Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4246-4251.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Silicon nanowire field effect transistor biosensors for protein detection
- Department of Endoscopy Surgery, Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2017-07-28Online:2017-09-18Published:2017-09-28 -
Contact:Wang Tong, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Endoscopy Surgery, Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Meng Qing-yang, Master, Department of Endoscopy Surgery, Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371683/H1819; Clinical Medicine Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BL2014023
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Meng Qing-yang, Wang Tong.
share this article
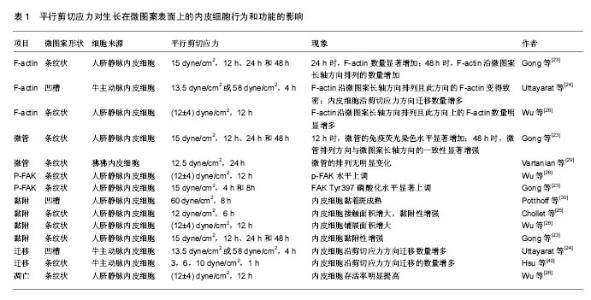
2.1 器件加工工艺的改进 影响硅纳米线传感器性能的因素有许多,如直径、载流子浓度、迁移率和表面化学特性。Li等[28]实验发现,较小直径的硅纳米线具有更高的敏感性,硅纳米线的直径减小(直径小于10 nm)会降低检测信号所需分析物的最小量。此外,研究表明,掺杂浓度能影响生物传感器的灵敏度。轻掺杂的纳米线比高掺杂或未掺杂的纳米线具有更高的灵敏度[29]。这些研究结果证明小尺寸和适当的掺杂浓度在器件的加工工艺方面的重要性。自下而上和自上而下是目前生产硅纳米线生物传感器的2个主要加工方式,见表1。 自下而上的技术,如蒸汽-液体-固体(VLS)、化学气相沉积法(CVD)等[30-31],已有报道用于制备硅纳米线[32],如利用金纳米团簇作为催化剂和乙硼烷或磷作为掺杂剂,制备出20 nm的N型或P型硅纳米线。目前高质量的纳米线已经被生产,但其在基板上(硅晶片)的方向随机和它们的尺寸变化显著,导致较差的装置均匀性和低的制备生产量。化学气相沉积法也因其混杂的制备方案、需要转移、低收成率和缺乏可靠地欧姆接触而受到限制[33],为了实现硅纳米线生物传感器批量可靠地生产,新的重要技术的开发将会是一项艰巨的任务。 另一种生产纳米线结构的技术自上而下法,通常使用电子束光刻技术[34]、光刻纳米图案电沉积法[35]、纳米模版光刻和纳米压印光刻[36-37]。各种尺寸的纳米线(50 nm的典型宽度,长度范围从20 m到1 mm)已经由电子束光刻等方法制备[38-39]。超晶格硅纳米线图案转移法(SNAP)已被用于设备的高度对齐,并成功在N或P型SOI晶片上制备出20 nm宽的纳米线[40]。Ayvazian和同事们开发的利用LPNE法制备金属纳米线的图案模型,结合光刻的属性和自底向上的电化学沉积法的多功能性[41],纳米线显示一个长方形的横截面,高度和宽度可以被独立地控制,可达到约20 nm的宽度和 6 nm的高度。Vu等[42]利用纳米压印光刻技术与标准的CMOS工艺来大规模生产硅纳米线阵列用于蛋白的检测,成功制备出直径小于100 nm的32×32硅纳米线阵列。虽然有大量的关于硅纳米线传感器的可用数据,CMOS工艺兼容的硅纳米线的设备在其制造和商业化方面仍然具有挑战性。Zhou等[43]通过对纳米器件在退火和钝化层方面的工艺改进提高了器件的成品率和器件加工的稳定性,并成功应用于血清中甲胎蛋白的检测。传统的加工方法很难使硅纳米线突破100 nm,Li等[44]利用光刻、化学刻蚀氧化等工艺制备出直径20 nm硅纳米线,并表现出更优异的电学特性。 2.2 修饰方法的改进 在硅纳米线的表面用探针修饰分子,使其能够识别特定的靶分子。目前主要采用2种方法:静电吸附和共价键结合。静电吸附主要依靠的是溶质离子与带有相反电荷吸附剂的吸引作用,因此容易受到温度等外界因素的干扰[45]。共价键结合因其稳定性和特异性强等优点成为目前最受欢迎的修饰方法,即通过烷氧基硅烷为基础的自组装化学链,即硅烷化。为了提高硅烷化质量用紫外线/臭氧等离子体来清洁硅纳米线表面是必不可少的。氧等离子体不仅能去除有机污染,而且能形成覆盖整个器件表面的单层化学链。3-氨基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(简称APTES)是第一个被用于纳米线二氧化硅表面功能化的硅烷。2013年Aissaoui等[46]研究表明APTES氨基功能团可以被用来修饰在硅纳米线表面,用于蛋白质/酶的检测。随后的研究就是APTES涂层的硅纳米线表面和醛酸酐、环氧化合物的反应,形成进一步功能化羧酸。其他硅烷衍生物,如3-巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPTES)等也可以用于硅纳米线表面的修饰[47]。APTES法在官能团的数量和稳定性方面都有较强的优势。2013年,Li等[48]对APTES法进行了改进,利用电阻加热法将化学链只修饰在硅纳米线表面(SSM),使得硅纳米线生物传感器具有更好的欧姆接触和信号传导特性,生物素/亲和素和多巴胺/苯基硼酸与硅纳米线传感器结合,使其具有更快的响应时间和较小的样本要求,且灵敏度提高2个数量级。 2.3 微流道的发展和不足 为实现硅纳米线生物传感器对蛋白的检测,流体交换系统是必不可少的,它能够使蛋白分子快速到达硅纳米线传感器表面。目前主要有两种流体交换系统:开放式液池和封闭式微流体通道。开放式液池具有制备成本低及工艺简单的优点,然而,其容易受到外部因素的影响而降低其灵敏度,且与整个器件接触面积大,影响了器件的可重复使用。聚二甲基硅氧烷(Polydimethylsiloxane,PDMS)具有良好的光学和化学性能,以及加工简单、价格便宜等优点,已成为目前制作封闭式微流体通道最为普遍的材料[49]。但聚二甲基硅氧烷的高疏水性、对蛋白等生物大分子的较强表面吸附特性和液体通过微流道需要耗时等缺点,限制了它的应用范围。 Lu等[50]利用20%聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)来改善聚二甲基硅氧烷的湿润性同时减少非特异性吸附位点,并利用氧等离子体等方法将双通道微流道模型与P-型互补金属氧化物半导体硅纳米线生物传感器集成,实现了对细胞角蛋白和前列腺特异性抗原2种肿瘤蛋白标志物的同时检测,其在缓冲液中检测水平低至1 pg/L,同时实现了对未稀释临床血清样品的检测,检测极限低至10 pg/L。Zhu等[51]利用0.1%牛血清白蛋白阻断蛋白分子的非特异性结合位点,将双通路微流道与硅纳米线生物传感器芯片集成,实现对脱盐人血清标本中甲胎蛋白和癌胚抗原2种肿瘤标志物的同时检测,其检测范围分别为500 pg/L-50 μg/L和50 pg/L-10 μg/L,微流道的成功应用,使硅纳米线生物传感器实现对多种肿瘤标志物的同时检测,为癌症和其他复杂疾病的早期诊断和改善预后带来了巨大希望。 2.4 器件检测灵敏度的改进 近年来,硅纳米线生物传感器在检测灵敏度方面已经取得许多突破性进展,下面将对2种增强检测灵敏度的方法进行重点讲述。 2.4.1 亚阈值区检测 最近,有研究报道硅纳米线生物传感器的灵敏度在电测量传输曲线的亚阈值区可以指数倍提高[52]。这种敏感性增强事实上是源于栅电极电势(Vg)在亚阈值区工作时,降低了硅纳米线的电荷载体的屏蔽效应。更明确的,它是由载体屏蔽长度(LSI)和硅纳米线半径的相对大小决定的,其中的硅纳米线的半径是恒定的,然而,载体屏蔽长度的大小取决于硅纳米线的掺杂浓度,对于高掺杂区,由于电荷的屏蔽作用,载体屏蔽长度比硅纳米线半径小得多。当硅纳米线FET工作在线性区时,表面电荷引起的的电导改变与栅电极电势呈线性相关。然而,在此区域靶分子诱导的表面电荷效应无法贯穿硅纳米线的整个横截面,从而限制了硅纳米线FET检测灵敏度。相反,当硅纳米线FET在亚阈值区工作时,低载流子浓度减少了屏蔽效应,目标分子引起的电导改变能够贯穿硅纳米线的整个截面,引起指数倍增强的响应强度。因此,硅纳米线生物传感器在亚阈值区工作能够充分利用其表面体积比来实现最佳检测灵敏度。 2.4.2 频域检测 漏电流即栅极和漏极之间的电流,能够影响源极和漏极之间的电流。Zheng等[53]研究发现漏电流具有频率相关性,他们使用同一设备分别用频域和传统的时域对前列腺特异性抗原进行检测,证明频域检测的敏感性是后者的数十倍,成功检测出5 pmol/L水平的前列腺特异性抗原,研究还证明由于受到信噪比的影响,其对前列腺特异性抗原理想最低极限为0.15 pmol/L。较早的频域检测方法具有耗时长(数分钟)且需要处理大量的信号水平,提高了其检测成本,Roinila等[54]利用反转重复二进制序列(IRS)和傅里叶方程等方法实现不同频率信息的同时捕获,使检测时间从数分钟减少到几秒钟,且显著降低了检测成本。虽然频域检测已经取得了如此多的进展,但要实现大批量实际应用,仍然需要更多的努力。 2.5 样本的预处理 硅纳米线生物传感器检测蛋白受德拜屏蔽效应的影响,周围溶液的离子浓度越高,德拜长度越小,其屏蔽效应越显著[55-57]。然而,在实际临床应用中,全血中含有一些杂质且大多数血清样品的盐浓度较高,因此,往往需要对全血进行预纯化和脱盐稀释处理,降低了某些生物标志物的浓度,为肿瘤的早期检测增加了难度。Zhang等[58]报道了一种将微流控过滤芯片和硅纳米线生物传感器集成在一起的可以直接检测全血心肌标志物的集成检测微系统,可对少至2 μL全血心肌标志物肌钙蛋白、肌酸激脢和肌酸激脢同工酶的检测,检测过程在45 min内完成,最低检测限为1 ng/L,此后,他们又报道了一种将传感器与用于直接读取结果的专用集成电路芯片集成在一起的检测系统,可对血清中的这3种心肌标志物同时检测。Krivitsky等[59]发明出一种垂直的IgG修饰的3D硅纳米线合成芯片,而且与硅纳米线生物传感器集成在同一芯片上,能够从全血中迅速、选择性分离、脱盐处理和预浓缩某一靶向蛋白质,而且随后实现对这一特定蛋白实时、超敏感、特异性检测,成功完成了对全血肌钙蛋白的检测,检测极限低至pmol/L水平,且全过程只需10 min甚至更低,第1次在1个芯片上实现对全血中蛋白质的直接检测。但仍然停留在实验室阶段且报道较少,缺少大规模的临床研究。 "
| [1]Moh SH, Kulkarni A, San BH, et al. Photocurrent enhancement of SiNW-FETs by integrating protein-shelled CdSe quantum dots. Nanoscale. 2016;8(4):1921-1925.[2]Choi JH, Kim H, Choi JH, et al. Signal enhancement of silicon nanowire-based biosensor for detection of matrix metalloproteinase-2 using DNA-Au nanoparticle complexes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(22):12023-12028.[3]Boughey FL, Davies T, Datta A, et al. Vertically aligned zinc oxide nanowires electrodeposited within porous polycarbonate templates for vibrational energy harvesting. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(28):28LT02.[4]Botos A, Biskupek J, Chamberlain TW, et al. Carbon Nanotubes as Electrically Active Nanoreactors for Multi-Step Inorganic Synthesis: Sequential Transformations of Molecules to Nanoclusters and Nanoclusters to Nanoribbons. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(26):8175-8183.[5]Qiu J, Ran D, Liu L, et al. Mueller Matrix of Specular Reflection Using an Aluminum Grating Surface with Oxide Nanofilm. Appl Spectrosc. 2016;70(6):1009-1017.[6]Tran DP, Winter MA, Wolfrum B, et al. Toward Intraoperative Detection of Disseminated Tumor Cells in Lymph Nodes with Silicon Nanowire Field Effect Transistors. ACS Nano. 2016; 10(2):2357-2364.[7]He J, Zhu J, Gong C, et al. Label-Free Direct Detection of miRNAs with Poly-Silicon Nanowire Biosensors. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145160.[8]Barsan MM, Pifferi V, Falciola L, et al. New CNT/poly(brilliant green) and CNT/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) based electrochemical enzyme biosensors. Anal Chim Acta. 2016; 927:35-45.[9]Chen M, Hou C, Huo D, et al. An electrochemical DNA biosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene/Au nanoparticles for human multidrug resistance gene detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85:684-691.[10]Weng X, Neethirajan S. A microfluidic biosensor using graphene oxide and aptamer-functionalized quantum dots for peanut allergen detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85: 649-656.[11]Pearton S, Lu Y, Reyes PI, et al. Multifunctional ZnO Nanostructure-Based Devices. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012:361-411.[12]Huang JM, Tsai SY, Ku CS, et al. Enhanced electrical properties and field emission characteristics of AZO/ZnO-nanowire core-shell structures. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016;18(22):15251-15259.[13]Liang X, Chou SY. Nanogap detector inside nanofluidic channel for fast real-time label-free DNA analysis. Nano Lett. 2008;8(5):1472-1476.[14]Cao Q, Han SJ, Tersoff J, et al. End-bonded contacts for carbon nanotube transistors with low, size-independent resistance. Science. 2015;350(6256):68-72.[15]Yu H, Tian X, Dong Z, et al. Fabrication of Schottky barrier carbon nanotube field effect transistors using dielectrophoretic-based manipulation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10(11):7000-7004.[16]Giovannetti G, Khomyakov PA, Brocks G, et al. Doping graphene with metal contacts. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;101(2): 026803.[17]Tran DP, Wolfrum B, Stockmann R, et al. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor compatible silicon nanowires-on-a-chip: fabrication and preclinical validation for the detection of a cancer prognostic protein marker in serum. Anal Chem. 2015;87(3):1662-1668.[18]Chen HC, Chen YT, Tsai RY, et al. A sensitive and selective magnetic graphene composite-modified polycrystalline-silicon nanowire field-effect transistor for bladder cancer diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;66:198-207.[19]Choi JH, Kim H, Choi JH, et al. Signal enhancement of silicon nanowire-based biosensor for detection of matrix metalloproteinase-2 using DNA-Au nanoparticle complexes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(22):12023-12028.[20]Zhang GJ. Silicon nanowire biosensor for ultrasensitive and label-free direct detection of miRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;676:111-121.[21]Lu N, Gao A, Dai P, et al. CMOS-compatible silicon nanowire field-effect transistors for ultrasensitive and label-free microRNAs sensing. Small. 2014;10(10):2022-2028.[22]Abiri H, Abdolahad M, Gharooni M, et al. Monitoring the spreading stage of lung cells by silicon nanowire electrical cell impedance sensor for cancer detection purposes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:577-585.[23]Chiang PL, Chou TC, Wu TH, et al. Nanowire transistor-based ultrasensitive virus detection with reversible surface functionalization. Chem Asian J. 2012;7(9):2073-2079.[24]Lieber CM. Semiconductor nanowires: A platform for nanoscience and nanotechnology. MRS Bull. 2011;36(12): 1052-1063.[25]Li BR, Chen CC, Kumar UR, et al. Advances in nanowire transistors for biological analysis and cellular investigation. Analyst. 2014;139(7):1589-1608.[26]Zhang GJ, Ning Y. Silicon nanowire biosensor and its applications in disease diagnostics: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;749:1-15.[27]Li BR, Hsieh YJ, Chen YX, et al. An ultrasensitive nanowire-transistor biosensor for detecting dopamine release from living PC12 cells under hypoxic stimulation. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(43):16034-16037.[28]Li L, Fang Y, Xu C, et al. Fabricating vertically aligned sub-20 nm Si nanowire arrays by chemical etching and thermal oxidation. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(16):165303.[29]Eisenhawer B, Zhang D, Clavel R, et al. Growth of doped silicon nanowires by pulsed laser deposition and their analysis by electron beam induced current imaging. Nanotechnology. 2011;22(7):075706. [30]Seo D, Lee J, Kim SW, et al. Structural modulation of silicon nanowires by combining a high gas flow rate with metal catalysts. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2015;10:190.[31]Yu L, O'Donnell B, Foldyna M, et al. Radial junction amorphous silicon solar cells on PECVD-grown silicon nanowires. Nanotechnology. 2012;23(19):194011.[32]Chou CY, Seo JH, Tsai YH, et al. Anomalous Stagewise Lithiation of Gold-Coated Silicon Nanowires: A Combined In Situ Characterization and First-Principles Study. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(31):16976-16983.[33]Lu N, Gao A, Dai P, et al. Ultra-sensitive nucleic acids detection with electrical nanosensors based on CMOS-compatible silicon nanowire field-effect transistors. Methods. 2013;63(3):212-218.[34]Smyrnakis A, Almpanis E, Constantoudis V, et al. Optical properties of high aspect ratio plasma etched silicon nanowires: fabrication-induced variability dramatically reduces reflectance. Nanotechnology. 2015;26(8):085301.[35]Kindra LR, Eggers CJ, Liu AT, et al. Lithographically Patterned PEDOT Nanowires for the Detection of Iron(III) with Nanomolar Sensitivity. Anal Chem. 2015;87(22):11492-11500.[36]Yesilkoy F, Flauraud V, Rüegg M, et al. 3D nanostructures fabricated by advanced stencil lithography. Nanoscale. 2016; 8(9):4945-4950.[37]Li J, Pud S, Mayer D, et al. Advanced fabrication of Si nanowire FET structures by means of a parallel approach. Nanotechnology. 2014;25(27):275302.[38]Smyrnakis A, Almpanis E, Constantoudis V, et al. Optical properties of high aspect ratio plasma etched silicon nanowires: fabrication-induced variability dramatically reduces reflectance. Nanotechnology. 2015;26(8):085301.[39]Han XL, Larrieu G, Dubois E. Realization of vertical silicon nanowire networks with an ultra high density using a top-down approach. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10(11): 7423-7427.[40]Heath JR. Superlattice nanowire pattern transfer (SNAP). Acc Chem Res. 2008;41(12):1609-1617.[41]Ayvazian T, Xing W, Yan W, et al. Field-effect transistors from lithographically patterned cadmium selenide nanowire arrays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(9):4445-4452.[42]Vu XT, Ghoshmoulick R, Eschermann JF, et al. Fabrication and application of silicon nanowire transistor arrays for biomolecular detection. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical. 2010; 144 (2):354-360.[43]Zhou F, Li Z, Bao Z, et al. Highly sensitive, label-free and real-time detection of alpha-fetoprotein using a silicon nanowire biosensor. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015;75(7): 578-584.[44]Li L, Fang Y, Xu C, et al. Fabricating vertically aligned sub-20 nm Si nanowire arrays by chemical etching and thermal oxidation. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(16):165303.[45]Sprenger KG, Pfaendtner J. Strong Electrostatic Interactions Lead to Entropically Favorable Binding of Peptides to Charged Surfaces. Langmuir. 2016;32(22):5690-5701.[46]Aissaoui N, Landoulsi J, Bergaoui L, et al. Catalytic activity and thermostability of enzymes immobilized on silanized surface: influence of the crosslinking agent. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2013;52(6-7):336-343.[47]Aswal DK, Lenfant S, Guerin D, et al. A tunnel current in self-assembled monolayers of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane. Small. 2005;1(7):725-729.[48]Li BR, Chen CW, Yang WL, et al. Biomolecular recognition with a sensitivity-enhanced nanowire transistor biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;45:252-259.[49]Patolsky F, Zheng G, Lieber CM. Fabrication of silicon nanowire devices for ultrasensitive, label-free, real-time detection of biological and chemical species. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(4):1711-1724.[50]Lu N, Gao A, Dai P, et al. Ultrasensitive Detection of Dual Cancer Biomarkers with Integrated CMOS-Compatible Nanowire Arrays. Anal Chem. 2015;87(22):11203-11208.[51]Zhu K, Zhang Y, Li Z, et al. Simultaneous Detection of α-Fetoprotein and Carcinoembryonic Antigen Based on Si Nanowire Field-Effect Transistors. Sensors (Basel). 2015; 15(8):19225-19236.[52]Gao XP, Zheng G, Lieber CM. Subthreshold regime has the optimal sensitivity for nanowire FET biosensors. Nano Lett. 2010;10(2):547-552.[53]Zheng G, Gao XP, Lieber CM. Frequency domain detection of biomolecules using silicon nanowire biosensors. Nano Lett. 2010;10(8):3179-3183.[54]Roinila T, Yu X, Verho J, et al. Methods for rapid frequency-domain characterization of leakage currents in silicon nanowire-based field-effect transistors. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2014;5:964-972.[55]Stern E, Wagner R, Sigworth FJ, et al. Importance of the Debye screening length on nanowire field effect transistor sensors. Nano Lett. 2007;7(11):3405-3409.[56]Zhang GJ, Zhang G, Chua JH, et al. DNA sensing by silicon nanowire: charge layer distance dependence. Nano Lett. 2008;8(4):1066-1070.[57]Sorgenfrei S, Chiu CY, Johnston M, et al. Debye screening in single-molecule carbon nanotube field-effect sensors. Nano Lett. 2011;11(9):3739-3743.[58]Zhang GJ, Chai KT, Luo HZ, et al. Multiplexed detection of cardiac biomarkers in serum with nanowire arrays using readout ASIC. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012;35(1):218-223.[59]Krivitsky V, Hsiung LC, Lichtenstein A, et al. Si nanowires forest-based on-chip biomolecular filtering, separation and preconcentration devices: nanowires do it all. Nano Lett. 2012;12(9):4748-4756. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||