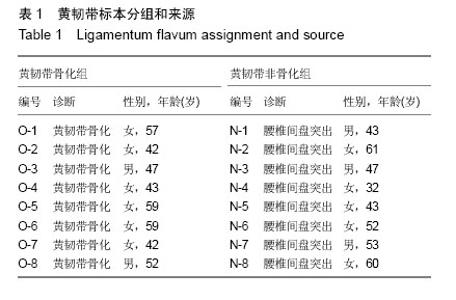
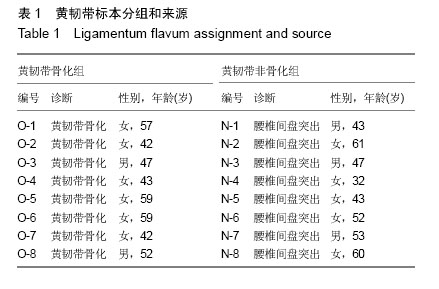
| [1] Epstein NE. Ossification of the yellow ligament and spondylosis and/or ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the thoracic and lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord. 1999;12(3):250-256.[2] Guo JJ, Luk KD, Karppinen J, et al. Prevalence, distribution, and morphology of ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a population study of one thousand seven hundred thirty-six magnetic resonance imaging scans. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(1):51-56.[3] Inamasu J, Guiot BH. A review of factors predictive of surgical outcome for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5(2):133-139.[4] Qu X, Chen Z, Fan D, et al. Notch signaling pathways in human thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(8):1481-1491.[5] Junaid A, Moon M C, Harding GE, et al. Osteopontin localizes to the nucleus of 293 cells and associates with polo-like kinase-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292(2):C919-C926.[6] Morinobu M, Ishijima M, Rittling SR, et al. Osteopontin expression in osteoblasts and osteocytes during bone formation under mechanical stress in the calvarial suture in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(9):1706-1715.[7] Kim HN, Min WK, Jeong JH, et al. Combination of Runx2 and BMP2 increases conversion of human ligamentum flavum cells into osteoblastic cells. BMB Rep. 2011;44(7):446-451.[8] Liu Y, Zhao Y, Chen Y, et al. RUNX2 polymorphisms associated with OPLL and OLF in the Han population. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(12):3333-3341.[9] Kong Q, Ma X, Li F, et al. COL6A1 polymorphisms associated with ossification of the ligamentum flavum and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(25):2834-2838.[10] Wongkhantee S, Yongchaitrakul T, Pavasant P. Mechanical stress induces osteopontin expression in human periodontal ligament cells through rho kinase. J Periodontol. 2007;78(6): 1113-1119.[11] Inoue H, Seichi A, Kimura A, et al. Multiple-level ossification of the ligamentum flavum in the cervical spine combined with calcification of the cervical ligamentum flavum and posterior atlanto-axial membrane. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 3: S416-S420.[12] Uchida K, Yayama T, Cai HX, et al. Ossification process involving the human thoracic ligamentum flavum: role of transcription factors. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R144.[13] Qu X, Chen Z, Fan D, et al. MiR-199b-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation in ligamentum flavum cells by targeting JAG1 and modulating the Notch signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(6):1159-1170.[14] Wan YM, Ma YJ, Zhang XY, et al. Effects of rotation on osteonectin and osteopontin mRNA level of cultured osteoblasts in rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005;57(3):384-388.[15] Hirota S, Asada H, Kohri K, et al. Possible role of osteopontin in deposition of calcium phosphate in human pilomatricomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;105(1):138-142.[16] Chen Q, Shou P, Zhang L, et al. An osteopontin-integrin interaction plays a critical role in directing adipogenesis and osteogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(2):327-337.[17] Inoue M, Shinohara M L. Intracellular osteopontin (iOPN) and immunity. Immunol Res. 2011;49(1-3):160-172.[18] Tammi R, Pasonen-seppanen S, Kolehmainen E, et al. Hyaluronan synthase induction and hyaluronan accumulation in mouse epidermis following skin injury. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124(5):898-905.[19] Noble PW. Hyaluronan and its catabolic products in tissue injury and repair. Matrix Biol. 2002;21(1):25-29.[20] Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, et al. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990; 61(7):1303-1313.[21] Yagishita K, Sekiya I, Sakaguchi Y, et al. The effect of hyaluronan on tendon healing in rabbits. Arthroscopy. 2005;21(11):1330-1336.[22] Tanno M, Furukawa KI, Ueyama K, et al. Uniaxial cyclic stretch induces osteogenic differentiation and synthesis of bone morphogenetic proteins of spinal ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Bone. 2003;33(4):475-484.[23] 许政,周盛源,李学斌,等.骨桥蛋白及其受体在黄韧带骨化症黄韧带细胞中的表达及其意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(2): 179-184.[24] Qu X, Chen Z, Fan D, et al. MiR-132-3p Regulates the Osteogenic Differentiation of Thoracic Ligamentum Flavum Cells by Inhibiting Multiple Osteogenesis-Related Genes. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081370.[25] Fan D, Chen Z, Chen Y, et al. Mechanistic roles of leptin in osteogenic stimulation in thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(41):29958-29966.[26] Zheng W, Li R, Pan H, et al. Role of osteopontin in induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta through the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(7):1957-1965.[27] Li C, Yang X, He Y, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 induces osteogenic differentiation of rat dental follicle stem cells in P38 and ERK1/2 MAPK dependent manner. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(10):862-871.[28] Ye G, Li C, Xiang X, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 induces PDLSCs osteogenic differentiation through the ERK and p38 signal pathways. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(10): 1065-1072.[29] Li XL, Liu YB, Ma EG, et al. Synergistic effect of BMP9 and TGF-beta in the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(3):7605-7615.[30] Ning S, Chen Z, Fan D, et al. Genetic differences in osteogenic differentiation potency in the thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum under cyclic mechanical stress. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(1):135-143. |