Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5240-5248.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.026
Stability improvement in adult maxillary transverse deficiency after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: a Meta-analysis
Fei Lu, Bai Yang, Yuan Xiao-ping
- (Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China)
-
Received:2017-06-25Online:2017-11-18Published:2017-11-15 -
Contact:Yuan Xiao-ping, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Fei Lu, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fei Lu, Bai Yang, Yuan Xiao-ping. Stability improvement in adult maxillary transverse deficiency after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5240-5248.
share this article
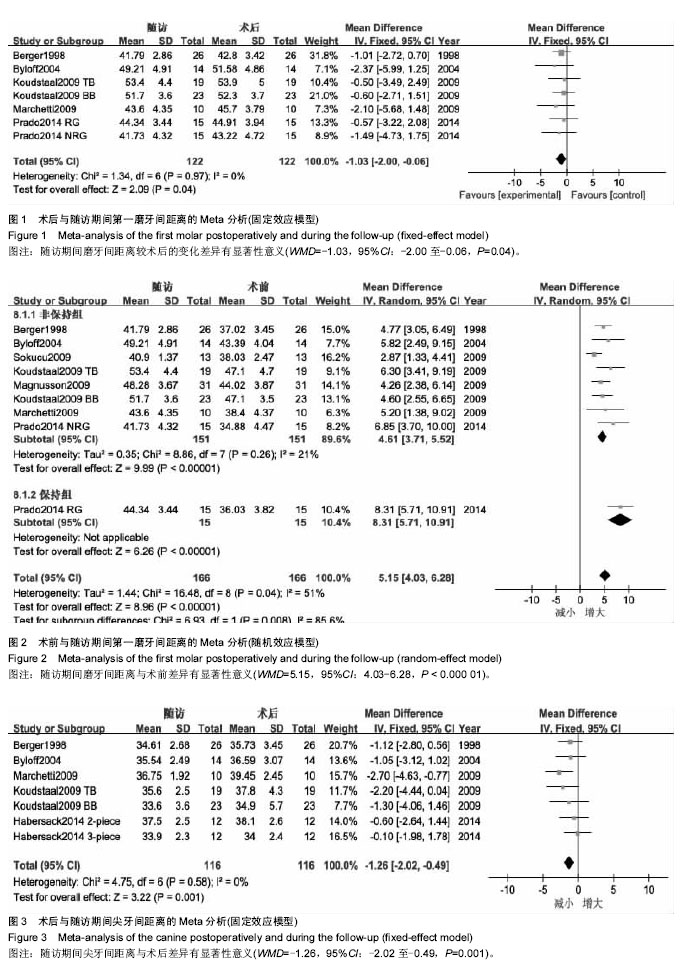
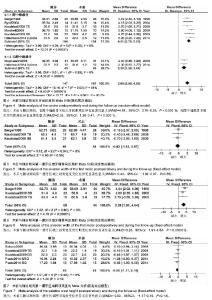
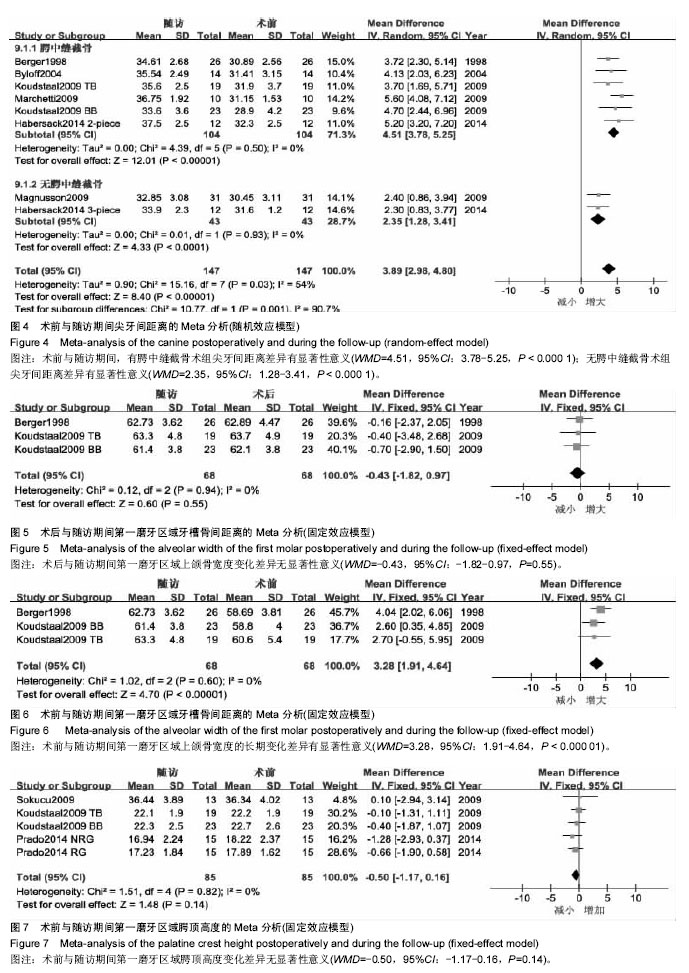
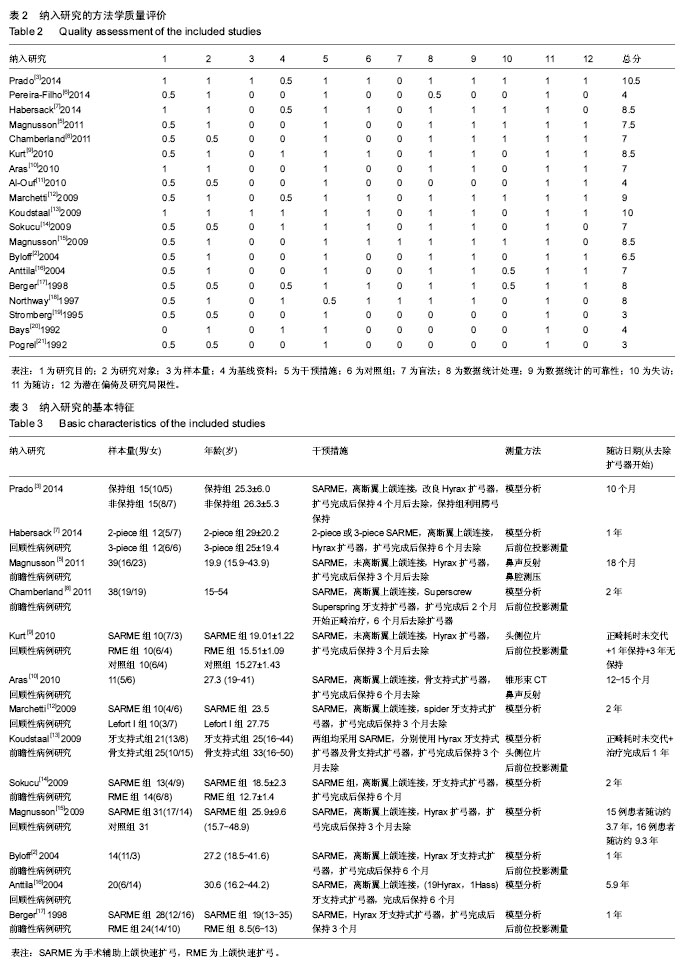
2.1 文献筛选结果及纳入文献的特征 初检后获得769篇相关文献,2名研究员通过阅读文题和摘要筛出与本研究相关的文献42篇,阅读全文后排除23篇研究,对纳入19篇文献进行质量评价后[2-3,5-21],排除5篇低等质量的研究后,纳入14篇文献,其中2篇为高等质量,12篇为中等质量,在提取资料的过程中,Northway[18]的表中数据与文中叙述不一致,予以排除,最终纳入13篇研究。纳入研究的方法学质量评价见表2,纳入研究的基本特征见表3。 2.2 Meta分析结果 本文主要从牙、上颌骨、鼻气道几个方面来分析手术辅助上颌扩弓矫治上颌横向发育不足的稳定性。选取治疗前、去除扩弓器后正畸治疗前、随访3个时期的数据进行Meta分析,共9篇研究进行比较。 2.2.1 术后牙的稳定性 主要对磨牙、尖牙间距离的变化进行分析。 5个研究报道了随访期磨牙间距离的变化[2-3,12-13,17]。各研究结果间同质性较好(P=0.97,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型,合并后结果显示,随访期磨牙间距离的变化差异有显著性意义(WMD=-1.03,95%CI:-2.00至-0.06),提示在随访期磨牙间距离有少量复发,约为1.03 mm(图1)。 7个研究报道了磨牙间距离的长期变化[2-3,12-15,17]。异质性检验显示各研究间有较大异质性(P=0.04,I2=51%),产生异质性的原因可能是由于Prado[3]的研究在随访期内一直佩戴腭弓对扩弓效果进行保持,术后复发较少。按照随访期内是否佩戴保持期分为两个亚组进行分析,非保持组数据合并后,各结果间无统计学异质性(P=0.26,I2=21%)。采用随机效应模型合并后,磨牙间距离的变化差异有显著性意义(WMD=5.15,95%CI:4.03-6.28),提示手术辅助上颌快速扩弓术后的长期观察中,磨牙间距离较术前平均增加了约5.15 mm(图2)。 5个研究报道了随访期尖牙间距离的变化[2,7,12-13,17],各研究结果间同质性较好(P=0.58,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型合并,Meta分析结果显示,随访期尖牙间距离的变化差异有显著性意义(WMD=-1.26,95%CI:-2.02至-0.49),提示在随访期尖牙间距离有所减小,约为1.26 mm(图3)。 6个研究报道了尖牙间距离的长期变化[2,7,12-13,15,17]。"
| [1] Brown GVI, Epker BN, Wolford LM. Transverse maxillary deficiency dentofacial deformities:integrated orthodontic and surgical correction.St Louis:Mosby;1980.[2] Byloff FK, Mossaz CF. Skeletal and dental changes following surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion.Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(4):403-409. [3] Prado GP, Furtado F, Aloise AC, et al. Stability of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion with and without retention analyzed by 3-dimensional imaging.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;145(5):610-616.[4] 聂萍,陶丽,唐艳梅,等. 手术辅助上颌快速扩弓对鼻气道形态和鼻阻力的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2015,13(2):147-150.[5] Magnusson A, Bjerklin K, Nilsson P, et al. Nasal cavity size,airway resistance,and subjective sensation after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion:a prospective longitudinal study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;140(5):641-651.[6] Pereira-Filho VA, Monnazzi MS, Gabrielli MA, et al. Volumetric upper airway assessment in patients with transverse maxillary deficiency after surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43(5):581-586.[7] Habersack K, Becker J, Ristow O, et al. Dental and skeletal effects of two-piece and three-piece surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with complete mobilization:a retrospective cohort study.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(11):2278-2288.[8] Chamberland S, Proffit WR. Short-term and long-term stability of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion revisited.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;139(6):815-822.[9] Kurt G, Altug-Atac AT, Atac MS, et al. Stability of surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion and orthopedic maxillary expansion after 3 years’ follow-up.Angle Orthod. 2010;80(4): 425-431.[10] Aras A, Akay MC, Cukurova I, et al. Dimensional changes of the nasal cavity after transpalatal distraction using bone-borne distractor:an acoustic rhinometry and computed tomography evaluation.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(7):1487-1497.[11] Al-Ouf K, Krenkel C, Hajeer MY, et al. Osteogenic uni- or bilateral form of the guided rapid maxillary expansion.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2010;38(3):160-165.[12] Marchetti C, Pironi M, Bianchi A, et al. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion vs. segmental Le Fort I osteotomy:transverse stability over a 2-year period.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009; 37(2):74-78.[13] Koudstaal MJ, Wolvius EB, Schulten AJ, et al. Stability,tipping and relapse of bone-borne versus tooth-borne surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion:a prospective randomized patient trial.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;38(4):308-315.[14] Sokucu O, Kosger HH, Bicakci AA, et al. Stability in dental changes in RME and SARME:a 2-year follow-up.Angle Orthod. 2009;79(2):207-213.[15] Magnusson A, Bjeklin K, Nilsson P, et al. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion:long-term stability.Eur J Orthod. 2009;31(2):142-149.[16] Anttila A, Finne K, Keski-Nisula K, et al. Feasibility and long-term stability of surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with lateral osteotomy.Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(4):391-395.[17] Berger JL, Pangrazio-Kulbersh V, Borgula T, et al. Stability of orthopedic and surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion over time.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1998;114(6):638-645.[18] Northway WM, Meade JB. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion:a comparison of technique,response,and stability. Angle Orthod. 1997; 67(4):309-320.[19] Stromberg C, Holm J. Surgically assisted,rapid maxillary expansion in adults.A retrospective long-term follow-up study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg.1995,23(4):222-227.[20] Bays RA, Greco JM. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion:an outpatient technique with long-term stability.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992;50(2):110-113.[21] Pogrel MA, Kaban LB, Vargervik K, et al. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion in adults.Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1992;7(1):37-41.[22] Epker BN, Wolford LM. Transverse maxillary deficiency dentofacial deformities:integrated orthodontic and surgical correction.St Louis:Mosby;1980.[23] Timms DJ,Vero D. The relationship of rapid maxillary expansion to surgery with special reference to midpalatal synostosis.Br J Oral Surg. 1981;19(3):180-196.[24] Korn EL, Baumrind S. Transverse development of human jaws between the ages of 8.5 and 15.5 years,studied longitudinally with the use of implant.J Dent Res. 1990;69(6):1298-1306.[25] Deeb W, Hansen L, Hotan T, et al. Changes in nasal volume after surgically assisted bone-borne rapid maxillary expansion.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;137(6): 782-789.[26] Doruk C, Sokucu O, Bicakci AA, et al. Comparison of nasal volume changes during rapid maxillary expansion using acoustic rhinometry and computed tomography.Eur J Orthod. 2007; 29(3):251-255.[27] Laudemann K, Petruchin O, Nafzger M, et al. Long-term 3D cast model study:bone-borne vs. tooth-borne surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion due to secondary variable.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;14(2):105-114.[28] Landes CA, Laudemann K, Petruchin O, et al. Advantages and limits of 3-segmen(paramedian) versus 2-segment(median) surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion(SARME).Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113(1):29-40.[29] Sygouros A, Motro M, Ugurlu F, et al. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion:cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of different surgical techniques and their effects on the maxillary dentoskeletal complex.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;146(6):748-757.[30] Kilic E, Kilic B, Kurt G, et al. Effects of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion with and without pterygomaxillary disjunction on dental skeletal structures:a retrospective review.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;115(2):167-174.[31] Laudemann K, Petruchin O,Mack MG, et al. Evaluation of surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with or without pterygomaxillary disjunction based upon preoperative and post-expansion 3D computed tomography data.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;13(3):159-169.[32] Ergina PL, Cook JA, Blazeby JM, et al. Challenges in evaluating surgical innovation. Lancet. 2009;374(9695):1097-1104.[33] Tausche E, Hansen L, Hietschold V, et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of surgically assisted implant bone-borne rapid maxillary expansion:a pilot study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;131(4 suppl):S92-99. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [3] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [4] | Wu Min, Zhang Yeting, Wang Lu, Wang Junwei, Jin Yu, Shan Jixin, Bai Bingyi, Yuan Qiongjia. Effect of concurrent training sequences on body composition and hormone response: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1305-1312. |
| [5] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [8] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [9] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [10] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [11] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [12] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [13] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [14] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [15] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||