Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (29): 4654-4659.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.29.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
A comparative study on two culture methods for adipose-derived stem cells from mice with osteoporosis
Huang Cheng-long1, Li Qing2, Wang Lei2, Huang Kui2, Luo Dao-wen2, Xiao Jin-gang1, 2
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2Orofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2017-05-01Online:2017-10-18Published:2017-11-08 -
Contact:Xiao Jin-gang, Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Huang Cheng-long, Master, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371125; the Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Department, No. 2014JY0044; the Project of Sichuan Education Department, No. 10ZB030; the Project of Sichuan Health Department, No. 80170; the Major Project of Southwest Medical University, No. 201207; the Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation Project of Luzhou Municipal People’s Government-Southwest Medical University, No. 2015LZCYD-S05(2/12); a grant from the Hospital of Stomatology of Southwest Medical University, No. (2017)20
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Cheng-long, Li Qing, Wang Lei, Huang Kui, Luo Dao-wen, Xiao Jin-gang. A comparative study on two culture methods for adipose-derived stem cells from mice with osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(29): 4654-4659.
share this article
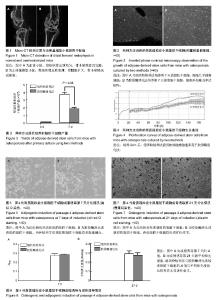
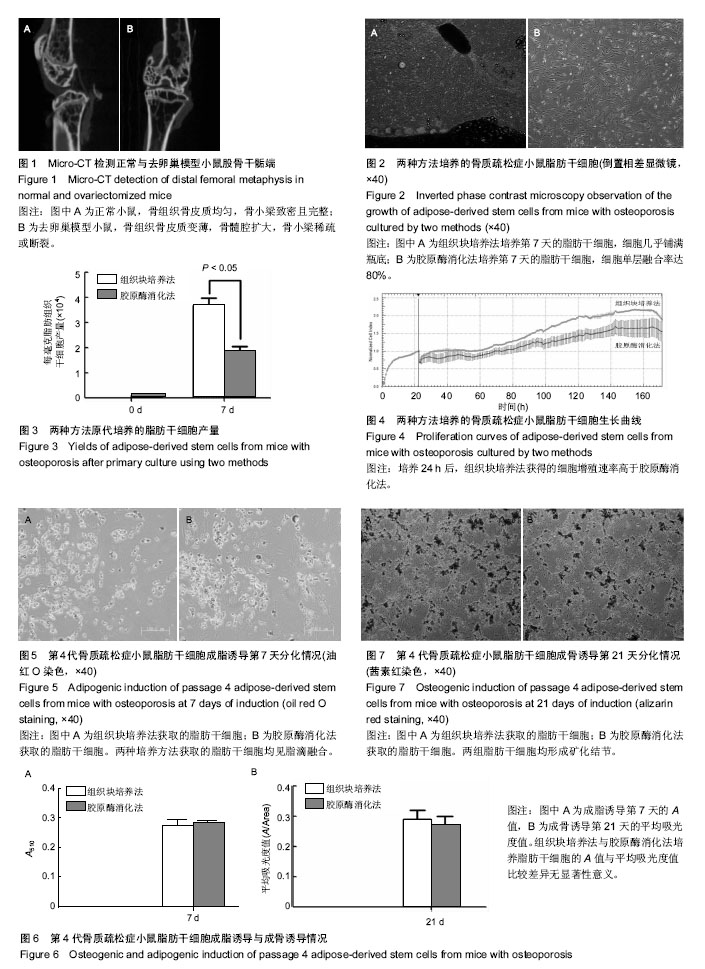
2.1 骨质疏松症小鼠模型构建情况 与正常小鼠相比,去卵巢模型小鼠micro-CT可见骨皮质变薄,骨髓腔扩大,骨小梁稀疏或断裂,骨小梁宽度变窄,骨小梁间距变宽,骨小梁占视野面积降低,证明成功构建骨质疏松小鼠(图1)。 2.2 脂肪干细胞生长情况 组织块培养法培养第 3 天,少量细胞从组织块边缘爬出,贴壁生长,形态为梭形、纺锤形,也可见多角形;培养第7天,细胞几乎铺满瓶底(图2),重复培养23次,成功18次,成功率为78%。胶原酶消化法培养第12-24小时,细胞开始贴壁生长,形态为为多角形,第二三天,细胞贴壁伸展,长梭形或多角形;第7天,细胞单层融合率达80% (图2),重复培养19次,成功6次,成功率为32%。两种方法获取的细胞传至第3代,细胞多为成纤维细胞样,长梭形或纺锤形,形态学无差异,传至第9代,细胞生长状态良好,细胞性状均一,生物学特性稳定。 2.3 流式细胞仪检测结果 组织块法培养的第3代脂肪干细胞表达CD34、CD146及Sca-1,表达率分别为(15.22± 1.85)%、(75.55±3.36)%及(83.48±4.22)%。胶原酶消化法培养的第3代脂肪干细胞表达CD34、CD146及Sca-1,表达率分别为(13.46±2.21)%、(76.62±2.47)%及(84.84± 3.56)%。表明两种方法培养的细胞都是脂肪干细胞。 2.4 脂肪干细胞产量情况 组织块培养法获得的脂肪干细胞培养至第3天,有细胞从组织块边缘爬出,而胶原酶消化法早期即可获得脂肪干细胞;培养第7天,组织块培养法每毫克脂肪组织获得的细胞产量高于胶原酶消化法(P=0.013),见图3。 2.5 脂肪干细胞增殖情况 将组织块培养法和胶原酶消化法获得的第3代脂肪干细胞分别接种到孔板中,在接种后的24 h换液,随后在孵箱中连续培养6 d,通过xCELLigence system 实时检测细胞增殖情况,并生成生长曲线(图4),该曲线是3复孔的平均值生成的实时动态曲线,生长曲线均有明显的滞留期、对数生长期和平台期。方面,培养24 h后,组织块培养法培养细胞增殖速率一直高于胶原酶消化法。 2.6 脂肪干细胞多向分化情况 两种培养方法所得的第4代脂肪干细胞,于成脂诱导后第 4 天可见细胞胞体回缩,胞浆中有脂滴形成,第7天可见脂滴融合,油红O染色脂滴呈橘红色(图5);油红O萃取实验表明两组成脂量比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.065)(图6A)。 两种培养方法所得的第4代脂肪干细胞,成骨诱导第18天可见类似细胞岛的小结节,第 21天可见白色小点,茜素红染色证明为矿化结节(图7),两组间成骨量比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.071)(图6B)。未加成脂或成骨诱导剂的脂肪干细胞未见成脂、成骨分化。"
| [1] Jain S,Krishna Meka SR,Chatterjee K.Curcumin eluting nanofibers augment osteogenesis toward phytochemical based bone tissue engineering.Biomed Mater. 2016;11(5): 055007.[2] Erjavec I,Brkljacic J,Vukicevic S,et al.Mushroom Extracts Decrease Bone Resorption and Improve Bone Formation.Int J Med Mushrooms.2016;18(7):559-569. [3] Chen S,He Z,Xu G,et al.Fabrication and characterization of modified nanofibrous poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds by thermally induced phase separation technique and aminolysis for promoting cyctocompatibility.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016; 27(10):1058-1068.[4] 金玲玲,胡颖,郭庆东等. MC3T3-E1Subclone14体外诱导成骨模型的建立及Ano5基因表达的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2015,23(2): 73-79.[5] Ying H,Li Q,Zhao C.Interleukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor α promote hFOB1.19 cell viability via activating AP1.Am J Transl Res.2016;8(5):2411-2418. [6] Tong S, Xue L, Xu DP, et al. In vitro culture of hFOB1.19 osteoblast cells on TGF-β1-SF-CS three-dimensional scaffolds.Mol Med Rep.2016;13(1):181-187. [7] Liu SH,Wang H,Zhai YM,et al.Comparison of Adipogenesis and Adipocyte Functions of 3T3-L1 Cells and Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.2015;23(6):1729-1733. [8] Boerma M,Burton GR,Wang J,et al.Comparative expression profiling in primary and immortalized endothelial cells: changes in gene expression in response to hydroxy methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibition.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17(3):173-180.[9] Ma Q,Yang JJ,Zhou H,et al.Exenatide promotes chemotactic migration of adipose-derived stem cells through SDF-1/CXCR-4/Rho GTPase pathway.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2016;36(8):1034-1040. [10] Niemeyer P,Fechner K,Milz S,et al.Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue for bone regeneration in a critical size defect of the sheep tibia and the influence of platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials.2010;31(13): 3572-3579. [11] Shi Y,Niedzinski JR,Samaniego A,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells combined with a demineralized cancellous bone substrate for bone regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18 (13-14):1313-1321. [12] Chen HT,Lee MJ,Chen CH,et al.Proliferation and differentiation potential of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells isolated from elderly patients with osteoporotic fractures.J Cell Mol Med.2012;16(3):582-593.[13] Liu HY,Chiou JF,Wu AT,et al.The effect of diminished osteogenic signals on reduced osteoporosis recovery in aged mice and the potential therapeutic use of adipose-derived stem cells.Biomaterials.2012;33(26):6105-6112. [14] Yoon JH,Roh EY,Shin S,et al.Comparison of explant-derived and enzymatic digestion-derived MSCs and the growth factors from Wharton's jelly.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013: 428726.[15] Fu Y,Li R,Zhong J,et al.Adipogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from ovariectomized mice.Cell Prolif.2014;47(6):604-614.[16] Xiao J,Yang X,Jing W,et al.Adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of Lin(-)CD271(+)Sca-1(+) adipose-derived stem cells.Mol Cell Biochem.2013;377(1-2):107-119.[17] Stefanowicz-Hajduk J,Adamska A,Bartoszewski R,et al. Reuse of E-plate cell sensor arrays in the xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analyzer.Biotechniques.2016;61(3):117-122.[18] Sang C,Zhang Y,Chen F,et al.Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses osteogenic differentiation of MSCs by inhibiting semaphorin 3B via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in estrogen-deficiency induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2016;84: 78-87. [19] Yang N,Wang G,Hu C,et al.Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis promoter miR-21 in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res.2013;28(3):559-573. [20] Boeloni JN,Ocarino NM,Goes AM,et al.Comparative study of osteogenic differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue of osteoporotic female rats.Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(2): 103-114. [21] Pan C,Kumar C,Bohl S,et al.Comparative proteomic phenotyping of cell lines and primary cells to assess preservation of cell type-specific functions. Mol Cell Proteomics.2009;8(3):443-450.[22] Oh HY,Jin X,Kim JG,et al.Characteristics of primary and immortalized fibroblast cells derived from the miniature and domestic pigs.BMC Cell Biol.2007;8(1):20-27.[23] Shebaby W,Abdalla EK,Saad F,et al.Data on isolating mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue using a collagenase-free method.Data Brief. 2016;6:974-979. [24] Raposio E,Bonomini S,Calderazzi F.Isolation of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2016;102(7):909-912. [25] Gartland A,Rumney RM,Dillon JP,et al.Isolation and culture of human osteoblasts. Methods Mol Biol.2012;806(1):337-355.[26] Zhong J,Guo B,Xie J,et al.Crosstalk between adipose-derived stem cells and chondrocytes: when growth factors matter. Bone Res.2016;4:15036.[27] Sarkanen JR,Kaila V,Mannerström B,et al.Human adipose tissue extract induces angiogenesis and adipogenesis in vitro.Tissue Eng Part A.2012;18(1-2):17-25.[28] Xu WW,Huang L,Chong KK,et al.Differentiation potential of human adipose tissue derived stem cells into photoreceptors through explants culture and enzyme methods. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017;10(1):23-29.[29] Jing W,Xiao J,Xiong Z,et al.Explant culture:an efficient method to isolate adipose-derived stromal cells for tissue engineering.Artif Organs.2011;35(2):105-112.[30] Priya N,Sarcar S,Majumdar AS,et al. Explant culture:a simple,reproducible, efficient and economic technique for isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue and lipoaspirate.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2014;8(9): 706-716. [31] Hendijani F.Explant culture: An advantageous method for isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human tissues.Cell Prolif.2017.doi:10.1111/cpr.12334.[Epub ahead of print] |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [4] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [5] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [7] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [8] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [9] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [10] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [11] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [12] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [14] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [15] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||