Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (28): 4536-4542.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.28.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of an animal model of osteoarthritis and its application in functional food research
Chen Shi-jie1, Lao Wen-yan1, 2, Zhou Yan-li1, Li Yan-mei3, Zhao Xiao-hong1, 2
- 1Beijing Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functional Foods, College of Applied Arts and Science of Beijing Union University, Beijing 100191, China; 2Research Institute for Science and Technology of Functional Food, Beijing Union University, Beijing 100191, China; 3Beijing Gingko-group Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100081, China
-
Revised:2017-04-23Online:2017-10-08Published:2017-11-10 -
Contact:Zhao Xiao-hong, M.D., Researcher, Beijing Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functional Foods, College of Applied Arts and Science of Beijing Union University, Beijing 100191, China; Research Institute for Science and Technology of Functional Food, Beijing Union University, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Chen Shi-jie, Studying for master’s degree, Beijing Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functional Foods, College of Applied Arts and Science of Beijing Union University, Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:the Open Project of the Beijing Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functional Foods, No. Zk70201501
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Shi-jie, Lao Wen-yan, Zhou Yan-li, Li Yan-mei, Zhao Xiao-hong. Establishment of an animal model of osteoarthritis and its application in functional food research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(28): 4536-4542.
share this article

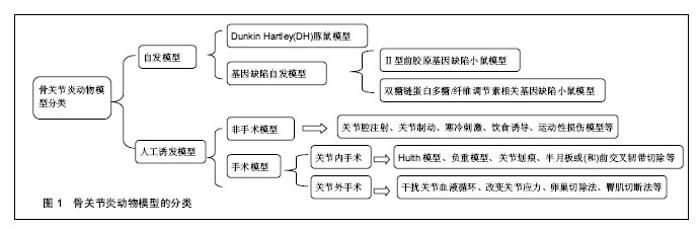
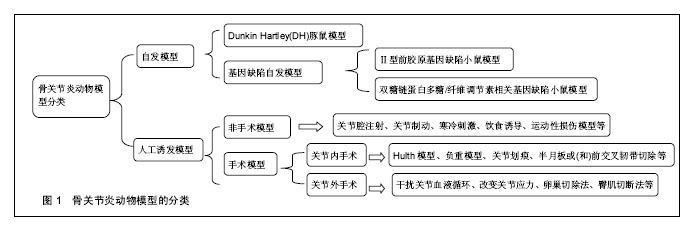
2.1.1 模型动物的选择 模型动物的选择可以遵循Pritzker[13]提出的3个原则:相关性、适当性和实用性。相关性指所选动物能够模拟人类发病过程中的病理现象,其模型可以较好地体现出动物的特点以及类似人类疾病的特征;适当性首先是应用动物而非简单的调查研究,其次是根据实验目的和要求选择合适的动物品种;实用性是指根据动物是否易于控制、动物来源是否充分、维护条件以及费用等进行选择。目前用于骨关节炎研究的模型动物主要有啮齿类、家禽类、哺乳类以及灵长类动物。理论上讲,哺乳动物的关节解剖结构、生物力学与人类相似,而且其下肢负重载荷较多,无论是自然环境还是人工环境,哺乳动物患上骨关节炎的可能性是很大的[14]。因此目前主要是利用哺乳动物来制备骨关节炎动物模型以开展研究工作,其中由于羊、狗、猴等费用较高,操作相对困难,实验适用度低;而兔、鼠具有容易获得、价格便宜、饲养经济等特点,是目前普遍选用的动物,适用于各类模型的研究[15]。 2.1.2 骨关节炎动物模型的种类 (1)动物自发模型: Dunkin Hartley(DH)豚鼠模型:Hartley豚鼠关节软骨的退变过程与人类骨关节炎病理变化过程非常相似。约3个月大的豚鼠体质量达到700 g 时,其内侧胫骨平台可出现骨关节炎表现,其组织学表现为软骨表层不平整,软骨细胞减少,胶原蛋白发生溶解、断裂及排列紊乱,软骨中糖胺聚糖分布异常等[16]。此类模型多可成批获得,生理及病理性状稳定,但价格较昂贵。 基因缺陷自发骨关节炎模型:①Ⅱ型前胶原基因缺陷小鼠模型:正常软骨基质胶原以Ⅱ型为主,Ⅱ型胶原合成障碍与骨关节炎发病有关。Pun等[17]报道Ⅱ型前胶原基因点突变(519位精氨酸被半胱氨酸取代,Arg→Cys 519)可导致家族性的骨关节炎,具有早发、侵蚀性及全身性的特点,呈常染色体显性遗传,并伴有轻度的脊柱软骨发育不良;②双糖链蛋白多糖/纤维调节素相关基因缺陷小鼠模型:小鼠双糖链蛋白多糖基因敲除后,其骨前体细胞形成障碍且对转化生长因子β反应低下,胶原合成减少,细胞凋亡增加[18]。 (2)人工诱发模型: 关节制动诱发模型:该模型主要是用石膏将动物下肢关节长时间固定在某一位置,如屈曲、伸展、中间位等,由于关节应力的改变引发关节软骨的退变而形成骨关节炎[19-20]。有研究用管型石膏固定兔左后膝关节于伸直位,6周后发现滑膜和软骨细胞增生,关节软骨变薄、纤维化,出现裂隙,炎症细胞浸润,与人类膝骨关节炎的病理表现相似。 关节腔注射诱发模型:通过在关节腔内注射药物来破坏关节软骨细胞或细胞外基质而诱导骨关节炎[21]。Burnham等[22]通过在雄性SD大鼠的膝关节腔内注射碘乙酸钠成功制造了骨关节炎疼痛模型,研究米那普仑的镇痛作用。另外,向关节腔内注射透明质酸酶、肾上腺皮质激素、白陶土和鹿角菜胶、软骨碎片或微粒、异物等也可导致关节软骨退变,形成骨关节炎模型[23]。 寒冷刺激诱发模型:寒冷刺激可以通过改变滑膜的通透性和关节液成分而影响关节软骨所在的内环境,从而诱发骨关节炎[24]。刘安军等[25]采取4 ℃冷水冷冻刺激小鼠膝关节制作骨关节炎模型,在造模30 d时模型组小鼠出现典型的骨关节炎病变症状,这为研究骨关节炎的发病机制提供了一种简便实用的动物模型。 关节内手术诱发模型:①Hulth 模型:这是目前经典的骨关节炎造模方法。手术切断前后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带,切除内侧半月板,术中避免损伤关节软骨,术后不固定伤肢,动物可自由活动,适当给予抗生素预防感染。由于手术造成关节不稳从而诱发骨关节炎,术后3个月软骨出现裂隙、破坏[26];②半月板或(和)前交叉韧带切除:当半月板或(和)前交叉韧带切除时,关节稳定性受到破坏而使关节应力发生改变,造成关节的退行性变化,从而诱发骨关节炎。Knighos等[27]切除雌性C57BL/6小鼠内侧半月板,观察到小鼠退行性关节损伤以及疼痛行为等骨关节炎的表现。Khorasani等[28]通过胫骨压缩过载造成前交叉韧带断裂而成功制造雌性小鼠膝骨关节炎模型;③负重模型:负重法能造成关节负荷传导紊乱,加速骨关节炎的发生发展。王君等[29]将兔右侧膝关节前交叉韧带切断,建成前交叉韧带切断模型后,以石膏将左腿固定于腹部,右腿负重锻炼建成负重模型,术后4周出现软骨病变,此种方法关节退变比同期前十字韧带切断组更加明显;④关节划痕:Marijnissen等[30]在犬的膝关节股骨髁上刻痕,但不损伤软骨下骨,术后将对侧肢固定于躯体上,前20周迫使手术肢体负重,后20周关节正常负重,通过实验观察到关节软骨的生化表现与临床非常相似,且关节炎症反应轻微,适合于观察治疗措施对软骨保护和修复的效果。 关节外手术诱发模型:①干扰关节血液循环:血液循环的异常可以致使关节发生病变。有学者通过无菌手术结扎并切断新西兰兔股静脉、大隐静脉和臀下静脉,可在术后8 周成功诱发早中期骨关节炎动物模型;②改变关节应力:Palmoski等[34]在实验中发现,长期低应力可导致关节软骨厚度减少,水分增加,番红O染色变浅,蛋白聚糖聚集度受到损害等变化。朱鸿飞等[35]通过切除兔双后膝内侧2/3髌韧带造成下肢生物力学改变,术后1周进行运动锻炼,术后6周出现滑膜增生、关节软骨细胞破坏、基质分解等早期退行性变,术后8周则表现为中期膝骨关节炎病理改变;③卵巢切除法:此模型通过切除卵巢模拟女性绝经后雌激素缺乏导致骨关节炎,可运用于雌激素及其类似物等对关节软骨的保护作用的研究。Pernille等[33]将SD鼠卵巢切除制作绝经后骨关节炎模型,结果表明代表软骨流失的Ⅱ型胶原降解产物及代表骨吸收的骨胶原Ⅰ型片段的水平与关节最终的退变呈明显正相关;④臀肌切断法:臀肌切断诱导法为关节外手术途径,可以避免关节内手术所致创伤性滑膜炎对实验的干扰。白希壮等[32]通过选择性切断豚鼠一侧臀大、中、小肌,使髋关节不稳,关节生物力学紊乱,从而获得了满意的髋关节骨关节炎模型。 (3)其他类别模型: 转基因动物模型:近年来随着转基因技术的发展,出现了转基因动物模型,使得骨关节炎的研究有了新的进展。Rodriguez等[33]研究发现小鼠COL11A1基因的核苷酸缺失会导致软骨蛋白多糖的增加和胶原纤维的异常增厚,从而导致小鼠出现骨关节炎表现。Salminen等[36]研究发现Del1突变可增加了骨关节炎的发病率和严重程度,Del1 转基因小鼠在3个月时膝关节的关节软骨有表浅的原纤维形成,并迅速进展为侵蚀,渗透到软骨并伴随有骨硬化、软骨下骨裸露,囊肿形成及半月板退变。 饮食诱导模型:肥胖是发展为骨关节炎的一个重要的危险因素,除了影响关节负荷外,脂肪组织中的促炎性代谢因子也增加了骨关节炎的风险[37]。Silberberg等[38]研究发现在喂养C57BL小鼠时采用脂肪含量较高的饲料将会加速其关节退变过程,如果采用动物性油脂喂养,将进一步提高其骨关节炎发生率。Louer等[39]研究发现高脂饮食引起的肥胖明显增加了小鼠创伤性关节炎的严重程度。 运动性损伤模型:运动常导致关节损伤,体育运动者尤其是专业运动员,因长期从事专业体育训练,负重的关节发生不同程度的损伤及韧带撕裂伤,关节的修复能力较差,一旦损伤即可造成永久性病变,导致关节功能性障碍[40]。Yun等[41]通过迫使Wistar大鼠进行跑台运动成功诱导了大鼠骨关节炎模型,其组织病理学变化与早期骨关节炎病理改变一致。Beckett等[42]研究发现,过度运动可诱导大鼠膝关节软骨退变并改变大鼠步态。 由此可见,有关骨关节炎研究的模型和方法很多,建立骨关节炎动物模型也是研究其发病机制和寻找有效治疗措施的重要途径。各种造模方法各有优缺点,应用范围也不相同,见表1。因此,研究时应根据实际的需要,选择最合适的动物模型。"

| [1] Prieto-Alhambra D, Judge A, Javaid MK, et al. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: influence of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(9): 1659-1664. [2] Moyer RF, Ratneswaran A, Beier F, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2014: mechanics-basic and clinical studies in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(12): 1989-2002. [3] Bijlsma J, Berenbaum F, Lafeber F. Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783): 2115-2126. [4] 潘丁.人膝骨关节炎滑液蛋白质组学研究及国人骨关节炎流行病学Meta分析[D]. 中南大学, 2014.[5] 黄洪容. 我国社区中老年人膝骨关节炎的发病趋势分析[J]. 当代医学, 2012,18(12): 59-60. [6] Bannuru RR, Vaysbrot EE, Sullivan MC, et al. Relative efficacy of hyaluronic acid in comparison with NSAIDs for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43(5):593-599.[7] Balmaceda CM. Evolving guidelines in the use of topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15(1):1-5.[8] Railhac J, Zaim M, Saurel A, et al. Effect of 12 months treatment with chondroitin sulfate on cartilage volume in knee osteoarthritis patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study using MRI. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(9):1347-1357.[9] Henrotin Y, Mobasheri A, Marty M, et al. Is there any scientific evidence for the use of glucosamine in the management of human osteoarthritis? Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(1): 201-201.[10] Mccoy AM. Animal Models of Osteoarthritis: Comparisons and Key Considerations. Vet Pathol. 2015;52(5):803-818. [11] Zamli Z, Robson BK, Tarlton JF, et al. Subchondral bone plate thickening precedes chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in spontaneous animal models of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014(6):751-759.[12] Kalliopi LA, Pavlos L, Karadimas EV, et al. Useful animal models for the research of osteoarthritis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(3): 263-271. [13] Pritzker KP. Animal models for osteoarthritis: processes, problems and rospects. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994;53(6): 406-420. [14] Lascelles BD. Feline degenerative joint disease. Vet Surg. 2010;39(1): 2-13. [15] Gregory MH, Capito N, Kuroki K, et al. A Review of Translational Animal Models for Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis. 2012;2012(7):764621-764621. [16] Wang T, Wen C, Lu W, et al. A study on the role of subchondral bone change in very early stage of osteoarthritis with Dunkin-Hartley guinea pigs. International Congress of Chinese Orthopaedic Association COA, 2011.[17] Pun YL, Moskowitz RW, Lie S, et al. Clinical correlations of osteoarthritis associated with a single-base mutation (arginine519 to cysteine) in type II procollagen gene. A newly defined pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(2): 264-269.[18] Young MF, Bi Y, Ameye L, et al. Biglycan knockout mice: new models f or musculoskeletal diseases. Glycoconj J. 2002; 19(4-5): 257-262. [19] Vincent TL, Williams RO, Rose M, et al. Mapping pathogenesis of arthritis through small animal models. Rheumatology. 2012;51(11):1931-1941. [20] Ando A, Suda H, Hagiwara Y, et al. Reversibility of Immobilization-Induced Articular Cartilage Degeneration after Remobilization in Rat Knee Joints. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2011; 224(2):77-85.[21] 魏苗, 胥方元. 骨性关节炎动物模型的建立与比较[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(8): 777-781.[22] Burnham LJ, Dickenson AH. The anti-nociceptive effect of milnacipran in the monosodium iodoacetate model of OA pain and its relation to changes in descending inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;344(3):696-707.[23] Little CB, Zaki S. What constitutes an "animal model of osteoarthritis"--the need for consensus? Osteoarthrit Cartilage. 2012;20(20): 261-267.[24] Teeple E, Jay GD, Elsaid KA, et al. Animal Models of Osteoarthritis: Challenges of Model Selection and Analysis. Aaps J. 2013;15(2):438-446.[25] 刘安军,陈宏硕,刘颖芬,等. 小鼠骨性关节炎的模型制备及评价[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2008,18 (8) :1045-1047+1051. [26] Peters ST, Tanja S, Markus W. Arthroscopic Approach and Anatomy of the Rabbit Stifle Joint. Vet Surg. 2014;43(6) : E192-E193.[27] Knights CB, Gentry C, Bevan S. Partial medial meniscectomy produces osteoarthritis pain-related behaviour in female C57BL/6 mice. Pain. 2012;153(2):281-292.[28] Khorasani MS, Diko S, Hsia AW, et al. Effect of alendronate on post-traumatic osteoarthritis induced by anterior cruciate ligament rupture in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):1-11.[29] 王君,何炳书,李笑萍.兔膝骨关节炎负重模型的建立[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2005, 25(9): 1079-1080. [30] Marijnissen AC, Van Roermund PM, T eKoppele JM, et al. The canine 'groove' model, compared with the ACLT model of Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(2): 145-155 .[31] Pernille HA, Laszlo BT, Thomas LA, et al. Ovariectomized rats as a model of postmenopausal osteoarthritis: validation and application. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6:169-180.[32] 白希壮,任继尧.选择性臀肌切断诱发骨关节炎实验模型[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 1994,14(2): 118-120.[33] Rodriguez RR, Seegmiller RE, Stark MR, et al. A type XI collagen mutation leads to increased degradation of type II collagen in articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004; 12(4): 314-320.[34] Palmoski MJ, Colver RA, Brandt KD. Marked suppression by salicylate of the augmented proteoglycan synthesis in osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23(1): 83-91.[35] 朱鸿飞,冯伟,刘益杰,等.髌韧带内侧缺损构建兔膝骨关节炎模型初探[J].上海中医药杂志, 2012,46(1):11-14, 18.[36] Salminen HJ, Säämänen AM, Vankemmelbeke MN, et al. Differential expression patterns of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors during development of osteoarthritis in a transgenic mouse model. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61(7): 591-597.[37] Issa RI, Griffin TM. Pathobiology of obesity and osteoarthritis: integrating biomechanics and inflammation. Pathobiol Aging Age Relat Dis. 2012;2(2012):10.3402/pba.v2i0.17470. [38] Silberberg M, Silberberg R. Effects of a high fat diet on the joint of aging mice. AMA Arch Pathol. 1950; 50(6): 828-846.[39] Louer CR, Furman BD, Huebner JL, et al. Diet-induced obesity significantly increases the severity of posttraumatic arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3220-3230.[40] Ni GX, Lei L, Zhou YZ. Intensity-dependent effect of treadmill running on lubricin metabolism of rat articular cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(6):1-10.[41] Yun JL, Ji AP, Yang SH, et al. Evaluation of osteoarthritis induced by treadmill-running exercise using the modified Mankin and the new OARSI assessment system. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31(12):1571-1576.[42] Beckett J, Wu J, Schultz M, et al. Excessive running induces cartilage degeneration in knee joints and alters gait of rats. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(10):1604-1610.[43] Raynauld JP, Martelpelletier J, Dorais M, et al. Prediction of total knee replacement in a 6-month multicentre clinical trila with chondroitin sulfate in knee osteoarthritis: results from a 4-year observation. Ann Rheum Dis.2014;71(Suppl 3):420-420.[44] Gibson M, Li H, Coburn J, et al. Intra-articular delivery of glucosamine for treatment of experimental osteoarthritis created by a medial meniscectomy in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(2):302-309.[45] Huang LJ, Chen WP. Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(5):1-19.[46] Christoph B, Eugenia NM, Vivek J, et al. Chondroprotective effect of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid on osteoarthritic chondrocytes in a co-cultivation inflammation model with M1 macrophages. J Inflamm. 2016;13(1):31.[47] Bendele AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis in an era of molecular biology. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2002;2(6): 501-503.[48] Knott L, Avery NC, Hollander AP, et al. Regulation of osteoarthritis by omega-3(n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids in a naturally occurring model of disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(9) : 1150-1157.[49] 李芃,张俐.强骨宝对疲劳性损伤诱发膝骨关节炎模型大鼠的作用[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2015, 2:30-33+43. [50] Gu Q, Li D, Wei B, et al. Effects of nicotine on a rat model of early stage osteoarthritis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(4): 3602-3612.[51] Park DS, Huh JE, Baek YH. Therapeutic effect of Aralia cordata extracts on cartilage protection in collagenase-induced inflammatory arthritis rabbit model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;125 (2): 207-217.[52] Gong D, Chu W, Jiang L, et al. Effect of fucoxanthin alone and in combination with D-glucosamine hydrochloride on carrageenan/kaolin-induced experimental arthritis in rats. Phytotherapy Research Ptr. 2014;28(7):1054.[53] 柯晖.怀牛膝对兔骨性关节炎软骨组织影响的实验研究[D]. 湖北中医药大学, 2012.[54] Terencio MC, Ferrándiz ML, Carceller MC, et al. Chondroprotective effects of the combination chondroitin sulfate-glucosamine in a model of osteoarthritis induced by anterior cruciate ligament transection in ovariectomised rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;79:120.[55] Huang LJ, Chen WP. Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(5):1-19.[56] Li ZH, Zhao WH, Zhou QL. Experimental study of velvet antler polypeptides against oxidative damage of osteoarthritis cartilage cells. Chin J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;24(3):245-248.[57] 李姗姗.骨碎补对模型兔膝骨关节炎关节滑膜细胞因子凋亡影响的实验研究[D]. 辽宁中医药大学, 2013.[58] 刘杰.口服透明质酸对实验性小鼠骨关节炎的作用及其药物动力学的初步探讨[D]. 第二军医大学, 2011.[59] Guzman RE, Evans MG, Bore S, et al. Mono-iodoacetate- induced histologic changes in subchondral bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotibial joints: an animal model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol Pathol. 2003;31(6):619-624. |
| [1] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [8] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [9] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [10] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [11] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [13] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [14] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [15] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||