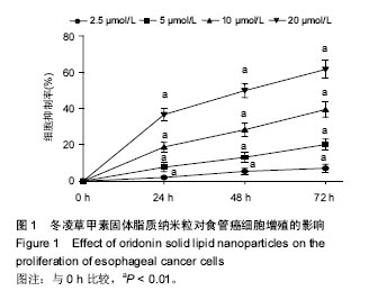
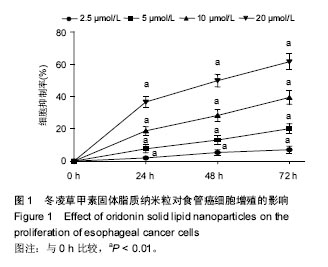
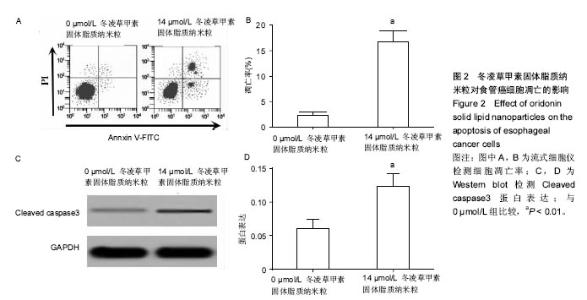
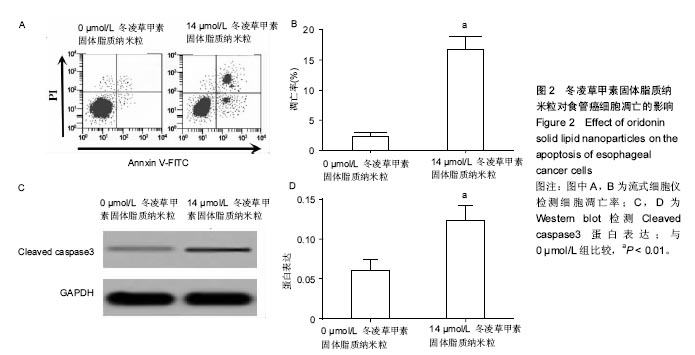
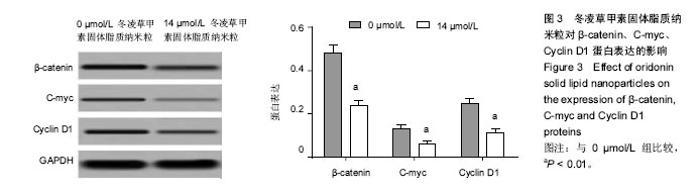
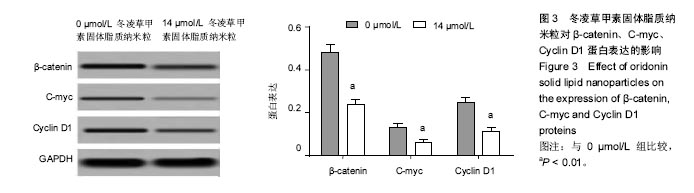
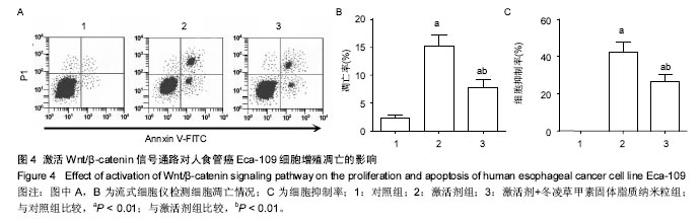
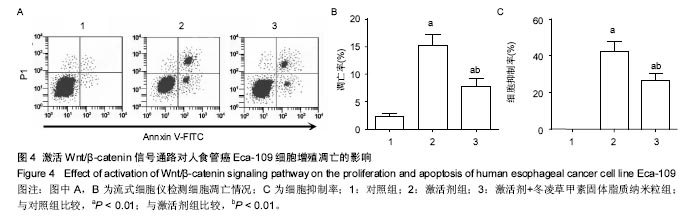
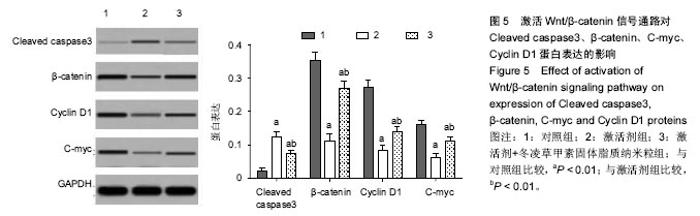
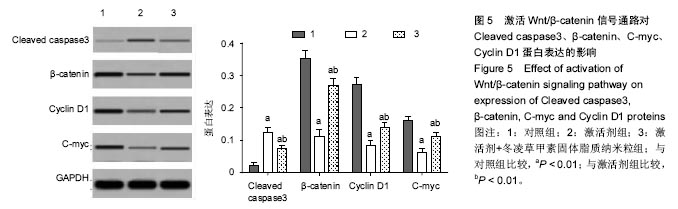
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5460-5466.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Oridonin solid lipid nanoparticles inhibit proliferation of esophageal cancer cells
- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2the National & International Research Center for Micro-Nano Molding Technology, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2017-08-03Online:2017-12-08Published:2018-01-04 -
Contact:Chen Xin-ju, Chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Xiao-qi, M.D., Attending physician, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Tackle Key Project of Henan Province, No. 162102310106; the 2017 Basic Research Project of Higher Education in Henan Province, No. 17B320005
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xiao-qi, Jiang Jing, Chen Xin-ju, Zhang Chuan-lei, Wang Xin-ting, Ji Ai-ying.
share this article
| [1]Hou X, Li T, Ren Z, et al. Novel BRCA2-Interacting Protein, LIMD1, Is Essential for the Centrosome Localization of BRCA2 in Esophageal Cancer Cell. Oncol Res. 2016;24(4): 247-253.[2]Song S, Honjo S, Jin J, et al. The Hippo Coactivator YAP1 Mediates EGFR Overexpression and Confers Chemoresistance in Esophageal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(11):2580-2590.[3]Ohnaga T, Shimada Y, Takata K, et al. Capture of esophageal and breast cancer cells with polymeric microfluidic devices for CTC isolation. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016;4(4):599-602.[4]Cao S, Xia M, Mao Y, et al. Combined oridonin with cetuximab treatment shows synergistic anticancer effects on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: involvement of inhibition of EGFR and activation of reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK pathway. Int J Oncol. 2016;49(5):2075-2087.[5]Zang KH, Shao YY, Zuo X, et al. Oridonin Alleviates Visceral Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Postinflammatory Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Role of Colonic Enterochromaffin Cell and Serotonin Availability. J Med Food. 2016;19(6):586-592.[6]Shi M, Ren X, Wang X, et al. A novel combination of oridonin and valproic acid in enhancement of apoptosis induction of HL-60 leukemia cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(2): 734-746.[7]Gu Z, Wang X, Qi R, et al. Oridonin induces apoptosis in uveal melanoma cells by upregulation of Bim and downregulation of Fatty Acid Synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457(2):187-193.[8]Pi J, Cai H, Jin H, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of ROS-Mediated Oridonin-Induced Oesophageal Cancer KYSE-150 Cell Apoptosis by Atomic Force Microscopy. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140935.[9]Liu M, Zhang Y, Liao Y, et al. Evaluation of the Antitumor Efficacy of RNAi-Mediated Inhibition of CDC20 and Heparanase in an Orthotopic Liver Tumor Model. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015;30(6):233-239.[10]Gao S, Tan H, Zhu N, et al. Oridonin induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(6):2453-2460.[11]Thakkar A, Chenreddy S, Thio A, et al. Preclinical systemic toxicity evaluation of chitosan-solid lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated aspirin and curcumin in combination with free sulforaphane in BALB/c mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:3265-3276.[12]Shan D, Li J, Cai P, et al. RGD-conjugated solid lipid nanoparticles inhibit adhesion and invasion of αvβ3 integrin-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015;5(1):15-26.[13]Liu Q, Li J, Pu G, et al. Co-delivery of baicalein and doxorubicin by hyaluronic acid decorated nanostructured lipid carriers for breast cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(4): 1364-1368.[14]Rizwanullah M, Ahmad J, Amin S.Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Platform for Chemotherapeutics. Curr Drug Deliv. 2016;13(1):4-26.[15]Kageyama S, Ikeda H, Miyahara Y, et al. Adoptive Transfer of MAGE-A4 T-cell Receptor Gene-Transduced Lymphocytes in Patients with Recurrent Esophageal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(10):2268-2277.[16]Wakita A, Motoyama S, Sato Y, et al. REG Iα activates c-Jun through MAPK pathways to enhance the radiosensitivity of squamous esophageal cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(7): 5249-5254.[17]Gao S, Tan H, Zhu N, et al. Oridonin induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(6):2453-2460.[18]Hao Y, Zhao F, Luo Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of oridonin on proliferation of RPMI8226 cells and the possible underlying mechanism. J Tradit Chin Med. 2016;36(2):225-230.[19]Xia R, Chen SX, Qin Q, et al. Oridonin Suppresses Proliferation of Human Ovarian Cancer Cells via Blockage of mTOR Signaling. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(2): 667-671.[20]周泽雄,曲珍仪,刘颖.冬凌草甲素通过激活 ATR 通路诱导 HEPG_2 细胞凋亡实验研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2016, 18(7): 19-21.[21]Makwana V, Jain R, Patel K, et al. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) of Efavirenz as lymph targeting drug delivery system: Elucidation of mechanism of uptake using chylomicron flow blocking approach. Int J Pharm. 2015;495(1):439-446.[22]Wang T, Hu Q, Zhou M, et al. Preparation of ultra-fine powders from polysaccharide-coated solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers by innovative nano spray drying technology. Int J Pharm. 2016;511(1):219-222.[23]Ramalingam P, Ko YT. Enhanced oral delivery of curcumin from N-trimethyl chitosan surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticles: pharmacokinetic and brain distribution evaluations. Pharm Res. 2015;32(2):389-402.[24]Mock CD, Jordan BC, Selvam C. Recent Advances of Curcumin and its Analogues in Breast Cancer Prevention and Treatment. RSC Adv. 2015;5(92):75575-75588.[25]Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE. Strategy for selecting nanotechnology carriers to overcome immunological and hematological toxicities challenging clinical translation of nucleic acid-based therapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(7):1163-1175.[26]Kruiswijk F, Labuschagne CF, Vousden KH. p53 in survival, death and metabolic health: a lifeguard with a licence to kill. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16(7):393-405.[27]Bidaux G, Borowiec AS, Gordienko D, et al. Epidermal TRPM8 channel isoform controls the balance between keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in a cold-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112(26):E3345-3354.[28]Zhang S, Zou L, Yang T, et al. The sGC activator inhibits the proliferation and migration, promotes the apoptosis of human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via the up regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. Exp Cell Res. 2015;332(2):278-287.[29]Han BJ, Li W, Jiang GB, et al. Effects of daidzein in regards to cytotoxicity in vitro, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species level, cell cycle arrest and the expression of caspase and Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(3):1115-1120.[30]Wu R, Tang S, Wang M, et al. MicroRNA-497 Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Proliferation via the Bcl-2/Bax-Caspase9-Caspase3 Pathway and Cyclin D2 Protein in HUVECs. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167052.[31]Fujii Y, Funakoshi T, Unuma K, et al. Hydrogen sulfide donor NaHS induces death of alveolar epithelial L2 cells that is associated with cellular shrinkage, transgelin expression and myosin phosphorylation. J Toxicol Sci. 2016;41(5):645-654.[32]Zhang X, Zhu Y, Duan W, et al. Allicin induces apoptosis of the MGC-803 human gastric carcinoma cell line through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4):2755-2760.[33]Dang YP, Yuan XY, Tian R, et al. Curcumin improves the paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of HPV-positive human cervical cancer cells via the NF-κB-p53-caspase-3 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 9(4): 1470-1476.[34]Kopanja D, Pandey A, Kiefer M, et al. Essential roles of FoxM1 in Ras-induced liver cancer progression and in cancer cells with stem cell features. J Hepatol. 2015; 63(2):429-436.[35]Takase HM, Nusse R. Paracrine Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates proliferation of undifferentiated spermatogonia in the adult mouse testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(11):E1489-1497.[36]Li J, Yang S, Su N, et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR leads to chemoresistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(2):2057-2065.[37]Sano M, Driscoll DR, DeJesus-Monge WE, et al. Activation of WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Enhances Pancreatic Cancer Development and the Malignant Potential Via Up-regulation of Cyr61. Neoplasia. 2016;18(12):785-794.[38]Wang Z, Li B, Zhou L, et al. Prodigiosin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exerts anticancer activity in breast cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(46): 13150-13155.[39]Jiang J, Yu C, Chen M, et al. Over-expression of TRIM37 promotes cell migration and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(4):1120-1127.[40]Yang C, Du W, Yang D. Inhibition of green tea polyphenol EGCG((-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate) on the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by suppressing canonical wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2016;67(7): 818-827. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [4] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [5] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [6] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [7] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [8] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [9] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [10] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [11] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [12] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [13] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [14] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [15] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||