Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5443-5448.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro properties of magnesium doped hydroxyapatite coating on the surface of carbon/carbon composites
- 1Second People’s Hospital of Changzhou, Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China; 2College of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, China; 3the 180th Hospital of PLA, Quanzhou 362000, Fujian Province, China; 4Xinguang Wu Ho Su Memorial Hospital of Taiwan, Taibei 11101, China; 5GoPath Diagnostic Laboratory Co., Ltd., Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2017-08-23Online:2017-12-08Published:2018-01-04 -
Contact:Ni Xin-ye, Second People’s Hospital of Changzhou, Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Ni Xin-ye, M.D., Associate researcher, Second People’s Hospital of Changzhou, Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51672178; the Social Development Program of Changzhou City, No. CJ20160029; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK20151181; the High-Level Talent Fund of Changzhou Municipal Health Department, No. 2016CZLJ004
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ni Xin-ye, Xiong Xin-bo,You Rui-jin, Wu Xing-sheng, Li Wan-shuai.
share this article
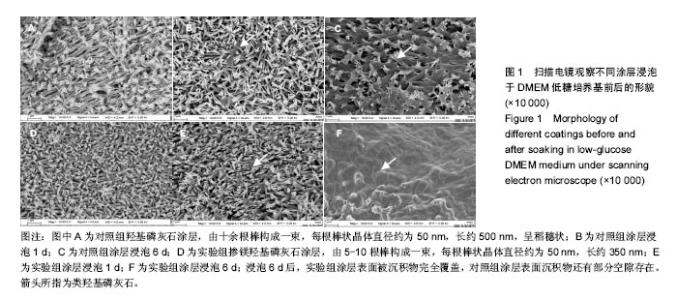
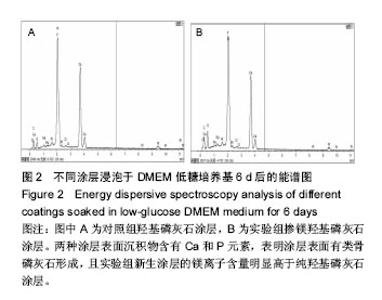
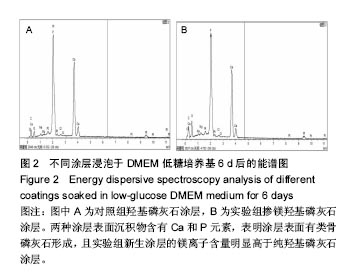
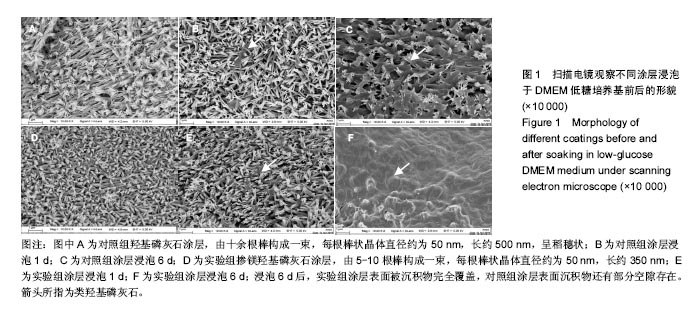
2.1 涂层的形貌 通过扫描电镜观察,纯羟基磷灰石涂层由十余根棒构成一束,每根棒状晶体直径约为50 nm,长约500 nm,呈稻穗状(图1A);掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层由 5-10根棒构成一束,每根棒状晶体直径约为50 nm,长约 350 nm(图1D)。有研究认为一定数量尺寸的微孔有利于细胞的生物代谢的吸收和黏附[16]。 图1B、C、E、F为涂层于DMEM 培养液中浸泡后的扫描电镜照片,图2为能谱分析图谱,浸泡1 d后,两涂层表面已经有沉积物形成,实验组涂层表面沉积物多于对照组;浸泡6 d后,实验组涂层表面被沉积物完全覆盖,而对照组涂层表面沉积物还有部分空隙存在。经图2的能谱分析(6 d后)得到,两种涂层表面沉积物含有Ca和P元素,表明涂层表面有类骨磷灰石形成,且实验组新生涂层的镁离子含量明显高于纯羟基磷灰石涂层。对照组和实验组涂层表面类骨磷灰石的Ca/P比分别为1.667和1.535。"
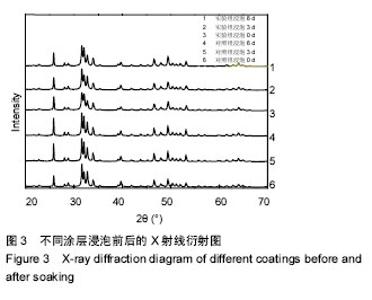
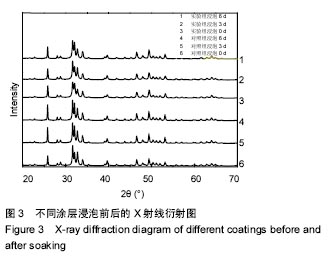
2.2 涂层的X射线衍射图 图3为X射线衍射检测到两组涂层浸泡前后的数据,涂层是由小尺寸晶粒和镁离子构成,涂层浸泡前后X射线衍射衍射图谱几乎出现羟基磷灰石晶面所有的特征衍射峰[(002)、(211)、(210)、(112)、(202)、(300)、(222)、(213)]。 浸泡前,实验组涂层28.032(102)和28.841(210)处的主X射线衍射峰相互靠拢,与对照组涂层相比间距缩小了0.08°;实验组涂层32.117(112)和(300) 32.814处的主X射线衍射峰逐渐靠拢,与对照组涂层相比间距缩小了0.04°,这是因为镁离子取代钙离子,镁离子半径为0.078 nm,小于钙离子半径(0.106 nm),从而引起晶面间距变小。 浸泡后同一时间内,与对照组涂层相比,实验组涂层衍射峰(002)2θ的角度均向右偏移了0.04°,造成这一现象的原因是:镁离子掺杂入晶格内部,导致衍射峰发生偏移。"
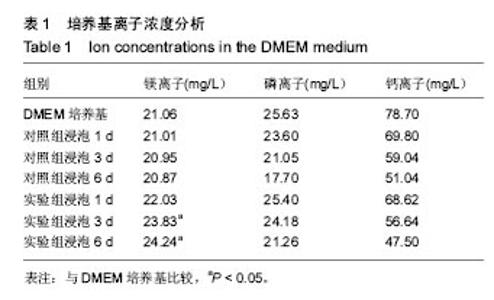
2.3 涂层浸泡后DMEM培养基的离子浓度 涂层浸泡前后DMEM培养基中的离子浓度见表1所示。浸泡1 d后,对照组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度下降,镁离子质量浓度稍有下降;实验组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度下降,镁离子质量浓度上升。浸泡3 d后,对照组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度继续下降,镁离子质量浓度继续轻微下降;实验组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度继续下降,镁离子质量浓度继续上升。浸泡6 d后,对照组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度继续下降,镁离子质量浓度继续轻微下降;实验组培养基中钙离子、磷离子质量浓度继续下降,镁离子质量浓度继续上升。对照组浸泡1,3,6 d后培养基中的镁离子质量浓度与DMEM培养基比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.938,0.872,0.761),实验组浸泡3,6 d后培养基中的镁离子质量浓度高于DMEM培养基(P=0.02,0.01)。 两种涂层浸泡后培养基中的钙离子、磷离子质量浓度下降,与涂层表面类骨磷灰石形成从而消耗了培养基钙离子、磷离子有关;实验组培养基中镁离子质量浓度升高与掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层缓慢释放镁离子有关,因为镁离子替代钙离子可能会导致晶格缺陷或不稳定,所以修饰过的涂层更容易溶解[17],形成了含高浓度钙离子、磷离子、镁离子的培养基,最终使得在这种培养基中沉积的类骨磷灰石中也含有更多的镁离子。"
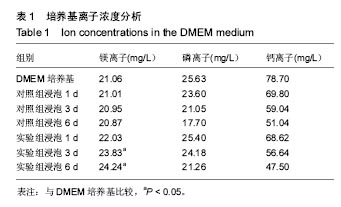
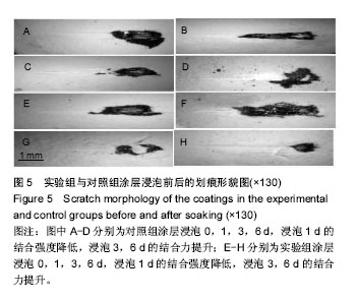
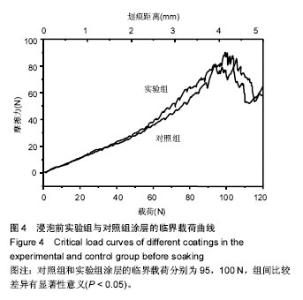
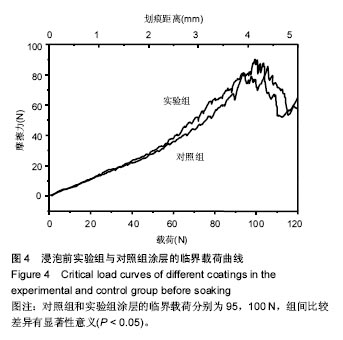
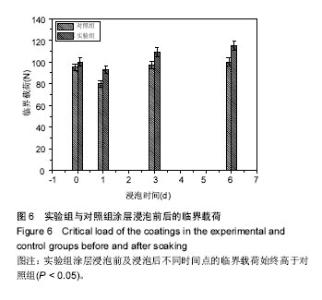
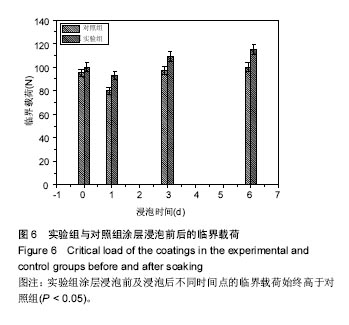
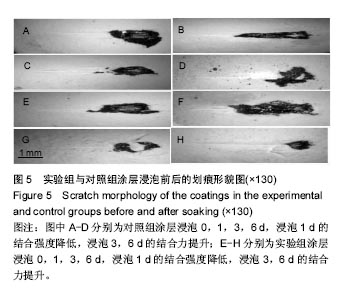
图5为两组涂层浸泡不同时间后划痕的光学形貌图,图6是相对应的临界载荷值,对照组和实验组涂层浸泡第1天的临界载荷分别为80,93 N,第3天的临界载荷分别为97,109 N,第6天的临界载荷分别为100,115 N,实验组涂层的临界载荷始终高于对照组(P=0.004,0.011,0.007)。除了浸泡第1天结合强度降低外,另外时间点观察到的结合力是提升的,这与陈海波等[19]观察到的涂层结合力持续降低结果有所不同,也有可能与他们采用的等离子喷涂技术有关[20]。此次研究使用的是电磁感应沉积法,在制备过程中没有高温产生,不会在涂层中产生内应力,使得涂层在培养基中更稳定,不易溶解。浸泡第1天后涂层结合力下降,因为在模拟体液环境中,羟基磷灰石涂层会发生一定程度的溶解[21];浸泡3,6 d后涂层结合力的提高,与在原始涂层上产生新的类骨磷灰石涂层有关,而掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层结合力提升的更快原因有可能与其表面类骨磷灰石涂层形成更快有关,因为其表面已被类骨磷灰石涂层完全覆盖,这些类骨磷灰石涂层与原始涂层一起构成了新的涂层。 "
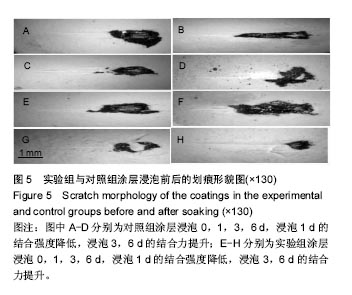
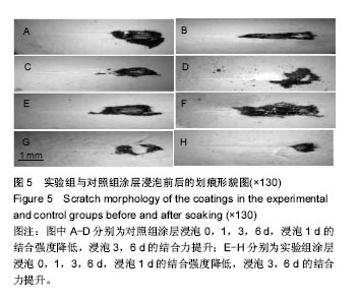
图5为两组涂层浸泡不同时间后划痕的光学形貌图,图6是相对应的临界载荷值,对照组和实验组涂层浸泡第1天的临界载荷分别为80,93 N,第3天的临界载荷分别为97,109 N,第6天的临界载荷分别为100,115 N,实验组涂层的临界载荷始终高于对照组(P=0.004,0.011,0.007)。除了浸泡第1天结合强度降低外,另外时间点观察到的结合力是提升的,这与陈海波等[19]观察到的涂层结合力持续降低结果有所不同,也有可能与他们采用的等离子喷涂技术有关[20]。此次研究使用的是电磁感应沉积法,在制备过程中没有高温产生,不会在涂层中产生内应力,使得涂层在培养基中更稳定,不易溶解。浸泡第1天后涂层结合力下降,因为在模拟体液环境中,羟基磷灰石涂层会发生一定程度的溶解[21];浸泡3,6 d后涂层结合力的提高,与在原始涂层上产生新的类骨磷灰石涂层有关,而掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层结合力提升的更快原因有可能与其表面类骨磷灰石涂层形成更快有关,因为其表面已被类骨磷灰石涂层完全覆盖,这些类骨磷灰石涂层与原始涂层一起构成了新的涂层。 "
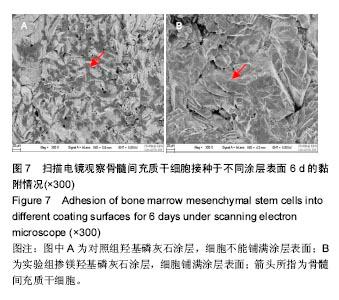
2.5 骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖结果 实验观察了掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响,在实验组涂层上的细胞增殖速度显著快于对照组(图7),含镁涂层能够显著加快骨髓间充质干细胞的生长,可能与掺镁涂层和真实骨都含有一定量的镁离子有关[6]。研究发现与纯羟基磷灰石表面相比,掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层表面更能促进前成骨细胞的体外成骨分化,在骨愈合早期能提高种植体骨结合力[22]。将纯镁棒和不锈钢棒分别植入大鼠股骨骨髓腔,2周后纯镁棒可诱导更多的新骨形成且总骨体积更多[23]。Nakano等[24-26]认为TRPM7 通道(瞬时受体电位M型7)可调节成骨细胞内镁的平衡,促进镁离子内流,增加成骨细胞增殖和迁移。骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的相关机制也成为国内外研究的热点[27-28]。"
| [1]Xin-ye N,Xiao-bin T,Chang-ran G,et al.The Prospect of Carbon Fiber Implants in Radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys.2012;13(4):3821. [2]Zhou H,Hou S,Zhang M,et al.Deposition of calcium phosphate coatings using condensed phosphates (P2O74− and P3O105−) as phosphate source through induction heating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;69:337-342[3]杨晓玲,曹俊杰,杨建,等.C/C复合材料表面聚多巴胺涂层的制备及性能研究[J].军事医学,2016,40(12):941-945,963.[4]Ni XE,Tang B,Lin T,et al.Properties of plasma-spray coated hydroxyapatite on carbon/carbon composites pretreated by an argon plasma.New Carbon Mater.2013;28(3):215-221.[5]Zhong P,Ni XE, Miao YL,et al.Individual humeral head replacement by C/C composite implants coated with hydroxyapatite via rotation plasma spraying.Sci Eng Compos Mater. 2015;22(3):325-330.[6]倪昕晔,李爱军,白瑞成,等.掺镁羟基磷灰石涂层在碳/碳复合材料表面的制备[J].材料研究学报,2015,29(11):853-859.[7]Crespi R,Mariani E,Benasciutti E,et al.Magnesium-Enriched Hydroxyapatite Versus Autologous Bone in Maxillary Sinus Grafting: Combining Histomorphometry With Osteoblast Gene Expression Profiles Ex Vivo.J Periodontol. 2009;80(4): 586-593.[8]Nabiyouni M,Ren Y,Bhaduri SB.Magnesium substitution in the structure of orthopedic nanoparticles: A comparison between amorphous magnesium phosphates, calcium magnesium phosphates, and hydroxyapatites. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;52:11-17.[9]Park JW,Kim YJ,Jang JH,et al.Osteoblast response to magnesium ion-incorporated nanoporous titanium oxide surfaces.Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;21(11):1278-1287.[10]Park JW,An CH,JeongSH,et al.Osseointegration of commercial microstructured titanium implants incorporating magnesium: a histomorphometric study in rabbit cancellous bone.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(3):294-300.[11]周欢,杨蒙蒙,侯赛赛,等.掺杂不同离子的羟基磷灰石涂层研究现状[J].国际生物医学工程杂志, 2016,39(5):319-322.[12]Su Y,Li D,Su Y.Improvement of the Biodegradation Property and Biomineralization Ability of Magnesium-Hydroxyapatite Composites with Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate and Hydroxyapatite Coatings. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(5): 818-828.[13]Khalajabadi SZ,Ahmad N,Yahya A,et al.The role of titania on the microstructure, biocorrosion and mechanical properties of Mg/HA-based nanocomposites for potential application in bone repair. Ceram Int.2016;42(16):18223-18237.[14]Ni XY,Li AJ,Xiong XB,et al.Effect of electromagnetic induction deposition's heating time of magnesium-hydroxyapatite coating on carbon/carbon composites.J Biobased Mater Bio. 2014;8(6):603-609.[15]Xiong XB,Ni XY,Chu CC,et al.Effect of Induction Frequency of Chemical Liquid Vaporization Deposition on Preparation of Hydroxyapatite Coating on C/C composites.J Biobased Mater Bio.2015;9(5):537-543.[16]Hench LL.Sol-gel materials for bioceramic applications.Curr Opin Solid St M.1997;2:604-610.[17]LeGeros RZ.Properties of osteoconductive biomaterials: calcium phosphates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 395:81-98.[18]Xin-Bo X,Xin-Ye N,Ya-Yun L,et al.A Novel Strategy for Preparation of Si-HA Coatings on C/C Composites by Chemical Liquid Vaporization Deposition/Hydrothermal Treatments. Sci Rep.2016;6:31309.[19]陈海波,憨勇,徐可为.等离子喷涂-水热合成羟基磷灰石涂层的体外稳定性[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2005,34(5):754-757.[20]熊信柏,邹春莉,冯岩鹏,等.钛合金表面高频感应热梯度法制备生物活性钙磷涂层探索[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2007,36(7): 1249-1252.[21]周宏明,曾麟,易丹青,等.电泳沉积制备BG/BG—FHA复合涂层[J].复合材料学报,2011,28(6):194-199.[22]Zhao SF,Jiang QH,Peel S,et al.Effects of magnesium-substituted nanohydroxyapatite coating on implant osseointegration.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24 (A100):34-41.[23]Holmes D.Bone: Neuronal origin of osteogenic effects of magnesium.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(12):687.[24]Nakano Y,Le MH,Abduweli D,et al.A Critical Role of TRPM7 As an Ion Channel Protein in Mediating the Mineralization of the Craniofacial Hard Tissues.Front Physiol.2016;7:258.[25]Abed E,Martineau C,Moreau R.Role of melastatin transient receptor potential 7 channels in the osteoblastic differentiation of murine MC3T3 cells.Calcif Tissue Int. 2011;88(3):246-253.[26]Abed E,Moreau R.Importance of melastatin-like transient receptor potential 7 and magnesium in the stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and migration by platelet-derived growth factor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297(2): C360-C368.[27]Wang CL,Xiao F,Wang CD,et al.Gremlin2 Suppression Increases the BMP-2-Induced Osteogenesis of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via the BMP-2/Smad/Runx2 Signaling Pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(2):286-297.[28]Chatzinikolaidou M,Pontikoglou C,Terzaki K,et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2) immobilized on laser-fabricated 3D scaffolds enhance osteogenesis.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;149:233-242. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | Huang Shibo, Xie Hui, Wang Zongpu, Wang Weidan, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Application of degradable high-purity magnesium screw in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 493-498. |
| [5] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [6] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [9] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [12] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [13] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [14] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [15] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||