Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4222-4227.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
A novel single-sided groove target release biodegradable stent inhibits coronary artery intimal hyperplasia
- Department of Cardiology, Baotou Central Hospital, Baotou 014040, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2017-04-15Online:2017-09-18Published:2017-09-28 -
About author:Jin Hui, Associate chief physician, Department of Cardiology, Baotou Central Hospital, Baotou 014040, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jin Hui, Li Meng.
A novel single-sided groove target release biodegradable stent inhibits coronary artery intimal hyperplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(26): 4222-4227.
share this article
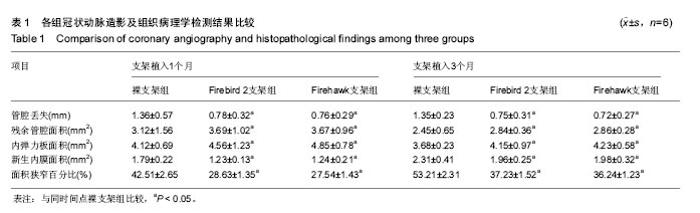
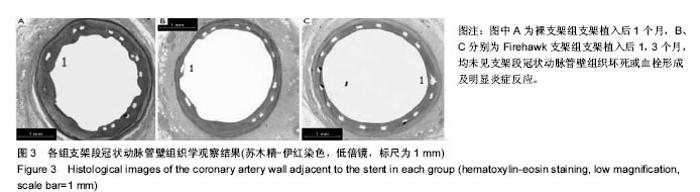
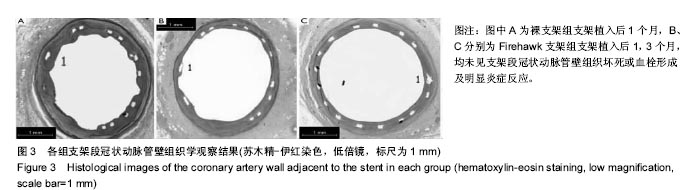
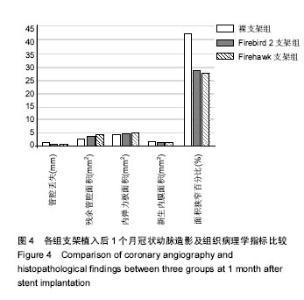
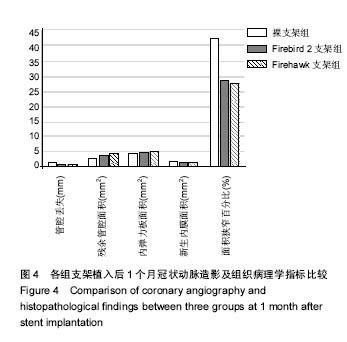
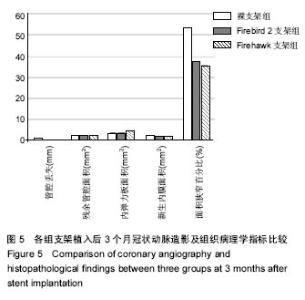
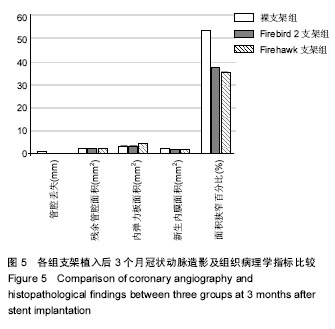
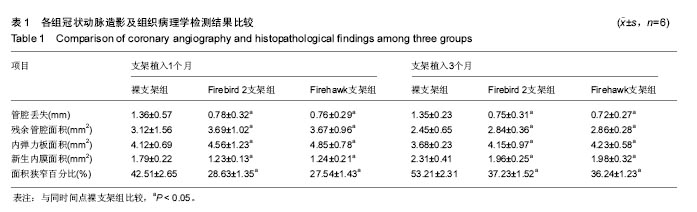
2.1 实验动物一般情况 18只小型猪冠状动脉内共植入36枚支架,其中裸支架组中有1只于支架植入中死亡,给予补齐,动物死亡与麻醉剂所致呼吸抑制有关;其余动物均顺利完成手术并进入结果分析,于支架植入后1,3个月时行冠状动脉造影复查。实验观察期内所有存活动物未出现死亡、食欲差、体质量下降等情况。 2.2 冠状动脉造影结果 植入1,3个月,冠状动脉造影显示3组所有支架段冠状动脉均无狭窄发生,支架段血管通畅,支架内未见血栓及动脉瘤等影像学表现。测量结果显示,Firebird 2支架组、Firehawk支架组支架植入1,3个月的管腔丢失均低于裸支架组(P < 0.05),Firebird 2支架组与Firehawk支架组管腔丢失比较差异无显著性意义,见表1。"
| [1]Shetty R,Prajapati J,Pai U,et al.Preliminary Evaluation of Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes with Biodegradable Polymer Coated Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in De Novo Coronary Artery Disease: Results of the MANIPAL-FLEX Study. Scientifica (Cairo). 2016;2016:9324279.[2]Liu HL,Jin ZG,Yang SL,et al.Five-year outcomes of ST-elevation myocardial infarction versus non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome treated with biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stents: Insights from the CREATE trial.J Cardiol.2016. pii:S0914-5087(16)00059-9. [3]Shetty R,Vivek G,Thakkar A,et al.Experience with biodegradable polymer coated sirolimus-eluting coronary stent system in "real-life" percutaneous coronary intervention: 24-month data from the manipal-s registry.J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7(9):1959-1963.[4]邱洪,罗彤,胡小莹,等.新型生物可降解聚合物雷帕霉素靶向洗脱支架预防支架内狭窄的动物实验研究[J].中国循环杂志, 2012, 27(3):220-223.[5]Suzuki T, Kopia G, Hayashi S, et a1.Stent-based delivery of sirolimus reduces neointimal formation in a potcine coronary model.Circulation.2001;104:1188-1193.[6]Lemos PA,Chandwani P,Saxena S,et al.Clinical outcomes in 995 unselected real-world patients treated with an ultrathin biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent: 12-month results from the FLEX Registry.BMJ Open. 2016; 6(2):e010028.[7]Lim KS,Park JK,Jeong MH,et al.Effect of stents coated with a combination of sirolimus and alpha-lipoic acid in a porcine coronary restenosis model.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016; 27(4):66. [8]Prado GF Jr,Ribeiro EE,Melo PH,et al.Clinical performance of a novel ultrathin strut, low-dose, sirolimus-eluting stent with abluminal-only biodegradable polymeric coating for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in the daily practice. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther.2015;5(6):414-419. [9]Chandwani P,Verma P,Saxena S,et al.Comparison of Clinical Outcomes Following Single versus Multivessel Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Using Biodegradable Polymer Coated Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in an All-comers Patient Population. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2016;14(1):39-48.[10]Polavarapu A,Polavarapu RS,Prajapati J,et al.Clinical Outcomes from Unselected "Real-World" Patients with Long Coronary Lesion Receiving 40 mm Biodegradable Polymer Coated Sirolimus-Eluting Stent. Scientifica(Cairo).2015; 2015: 613089. [11]Sarma R,Prajapati J,Raheem A,et al.Nine-Months Clinical Outcome of Biodegradable Polymer Coated Sirolimus-eluting Stent System: A Multi-Centre "Real-World" Experience. J Clin Diagn Res.2015;9(8):OC23-26. [12]Polavarapu A,Polavarapu RS,Prajapati J,et al.Favorable Outcomes after Implantation of Biodegradable Polymer Coated Sirolimus-Eluting Stents in Diabetic Population: Results from INDOLIMUS-G Diabetic Registry.Int J Vasc Med. 2015;2015:265670. [13]Lemos PA,Abizaid AA,Meireles GC,et al.Metallic Limus-Eluting Stents Abluminally Coated with Biodegradable Polymers: Angiographic and Clinical Comparison of a Novel Ultra-Thin Sirolimus Stent Versus Biolimus Stent in the DESTINY Randomized Trial. Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;33(6): 367-371.[14]Oliveira MD,Ribeiro EE,Campos CM,et al.Four-year clinical follow-up of the first-in-man randomized comparison of a novel sirolimus eluting stent with abluminal biodegradable polymer and ultra-thin strut cobalt-chromium alloy: the INSPIRON-I trial. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther.2015;5(4):264-270. [15]Sojitra P,Doshi M,Galloni M,et al.Preclinical evaluation of a novel abluminal surface coated sirolimus eluting stent with biodegradable polymer matrix. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2015;5(4):254-263. [16]Rajasekhar D,Vanajakshamma V,Vidyasagar A,et al. Evaluation of prolonged safety and efficacy of biodegradable polymer coated sirolimus-eluting coronary stent system: 1-year outcomes of the INDOLIMUS Registry.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther.2015;5(4):249-253. [17]Otsuka F,Cheng Q,Yahagi K,et al.Acute Thrombogenicity of a Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent Relative to Contemporary Drug-Eluting Stents With Biodegradable Polymer Coatings Assessed Ex Vivo in a Swine Shunt Model.JACC Cardiovasc Interv.2015;8(9):1248-1260.[18]Xu B,Zhang YJ,Sun ZW,et al.Comparison of long-term in-stent vascular response between abluminal groove-filled biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent and durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent: 3-year OCT follow-up from the TARGET I trial. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;31(8): 1489-1496. [19]Konishi A,Shinke T,Otake H,et al.Serial Optical Coherence Tomography Evaluation at 6, 12, and 24 Months After Biolimus A9-Eluting Biodegradable Polymer-Coated Stent Implantation.Can J Cardiol.2015;31(8):980-988. [20]Banker D,Ahuja A,Sanadhya H,et al.Clinical performance of biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stents in unselected real-world population with coronary artery disease: results from the multicenter CORE Registry.Minerva Cardioangiol.2016;64(1):9-14. [21]Gao Z,Zhang R,Xu B,et al.Safety and efficacy of a novel abluminal groove-filled biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent for the treatment of de novo coronary lesions: two-year results from a prospective patient-level pooled analysis of TARGET trials.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;85 Suppl 1:734-743. [22]Sprimont P,Pierard S,Vanoverschelde JL,et al.Efficacy and safety of biodegradable polymer biolimus A9-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent in diabetic patients: a prospective non-randomized single-centre long-term comparison.Acta Cardiol.2014;69(5):523-531.[23]Han Y,Xu B,Jing Q,et al.A randomized comparison of novel biodegradable polymer- and durable polymer-coated cobalt-chromium sirolimus-eluting stents. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(12):1352-1360. [24]Kumar P,Pillai R,Sreedharan M,et al.RAPSTROM™ first-in-man study long-term results of a biodegradable polymer sustained-release sirolimus-eluting stent in de novo coronary stenoses.J Interv Cardiol.2014;27(4):373-380. [25]Zhang Q,Qiu JP,Kirtane AJ,et al.Comparison of biodegradable polymer versus durable polymer sirolimus-eluting stenting in patients with acute st-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: results of the RESOLVE study.J Interv Cardiol.2014;27(2):131-141.[26]Zhang L,Li Y,Jing QM,et al.Dual antiplatelet therapy over 6 months increases the risk of bleeding after biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus eluting stents implantation: insights from the CREATE study.J Interv Cardiol.2014;27(2):119-126.[27]Finn AV,Nakagawa G,Joner M,et al.Vascular responses to drug eluting stents:importance of delayed healing.Arterioscler Thromb Vase Biol.2007;27:1500-1510.[28]Lowe HC,Schwartz RS,Mac NB,et al.111e porcine coronary model of in-stent restenosis:current status in the era of drug-eluting stents.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2003;60: 515-523.[29]金刚,高润霖,程树军,等.可降解雷帕霉素洗脱支架对猪冠状动脉支架置入术后内膜增生的影响[J].中国循环杂志, 2004,19(3): 190-193.[30]祁方家,冯莎,吴伟栋,等.药物洗脱支架火鹰(Firehawk)与XIENCE V治疗单支单处冠状动脉病变的卫生经济学评价[J].中国卫生资源,2015,15(4):283-286. [31]何强.新型单面刻槽载药支架内皮化的光学相干断层成像评价[D].天津医科大学,2014.[32]刘慧竹.雷帕霉素靶向洗脱支架治疗冠心病临床及血管内影像研究[D].上海交通大学,2015. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||