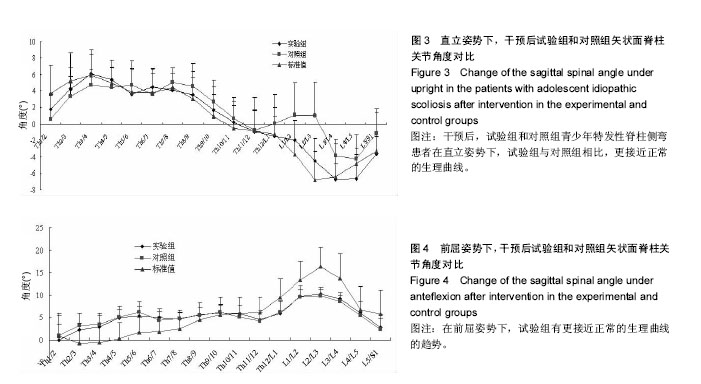
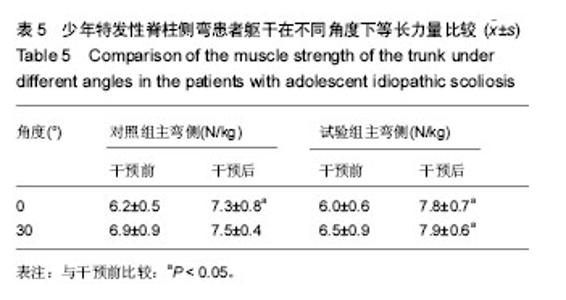
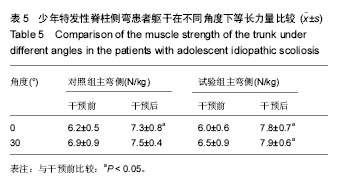
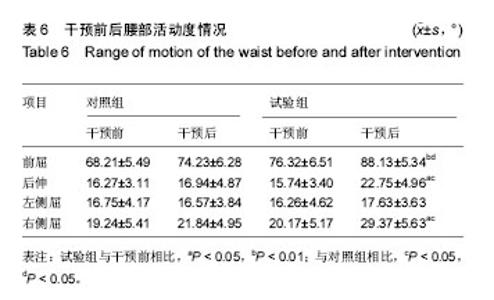
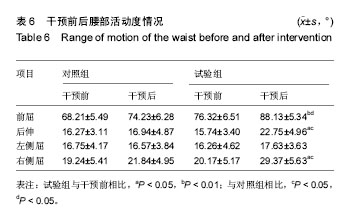
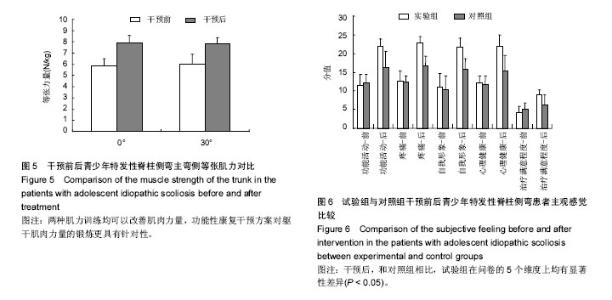
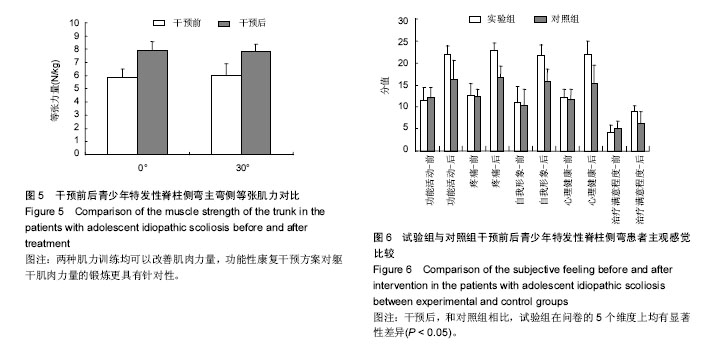
| [1] Horne JP, Flannery R, Usman S. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician.Am Fam Physician.2014;89:193-198.[2] Hong JY, Suh SW, Park HJ,et al. Correlations of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and pectus excavatum. Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8): 870-874.[3] Johari J, Sharifudin MA,Ab Rahman et al. Relationship between pulmonary function and degree of spinal deformity, location of apical vertebrae and age among adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients.Singapore Med J.2016; 57(1): 33-38.[4] Burwell RG, Dangerfield PH, Moulton A, et al. Whither the etiopathogenesis (and scoliogeny) of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Incorporating presentations on scoliogeny at the 2012 IRSSD and SRS meetings. Scoliosis. 2013;8(1):4.[5] 叶启彬. 调控脊柱侧弯椎体两侧的不对称应力是治疗脊柱侧弯的关键[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(1):5-6.[6] Letafatkar A, Hadadnezhad M, Shojaedin S, et al. Relationship between functional movement screening score and history of injury.Int J Sports Phys Ther.2014;9(1): 21-27.[7] Simon C. Mordecai, Harshad V. Dabke. Efficacy of exercise therapy for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a review of the literature.Eur Spine J.2012;21(3): 382-389.[8] Wang WJ, Yeung HY, Chu WC, et al. Top theories for the etiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.J Pediatr Orthop.2011;31:S14-27.[9] Matsunaga S, Hayashi K, Naruo T, et al. Psychologic management of brace therapy for patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine.2005;30:547-550.[10] Lombardi G, Akoume MY, Colombini A,et al. Biochemistry of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Adv Clin Chem.2011; 54: 165-182.[11] Parent S,Newton PO,Wenger DR.Adolescent idioPathic scoliosis: etiology, anatomy, naturalhistory, and bracing.Instr Course Lect.2005; 54:529-536.[12] Whitelaw E,Ong K, Albertsson-Wikland K. Child health, developmental plasticity, and epigenetic programming. Endocr Rev.2011;32(2):159-224.[13] Richard A. Magill. Motor Learning And Control (Seven Edition).Mc Graw High Education. 1992.[14] Zaina F,Donzelli S,Lusini M, et al.Swimming and Spinal deformities: a cross-sectional study.J Pediatr. 2014;166(1): 163-167.[15] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA. Adolescent idioPathic scoliosis. Lanet.2008;371:1527-1537.[16] 杨宁,徐盼.运动干预青少年脊柱侧弯Cobb角的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22): 4161-4168.[17] McMaster ME, Lee AJ, Burwell RG. Physical activities of Patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): preliminary longitudinal case–control study historical evaluation of possible risk factors. Scoliosis.2015;10: 6-16.[18] 张智海,李茂廷,于智勇,等. 脊柱形态测量仪(Spinal mouse)测评腰痛患者全脊柱运动能力[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2009,7(6): 346-349.[19] 唐盛平,付桂兵,孙客,等. 前屈试验、脊柱测量仪与Cobb角的比较[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2006,26(7):372-374.[20] Yu M, Silvestre C, Mouton T, Rachkidi R,et al. Analysis of the cervical spine sagittal alignment in young idiopathic scoliosis: a morphological classification of 120 cases. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(11): 2372-2381.[21] Canavese F,Turcot K,De Rosa V,et al.Cervical spine sagittal alignment variations following posterior spinal fusion and instrumentation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J.2011;12(7):1141–1148.[22] 南海鸥,王燕.核心肌力训练在康复医学中的意义[J].内蒙古医学院学报,2012,34 (3) :259-264.[23] kuthota V, Nadler SF.Core strengthening. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(3 Suppl 1):S86-92. [24] Jerome Nosily, Joseph A, Plainwell . Damien Labroicl On the collagen crises-cross angles in the annuli fibrosis of lumbar spine finite element models. Biotech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10:203 -219.[25] MF Garnet, BA Taylor, JH Pelosi, et,al. CERVICAL SPINE: The surgical treatment of painful disorders. Eur Spine.2009; 18 (Suppl4):S403 -S444.[26] 刘文军,邱勇,孙旭,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者脊柱柔韧性的影响因素[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009,19 (12): 882-886.[27] Misterska E, Glowacki M, Latuszewska J, et al. Perception of stress level, trunk appearance, body function and mental health in females with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated conservatively: a longitudinal analysis. Qual Life Res.2013; 22(7): 1633-1645.[28] Xu X, Wang F, Yang M,et al. Chinese Adaptation of the Bad Sobernheim Stress Questionnaire for Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Under Brace Treatment. Medicine (Baltimore).2015;94(31): 1236-1241. |