Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (33): 5249-5254.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.33.001
Tetracycline hydrochloride promotes rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells proliferation in vitro
Zhang Jue1, Xue Si-liang2, Luo Yuan3, Zhi Wei4
- 1Department of Pharmacy, Zunyi Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Dermatology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Pharmacy, Guizhou Province Osteological Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 4Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies of Materials, Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China)
-
Revised:2017-06-12Online:2017-11-28Published:2017-12-01 -
Contact:Zhi Wei, Doctor, Engineer, Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies of Materials, Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jue, Master, Associate professor, Department of Pharmacy, Zunyi Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China Xue Si-liang, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Dermatology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China Zhang Jue and Xue Si-liang contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31400809; the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Science and Technology Department, No [2012]2366; the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 2682015CX006
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jue, Xue Si-liang, Luo Yuan, Zhi Wei. Tetracycline hydrochloride promotes rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells proliferation in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(33): 5249-5254.
share this article
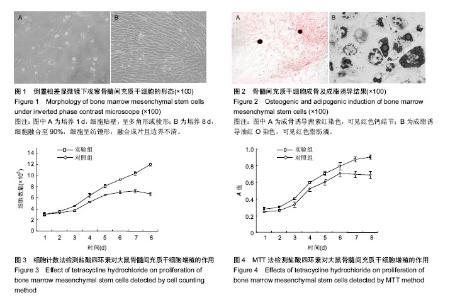
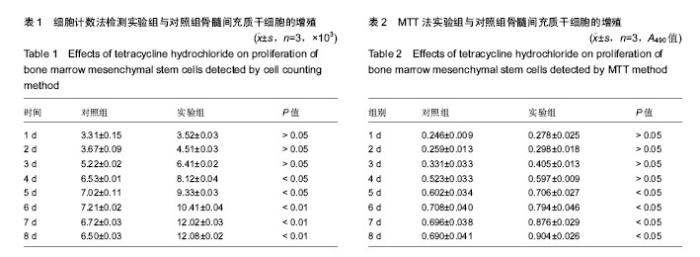
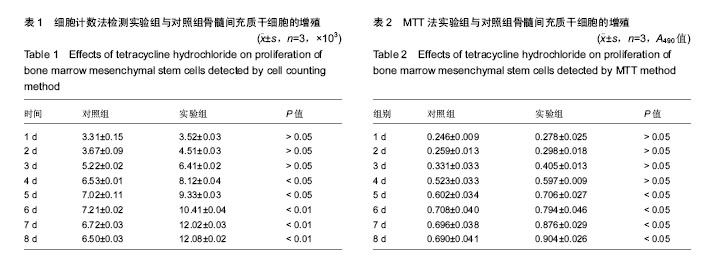
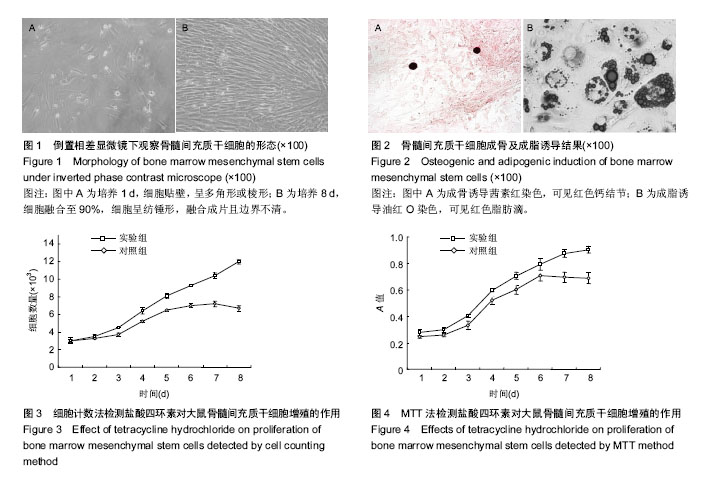
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的形态学观察 骨髓间充质干细胞经含体积分数10%胎牛血清的L-DMEM完全培养基培养1 d后贴壁,呈多角形或棱形(图1A);3 d后第1次换液,细胞数量增多;6 d后,细胞数量显著增多,且以较小的梭形细胞为主,漩涡状排列生长;8 d后,细胞融合至90%,细胞呈纺锤形,融合成片且边界不清(图1B)。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞的鉴定 骨髓间充质干细胞经成骨诱导21 d行茜素红染色,可见红色钙结节(图2A);骨髓间充质干细胞经成脂诱导14 d行油红O染色,出现红色脂肪滴(图2B)。 2.3 细胞计数法检测细胞增殖 连续8 d对两组进行细胞计数,从生长曲线图(图3)可以看出,随着培养时间的延长,骨髓间充质干细胞数量增加,实验组骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖能力强于对照组。数据分析(表1)显示:培养1-3 d,实验组和对照组细胞数量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养4-8 d,实验组细胞数量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。 2.4 MTT法检测细胞增殖 连续8 d经MTT检测,从生长曲线(图4)看出两组骨髓间充质干细胞数量均随培养时间的延长而增加。第1天为骨髓间充质干细胞的潜伏期,3-6 d为对数生长期,第7天,对照组骨髓间充质干细胞进入平台期,实验组骨髓间充质干细胞继续增殖。统计分析结果显示(表2):培养1-4 d,两组A值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第5-8天,实验组细胞增殖能力明显强于对照组(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Golub LM,Lee HM,Lehrer G,et al.Minocycline reduces gingival collagenolytic activity during diabetes:preliminary observations and a proposed new mechanism of action.J Periodontal Res. 1983;18(5):516-526.[2] Golub LM,Ramamurthy NS,McNamara TF,et al.Tetracyclines inhibit tissue collagenase activity:a new mechanism in the treatment of periodontal disease.J Periodontal Res. 1984;19: 651-655.[3] Golub LM,Goodson JM,Lee HM,et al.Locally and lowdose systemically administered tetracycline inhibitt issue collagenase activity:potential new approaches in the treatment of periodontal disease.J Periodontol.1985;56:93-97.[4] Golub LM,Wolf M,Lee HM,et al.Further evidence that Tetracyclines inhibit collagenase activity in human crevicular fluid and from other mammalian source.J Periodont Res. 1985;20:12-23.[5] Kaneko H,Sasaki T,Ramamurthy NS,et al.Tetracycline administration normalizes the struction and acid phosphatase activity of osteoclasts in sterptozotocin-induced diabetes rats. Antomical Record.1990,227:427.[6] Gerson SL.Mesenchymal stem cells: no longer second class marrow citizens.Nat Med.1999;5(3):262-264.[7] Bonab MM,Alimoghaddam K,Talebian F,et al.Aging of mesenchymal stem cell in vitro.BMC Cell Biol. 2006;7:14. [8] 孔清泉,项舟,杨志明.骨髓基质干细胞作软组织工程种子细胞研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(4):277-280.[9] 陈旭,杨志明,解慧琪,等.WO-1 对成骨细胞的生物学效应研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005, 19(10):822-825[10] 李莉,黄永灿,常丽,等.盐酸四环素缓释微球的制备[J].华西药学杂志,2008,23(4):391-393.[11] 张珏,陈晓和,李莉,等.盐酸四环素缓释微球对大鼠成骨细胞活性的影响[J].华西药学杂志,2010,25(1):1-3.[12] 张珏,邓媛媛,曾富佳.盐酸四环素缓释微球对成骨细胞增殖作用的研究[J].中国民族民间医药杂志,2013,22(18):19-20.[13] 李宁,李应福,谢兴文,等.中药诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的定向分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):135-139.[14] 鲍远,黄俊明,靖兴志,等.淫羊藿苷促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(24):3501-3507.[15] Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science.1999; 284(5411):143-147.[16] Prockop DJ.Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues.Science.1997; 276(5309):71-74.[17] Richards M,Huibregtse BA,Caplan AI,et al.Marrow-derived progenitor cell injections enhance new bone formation during distraction.J Orthop Res.1999;17(6):900-908. [18] Fukuda K.Molecular characterization of regenerated cardiomyocytes derived from adult mesenchymal stem cells. Congenit Anom(Kyoto).2002;42(1):1-9.[19] Lu P,Blesch A,Tuszynski MH.Induction of bone marrow stromal cells to neurons: differentiation, transdifferentiation, or artifact.J Neurosci Res.2004;77(2):174-191. [20] Clabaut A,Delplace S,Chauveau C,et al. Human osteoblasts derived from mesenchymal stem cells express adipogenic markers upon coculture with bone marrow adipocytes. Differentiation. 2010;80(1):40-45. [21] Cipriani P,Guiducci S,Miniati I,et al.Impairment of endothelial cell differentiation from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: new insight into the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(6):1994-2004.[22] Ouyang JF,Lou J,Yan C,et al.In-vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside.J Pharm Pharmacol.2010;62(4):530-538. [23] 杨志明.组织工程基础与临床[M].成都:四川科学技术出版社, 2000:4.[24] Xu S, De Becker A, Van Camp B, et al. An improved harvest and in vitro expansion protocol for murine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:105940.[25] Chi LLY, Bianco J, Giardini-Rosa R,et al.Direct and indirect co-culture of bone marrow stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells with chondrocytes in 3D scaffold-free culture. J Regen Med Tissue Eng.2016;2050-1218(5):1-5.[26] Zhao Y, Waldman SD, Flynn LE. Multilineage co-culture of adiposederived stem cells for tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015; 9:826-837.[27] Boyle J, Luan B, Cruz TF,et al.Characterization of proteoglycan accumulation during formation of cartilagenous tissue in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1995; 3:117-125.[28] 张岩,陈曦海,纪艳超,等.贴壁法体外分离培养大鼠间充质干细胞的效果验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(6): 1005-1008.[29] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng.2001; 7:211-228.[30] Flynn L,Prestwich GD,Semple JL,et al. Adipose tissue engineering with naturally derived scaffolds and adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials. 2007; 28: 3834-3842.[31] 石淙,万腊根.细胞增殖的检测方法[J].实验与检验医学,2012, 30(2):153-155.[32] Goel H0C,Prakash H,Ali A,et al.Podophyllum hexandrum modu -lates gamma radiation-induced immunosuppression in Balb/c mice:implications in radioprotection.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;295(1-2):93-103.[33] Lin P,Allison DC.Measurement of DNA content and of tritiated thymidine and bromodeoxyuridine incorporation by the same cells.J Ilistochem Cytochem.1993;41(9):1435-1439.[34] 赵嘉惠,张华屏,王春芳.MTT法在检测细胞增殖方面的探讨[J].山西医科大学学报,2007,38(3):262-264.[35] 文珠,胡国柱,俞火,等.黄精多糖干预长春新碱抑制骨髓基质细胞增殖的研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2011, 26(7):1630-1632.[36] Westendorf JJ,Kahler RA,Schroeder TM.Wnt signaling in osteoblasts and bone diseases.Gene. 2004;341:19-39.[37] 侯费祎,谢兴文,席芳琴.等.麝香酮含药血清对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖、分化的影响[J].西安交通大学学报,2013, 34(1): 110-114. [38] Burrow KL,Hoyland JA,Richardson SM.Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Exhibit Enhanced Proliferative Capacity and Retain Multipotency Longer than Donor-Matched Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells during Expansion In Vitro.Stem Cells Int.2017;2017:2541275. [39] Sherman AB,Gilger BC,Berglund AK,et al.Effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and stem cell supernatant on equine corneal wound healing in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther.2017;8(1):120. [40] da Silveira Gerzson A,Machado DC,Marinovic DR,et alAssessment of Adhesion and Proliferation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Polymer Matrices with rhGH.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(3):e183-e189. [41] Danisovic L,Oravcova L,Krajciova L,et al.Effect of long-term culture on the biological and morphological characteristics of human adipose tissue-derived stem Cells.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;68(1):149-158.[42] Blázquez-Prunera A,Díez JM,Gajardo R,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells maintain their phenotype, multipotentiality, and genetic stability when cultured using a defined xeno-free human plasma fraction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):103. [43] Batsali AK,Pontikoglou C,Koutroulakis D,et al.Differential expression of cell cycle and WNT pathway-related genes accounts for differences in the growth and differentiation potential of Wharton's jelly and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther.2017;8(1):102. [44] Maadawi ZME.Conditioned Medium Derived from Salidroside-Pretreated Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture Ameliorates Mouse Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cerebral Neuroinflammation- Histological and Immunohistochemical Study.Int J Stem Cells.2017;10(1):60-68. [45] Zeng YL,Zheng H,Chen QR,et al.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing MiR-21 efficiently repair myocardial damage in rats.Oncotarget.2017;8(17): 29161-29173. [46] Futrega K,Atkinson K,Lott WB,et al.Spheroid Coculture of Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells and Monolayer Expanded Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Polydimethylsiloxane Microwells Modestly Improves In Vitro Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cell Expansion.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2017; 23(4):200-218. [47] Bottagisio M,Lopa S,Granata V,et al.Different combinations of growth factors for the tenogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in monolayer culture and in fibrin-based three-dimensional constructs. Differentiation. 2017;95:44-53. [48] Cleary MA,Narcisi R,Albiero A,et al.Dynamic Regulation of TWIST1 Expression During Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev.2017;26(10):751-761. [49] Shou K,Niu Y,Zheng X,et al.Enhancement of Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Angiogenic Capacity by NPWT for a Combinatorial Therapy to Promote Wound Healing with Large Defect.Biomed Res Int.2017; 2017:7920265.[50] Perucca S,Di Palma A,Piccaluga PP,et al.Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) induce ex vivo proliferation and erythroid commitment of cord blood haematopoietic stem cells (CB-CD34+ cells).PLoS One.2017;12(2):e0172430.[51] Wang MY,Nestvold J,Rekdal Ø,et al.A novel rat fibrosarcoma cell line from transformed bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells with maintained in vitro and in vivo stemness properties.Exp Cell Res.2017;352(2):218-224.[52] Tsai TL,Li WJ.Identification of Bone Marrow-Derived Soluble Factors Regulating Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration.Stem Cell Reports.2017;8(2):387-400. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [8] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [9] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [10] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [11] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [14] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||