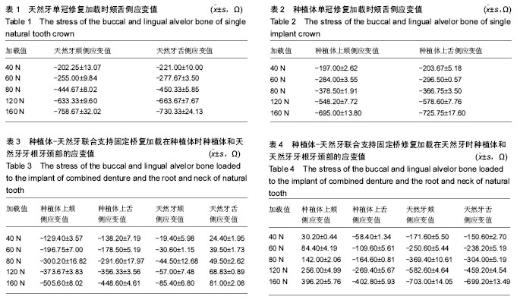
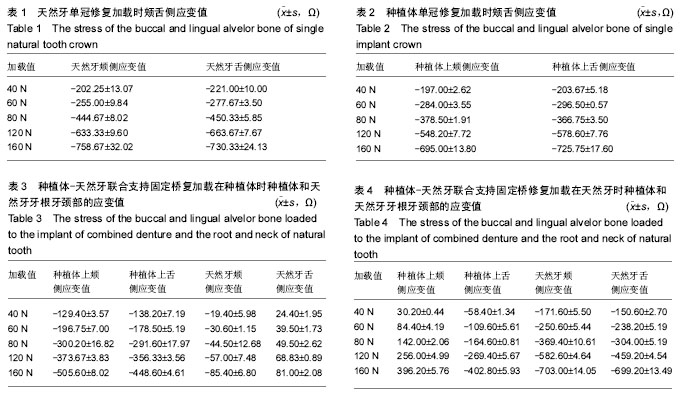
| [1] |
Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun.
Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5.
|
| [2] |
Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe.
Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao.
Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356.
|
| [4] |
Bai Zixing, Cao Xuhan, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Chen Si, Wen Jianmin, Lin Xinxiao, Sun Weidong.
Construction and biomechanical analysis of ankle joint finite element model in gait cycle
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366.
|
| [5] |
Liu Feng, Feng Yi.
Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371.
|
| [6] |
Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong.
Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382.
|
| [7] |
An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu.
Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong.
Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118.
|
| [9] |
Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang.
Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842.
|
| [10] |
Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti.
Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847.
|
| [11] |
Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde.
Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852.
|
| [12] |
Zheng Yongze, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Li Pengfei, Lin Ziling.
Extended finite element modeling analysis of femoral neck fracture based on ABAQUS software
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 853-857.
|
| [13] |
Li Shuo, Su Peng, Zhang Li, Wu Qiulong, Hu Xiangyu, Lai Yuliang.
Positive effect of supracondylar femoral osteotomy on the correction of knee varus based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 858-863.
|
| [14] |
Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie.
Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874.
|
| [15] |
Guo Xiaohui, Song Xizheng, Xiang Hanrui, Kang Zhaorong, Li Daming, Kang Yu, Hu Jun, Sheng Kai.
External spinal fixation elastic stress in the treatment of jumping spinal fracture
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 919-923.
|