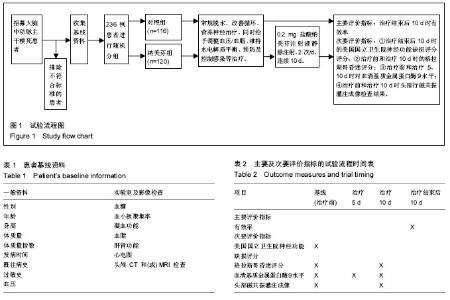
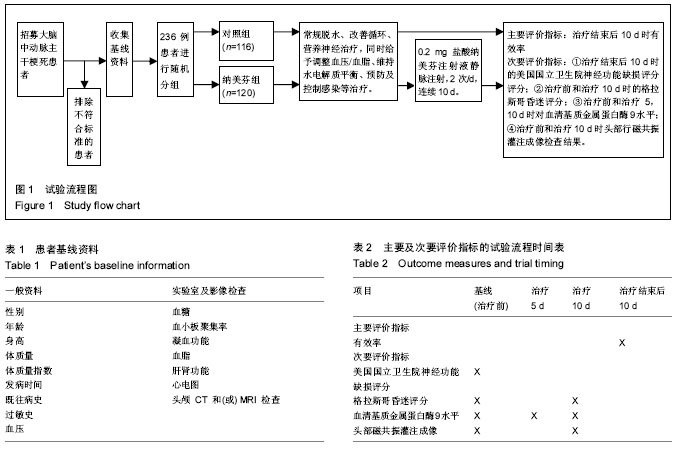
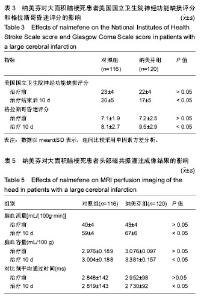
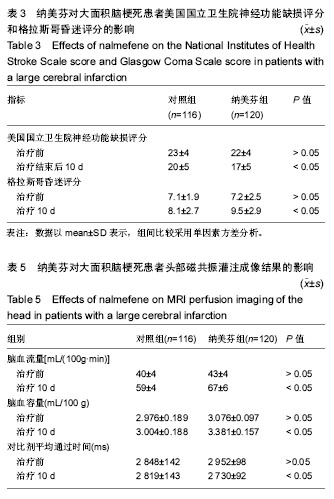
| [1] Yu J, Lian Z, Wang W, et al. Parapharyngeal space acinic cell carcinoma after operation in patients with internal carotid artery embolism caused by acute large area cerebral infarction: a case report. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;49(6):512-514.[2] Li T, Tian GJ, Yu JC, et al. Effects of acupuncture on nervous function in the patient of extensive cerebral infarction after operation. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2008;28(12):869-872.[3] Li XL, Xia Q, Cheng ZX, et al. Influence of beginning time of hypothermia treatment on prognosis of extensive cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005; 17(3):180-182.[4] Zheng PY, Jin Y, Zhang YE, et al. Treatment of large area acute cerebral infarction. Nao yu Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 2001;9(3):159-160.[5] Liao XL, Wang YL, Pan YS, et al. The Recanalization and Prognosis of Acute Cerebral Infarction Patients with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion after Intravenous Thrombolytic Treatment. Zhongguo Cuzhong Zazhi. 2016;11(10):824-828.[6] Jiang W, Zhou XY, Zhou SN. Clinical Application of Vasodilators in the Acute Phase of Ischemic Stroke. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2017;20(6):720-724.[7] Yan X. Research progress of decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction. Zhonghua Shiyong Zhenduan yu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2015;29(5):435-437.[8] Barrio P, Ortega L, Guardia J, et al. Who Receives Nalmefene and How Does It Work in the Real World? A Single-Arm, Phase IV Study of Nalmefene in Alcohol Dependent Outpatients: Baseline and 1-Month Results. Clin Drug Investig. 2017;doi: 10.1007/s40261-017-0590-4.[9] Millier A, Laramee P, Rahhali N, et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Nalmefene Added to Psychosocial Support for the Reduction of Alcohol Consumption in Alcohol-Dependent Patients With High/Very High Drinking Risk Levels: A Microsimulation Model. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2017;78(6):867-876.[10] Sugishita K, Su Z, Li F, et al. Gender influences [Ca(2+)](i) during metabolic inhibition in myocytes overexpressing the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger. Circulation. 2001;104(17): 2101-2106.[11] Matzke GR, Frye RF, Alexander AC, et al. The effect of renal insufficiency and hemodialysis on the pharmacokinetics of nalmefene. J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;36(2):144-151.[12] Zaki PA, Bilsky EJ, Vanderah TW, et al. Opioid receptor types and subtypes: the delta receptor as a model. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1996;36:379-401.[13] Akil H, Watson SJ, Young E, et al. Endogenous opioids: biology and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:223-255.[14] Chang RC, Rota C, Glover RE, et al. A novel effect of an opioid receptor antagonist, naloxone, on the production of reactive oxygen species by microglia: a study by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain Res. 2000; 854(1-2):224-229.[15] Soyka M. Nalmefene for the treatment of alcohol use disorders: recent data and clinical potential. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(4):619-626.[16] Du R, Teng JF, Wang Y, et al. Clinical study of Butylphthalide combined with Xue Shuan Tong on serum inflammatory factors and prognosis effect of patients with cerebral infarction. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015;28(5 Suppl):1823-1827.[17] Gao X, Ma F, Zhao Q, et al. Acupuncture method of "Huoxue Sanfeng, Shugan Jianpi" for morning blood pressure in patients with cerebral infraction combined with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2016;36(5):459-462.[18] Zhang C, Zhao S, Zang Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of Dl-3n-butylphthalide on progressive cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled STROBE study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(30):e7257.[19] Fu J, Zeng M, Shen F, et al. Effects of action observation therapy on upper extremity function, daily activities and motion evoked potential in cerebral infarction patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(42):e8080.[20] Jia XF, Hong Z, Fan JH, et al. Clinical effect of mechanical fragmentation combined with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator artery thrombolysis on acute cerebral infarction. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(3):821-826.[21] 中华神经科学会, 中华神经外科学会. 各类脑血管疾病诊断要点[J]. 中华神经科杂志,1996;29:379-380.[22] Siniscalchi A, Sztajzel R, Malferrari G, et al. The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale: Its Role in Patients with Posterior Circulation Stroke. Hosp Top. 2017:1-3.[23] Teasdale G, Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet. 1974;2(7872): 81-84. |