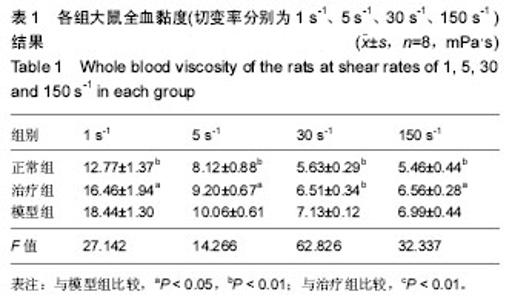
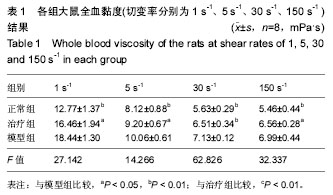
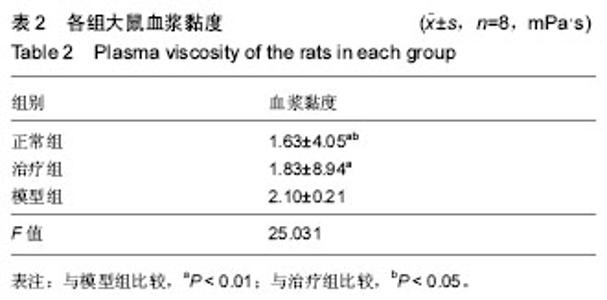
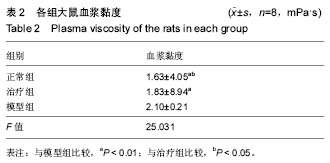
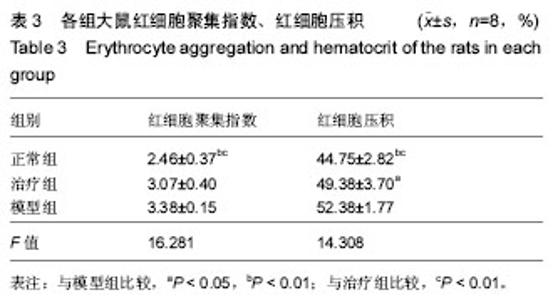
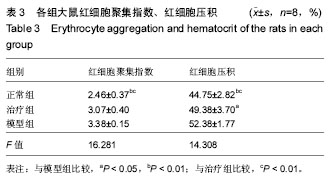
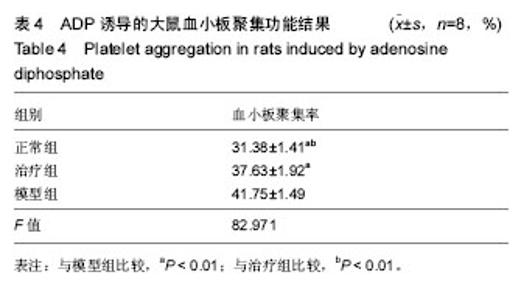
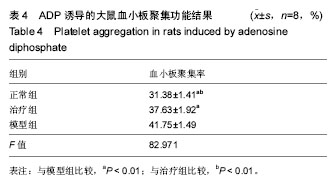
| [1] 郑春水,黄萍萍,廖军.电针对颈椎病模型大鼠椎间盘细胞β-catenin 和 Axin 蛋白表达的影响[J].时珍国医国药, 2015,26(5): 1259-1261[2] Feng MS,Gao JH,Zhu LG,et al. Analysis of X-ray signs of cervical spondylosis between vertebral artery type and radiculopathy.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2015;28( 4):330-334.[3] Yong CL, Bao GP.Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Cervical Vertigo.Pain Physician.2015;18( 4):583-595.[4] 刘智勇,郝阳泉.椎动脉型颈椎病的病因病机研究进展[J].实用中西医结合临床,2015,15(4):88-90.[5] 巩彦龙,宋敏,刘涛.3种方法评价椎动脉型颈椎病大鼠模型[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 2016,37(6):497-502.[6] 柯尊华,王静怡.颈椎病流行病学及发病机理研究进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014( 1):62-64.[7] 施杞,郝永强,彭宝淦,等. 动静力平衡失调与颈椎病-颈椎病动物模型的实验研究[J].上海中医药大学学报,1993,13(1):53-56.[8] 赵定麟, 陈德玉, 沈强. 实验性颈椎病模型的设计[J].中华外科杂志, 1993, 31(8):453-455.[9] 蔡钦林,黄云钟,杨文,等. 慢性压迫性颈脊髓超微病理变化的研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1996,6 (6):254-255.[10] 张军,孙树椿.神经根型颈椎病(急性期)动物模型的建立[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2000,8(1):12-16.[11] 郝永强,施杞,郑松国.大鼠颈椎病实验模型的设计与建立[J].中国矫形外科志,1999,6(4):282-284.[12] 戎利民,李佛保,蔡道章. 脊髓型颈椎病动物模型的初步建立[J].解剖学研究,2001,23(4):313-315.[13] 陈元川,王翔,庞坚,等.单纯口服中药治疗神经根型颈椎病用药分析[J].上海中医药杂志,2014,48(6):78-80.[14] 吴绪祥,钟洪,臧坤堂.乌龙丹治疗椎动脉型颈椎病75例[J].湖北中医杂志.1999,21(10):465[15] 高丽娜, 崔元璐,延阔.丹参红花配伍研究进展[J].中草药,2016,47 (4):671-679.[16] 徐玲. 丹参的药用成分与药理作用探析[J].健康前沿,2016,23(7): 278,214.[17] 胡波,范红伟,马广骏.丹参有效单体IH764-3药理作用研究及其临床应用前景述评[J].白求恩医学杂志,2016,14 (2) :233-235.[18] 杜旌畅,谢晓芳,熊亮,等.川芎挥发油的化学成分与药理活性研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2016,41(23):4328-4333.[19] 刘旭,程艳芹,崔晓博.中药川芎心肌缺血保护作用的谱效学研究[J].中国药业,2016,25(15) :9-12.[20] 刘絮,姜秀文,王立英.川芎生物碱对大鼠脑缺血-再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].北华大学学报(自然),2016,17 (3) :339-343.[21] 高海军,白焕焕,雷廷.川芎嗪在脑缺血再灌注损伤中的保护作用[J].中国老年学, 2015,35(17) :5019-5023.[22] 张红兵,李强,冯靖.川芎嗪下调炎症和黏附基因的表达而抑制血管新生内膜的形成[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2014,30(4) :340-343.[23] 赵文萃,张宁,周慧琴,等.三七总黄酮对高血脂大鼠血脂的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2016, (8) :143-147.[24] 刘苗苗,罗仕华,李中伟.三七断骨巴布膏对膝关节骨性关节炎患者膝关节功能的影响[J].河北中医,2016,38 (5) :679-681.[25] 朱少琴,江小萍.三七总皂苷对动脉粥样硬化患者颈动脉内膜中层厚度和斑块的影响观察[J].江西中医药,2017,48 (4) :40-41.[26] 尹金磊.浅谈葛根的临床应用[J].中国社区医师:综合版,2005, (6):9-9.[27] 刘旭.小议张仲景麻黄葛根先煎之理[J].国医论坛,2007,22(4 : 44-45.[28] 易增兴,周复辉.葛根临床应用体会[J].陕西中医,2006,27(11) : 1453-1454[29] 潘洪平,杨嘉玲,莫祥兰,等.葛根素注射液对急性脑缺血模型大鼠脑细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中国中药杂志,2005,30(6):457-459.[30] 齐学军.葛根素治疗脑血管痉挛性头痛120例疗效观察[J].浙江实用医学,2003,8(3):170-171.[31] 高尔,王金红,李洪军.乳化葛根素对高脂血症家兔血清NO及PGI_2的影响[J].潍坊医学院学报,2001,23 (1):1-3. |