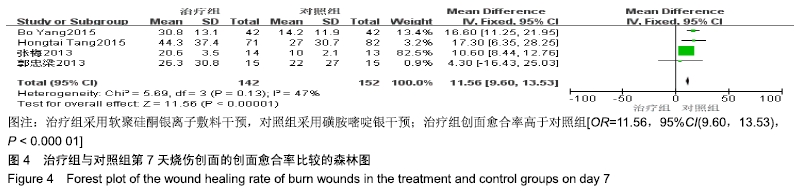
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 创面愈合率 4项研究报道了创面愈合率[5,7,11,14],对其结果进行异质性检验:第7天时各研究结果间异质性不大(I2=47%,P > 0.05),采用固定效应模型;第14天时各研究结果间异质性较大(I2=56%,P < 0.05),采用随机效应模型;第28天和最后一次测量时各研究结果间异质性不大(I2=46%,39%,P > 0.05),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示,治疗组第7,14,21天及最后一次测量时的烧伤创面愈合率均高于对照组[OR=11.56,95%CI(9.60,13.53),P < 0.000 01;OR=13.29,95%CI(7.54,19.04),P < 0.000 01;OR=4.10,95%CI(2.28,5.93),P < 0.000 1;OR=1.17,95%CI(0.42,1.93),P=0.002],见图4-7。 "
| [1] STANOJCIC M, VINAIK R, JESCHKE MG. Status and challenges of predicting and diagnosing sepsis in burn patients.Surg Infect(Larchmt). 2018;19(2):168-175. [2] AMERICAN BURN ASSOCIATION. Burn incidence and treatment in the United States:2016. http://ameriburn.org/who-we-are/ media/burn-incidence-fact-sheet,2016/2019-07-20. [3] 黄璐,姚丹,王莹.软聚硅酮泡沫敷料预防创伤后危重病人发生压疮的价值分析[J].皮肤病与性病,2019,41(4):616-617. [4] CHADWICK P, TAHERINEJAD F, HAMBERG K, et al. Clinical and scientific data on a silver-containing soft-silicone foam dressing: an overview.J Wound Care.2009;18(11):483-484,486-490. [5] 郭忠梁.美皮康银与磺胺嘧啶银在深II度烧伤创面应用的对比研究[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2013. [6] 魏莹,陈志坚,杨焕纳,等.软聚硅酮银离子敷料用于婴幼儿深Ⅱ度烧伤创面治疗的临床疗效观察[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2018,13(6): 459-461. [7] 张梅,唐洪泰,马兵,等.软聚硅酮银离子泡沫敷料在患者关节部位深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的应用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(3):315-317. [8] 张梅.软聚硅酮银离子泡沬敷料与磺胺嘧啶银霜治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的比较研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2013. [9] 王玉术.美皮康银与磺胺嘧啶银在深II度烧伤创面应用的对比研究[J].医学美学美容,2014,22(11):311-312. [10] HUNDESHAGEN G, COLLINS VN, WURZER P, et al. A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing the Outpatient Treatment of Pediatric and Adult Partial-Thickness Burns with Suprathel or Mepilex Ag.J Burn Care Res.2018;39(2):261-267. [11] TANG HT, LV GZ, FU JF, et al. An open, parallel, randomized, comparative, multicenter investigation evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of Mepilex Ag versus silver sulfadiazine in the treatment of deep partial-thickness burn injuries.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015; 78(5): 1000-1007. [12] SILVERSTEIN P, HEIMBACH D, MEITES H, et al. An open, parallel, randomized, comparative, multicenter study to evaluate the cost-effectiveness, performance, tolerance, and safety of a silver-containing soft silicone foam dressing (intervention) vs silver sulfadiazine cream.J Burn Care Res.2011;32(6):617-626. [13] CHOI YM, CAMPBELL K, LEVEK C, et al. Antibiotic ointment versus a silver-based dressing for children with extremity burns:A randomized controlled study.J Pediatr Surg.2019;54(7):1391-1396. [14] YANG B, WANG XD, LI ZH, et al. Beneficial effects of silver foam dressing on healing of wounds with ulcers and infection control of burn patients.Pak J Med Sci.2015;31(6):1334-1339. [15] KARLSSON M, ELMASRY M, STEINVALL I, et al. Superiority of silver-foam over porcine xenograft dressings for treatment of scalds in children: A prospective randomised controlled trial.Burns. 2019;45(6): 1401-1409. [16] WINTER GD. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelisation of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig.Nature. 1962; 193:293-294. [17] 夏照帆,胡晓燕,王光毅,等.烧伤休克的发病机制和病理生理[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2007,2(6):326-328. [18] 黄冰,任道琼,张玲,等.美皮康银离子联合维生素B12混合液治疗放射性湿性皮炎感染创面[J].护理学杂志,2011,26(13):53-55. [19] 赵海霞,闫清秀.软聚硅酮银离子敷料在腹部感染伤口中的应用效果研究[J].中国实用医药,2018,13(10):84-85. [20] 林静,陈向荣,马荣莉,等.美皮康银敷料治疗超高龄患者感染性Ⅱ、Ⅲ期压疮的效果观察[J].华南国防医学杂志,2017,31(6):394-397. [21] 王丽华.超薄型美皮康预防PICC术后机械性静脉炎的效果观察[J].护理研究,2013,27(9):807-808. [22] BARRETT S. Mepilex Ag: an antimicrobial, absorbent foam dressing with Safetac technology.Br J Nurs.2009;18(20):S28,S30-36. [23] 闫清秀,梁秀琴.软聚硅酮银离子敷料在腹部难愈性伤口中的护理应用研究[J].中国实用医药,2018,13(33):190-191. [24] 宋萌,陈庆杰,王宏宇,等.外用rhGM-CSF凝胶联合磺胺嘧啶银乳膏治疗小面积深Ⅱ度难愈创面的疗效及安全性[J].解放军医药杂志, 2019,31(5):67-70. [25] 何放,徐达圆,罗鹏飞,等.新型抗菌凝胶敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的疗效评价[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(21):4051-4054. [26] DAVIES P, MCCARTY S, HAMBERG K. Silver-containing foam dressings with Safetac: a review of the scientific and clinical data.J Wound Care. 2017,26:Sup6a:S1-S32. [27] 符敏.银离子抗菌敷料在压疮感染性伤口中的应用与效果观察[J].实用临床护理学电子杂志,2019,4(11):62,66. [28] OSTRIKOV K, MACGREGOR-RAMIASA MN, CAVALLARO AA, et al. A Comparative Assessment of Nanoparticulate and M etallic Silver Coated Dressings.Recent Pat Mater Sci. 2016;9(1):50-57. [29] LIN YH, HSU WS, CHUNG WY, et al. Silver-based wound dressings reduce bacterial burden and promote wound healing.Int Wound J. 2016;13(4):505-511. [30] SZWEDA P, GORCZYCA G, TYLINGO R. Comparison of antimicrobial activity of selected, commercially available wound dressing materials.J Wound Care.2018;27(5):320-326. [31] 张凤联,刘宸希,邢彩霞.软聚硅酮银离子泡沫敷料的临床应用[J].解放军护理杂志,2016,33(18):49-51. [32] PARK HS, PHAM C, PAUL E, et al. Early pathogenic colonisers of acute burn wounds: a retrospective review.Burns.2017;43(8):1757-1765. [33] LO SF, CHANG CJ, HU WY, et al. The effectiveness of silver-releasing dressings in the management of non-healing chronic wounds: a meta analysis.J Clin Nurs.2009;18(5):716-728. [34] 邱文波,吴小婉,韩慧,等.气管切口处应用泡沫敷料的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(22):3599-3603. [35] 范昔庚.水胶体敷料联合清创凝胶治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2019,12(9):39-40,43. [36] 莫立娟.水胶体敷料在新生儿高渗性液体外渗皮肤护理中的应用[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2019,6(39):125. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [5] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [6] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [7] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [8] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [9] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| [10] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Jack kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 487-492. |
| [11] | Li Gaofeng, Wang Jun. Effects of concurrent aerobic and strength training on locomotor performance: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4258-4264. |
| [12] | Wang Ao, Chu Hongshang, Wu Hongguang, Li Ke, Liu Huijuan. Expression of leptin receptor in mouse skin and the role of leptin receptor-positive cells in skin development and wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3993-3998. |
| [13] | Zhang Gaofei, Wang Di, Li Jiamei, Lou Hanxiao, Zeng Yueqin, Liu Wenjun. Mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing by regulating the autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4058-4063. |
| [14] | Zhao Shuying, Guo Guangling, Liu Chenchen, Zhang Chao, Dong Sirui, Gong Qinqin, Ji Luwei. Stem cell transplantation in the treatment of premature ovarian failure: a meta-analysis based on 13 animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4084-4092. |
| [15] | Shi Yao, Han Shufeng, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Jing Zhijie, Zhao Bichun, Zhang Ruxin, Zhang Yujuan, Wang Chunfang. Efficacy and safety of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4093-4100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||