Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (25): 3964-3970.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.25.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of miR-218 and miR-26a on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by polyethyleneimine delivery
Sun Xuan1, Wei Ze-quan1, Bu Wen-huan1, Fang Tengjiaozi2, Xiluopianduo1, Liu Qi-lin1, Sun Hong-chen1
- 1Dental Development and Jaw Remodeling, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China; 2Peking University School of Stomatology, Beijing 100034, China
-
Revised:2017-07-24Online:2017-09-08Published:2017-10-09 -
Contact:Sun Hong-chen, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Dental Development and Jaw Remodeling, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Sun Xuan, Dental Development and Jaw Remodeling, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81320108011; Jilin Province Industrial Innovation Special Fund Project, No. 2016C044-3; the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, No. 20170101093JC; the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Plan for Undergraduates, No. 2015781125
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Xuan, Wei Ze-quan, Bu Wen-huan, Fang Tengjiaozi, Xiluopianduo, Liu Qi-lin, Sun Hong-chen. Effects of miR-218 and miR-26a on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by polyethyleneimine delivery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(25): 3964-3970.
share this article
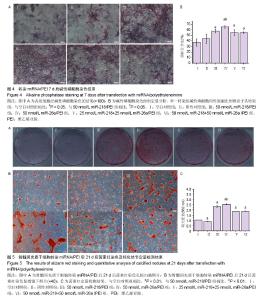
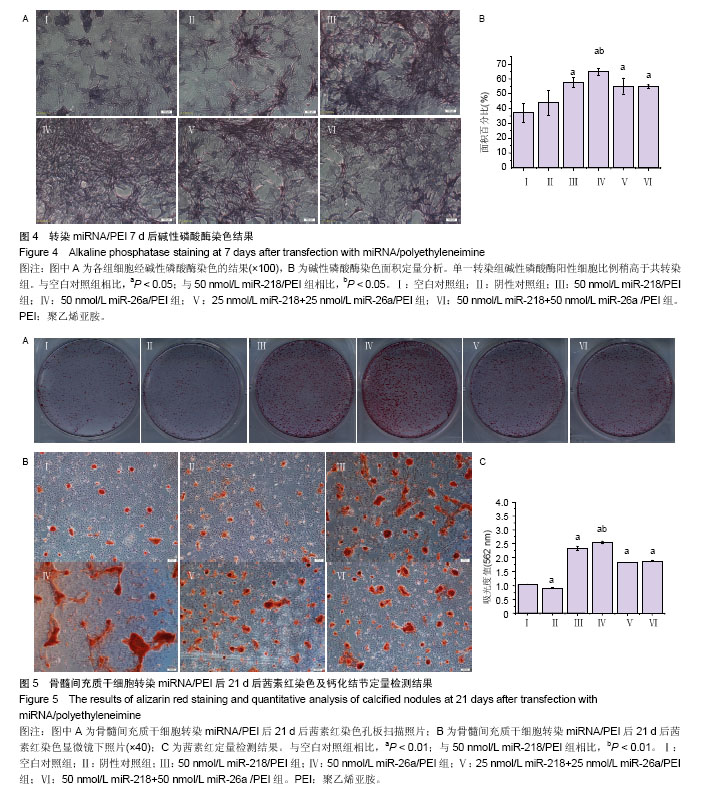
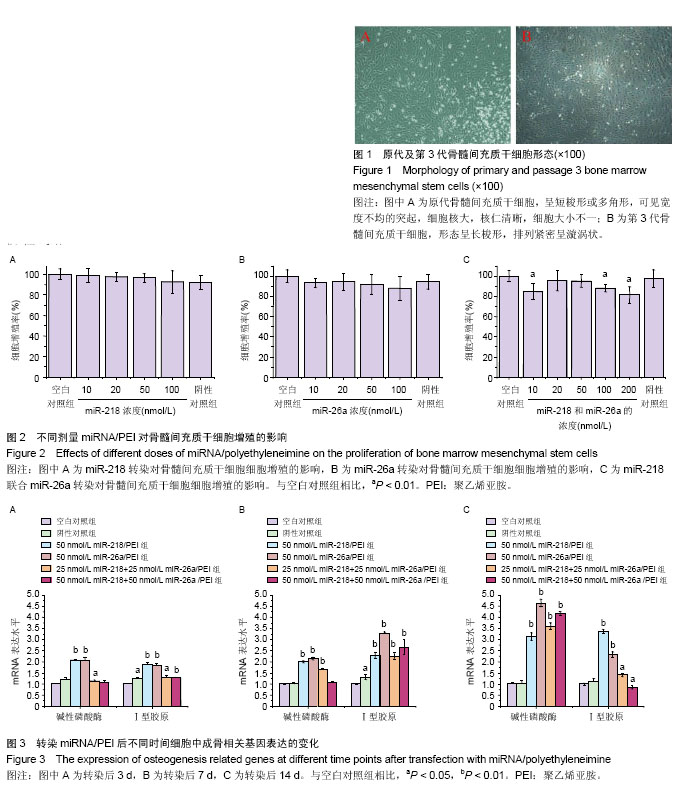
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的培养及形态观察 原代骨髓间充质干细胞贴壁后呈短梭形或多角形,可见宽度不均的突起,细胞核大,核仁清晰,细胞大小不一。消化传代至第3代,细胞生长速度加快,形态呈长梭形,排列紧密呈漩涡状,密度达80%-90%(图1)。 2.2 不同浓度miR/PEI复合物转染骨髓间充质干细胞 24 h后对增殖能力影响 在浓度10-100 nmol/L时miR-218/PEI组与miR-26a/PEI组细胞增殖率随浓度的增加而有下降趋势,但与空白对照组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而与空白对照组相比,100和200 nmol/L miR-218+miR-26a/PEI共转染组细胞增殖率降低(P < 0.01),其他浓度miR-218+miR-26a/PEI共转染组中细胞增殖率无明显变化(P > 0.05;图2)。 2.3 RT-PCR检测成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原的mRNA表达水平 转染后3,7,14 d时,与空白对照组相比,各组碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原mRNA水平均有升高(P < 0.05),其中miR-218/PEI组和miR-26a/PEI组最明显(图3)。 2.4 碱性磷酸酶染色及定量测定 成骨诱导7 d后,与空白对照组相比,阴性对照染色面积接近(P > 0.05),而各组胞质中均产生了较为明显的着色,其中 50 nmol/L miR-218/PEI组与50 nmol/L miR-26a/PEI组胞浆丰富,染色面积和染色程度明显增强,单一转染组碱性磷酸酶阳性细胞比例稍高于共转染组。定量分析也提示miR-26a/PEI组阳性细胞比例稍高于miR-218/PEI组(P < 0.05),见图4。 2.5 茜素红染色及定量分析 成骨诱导21 d后,茜素红染色结果显示,与空白对照组相比,其他组细胞均不同程度地产生了矿化结节(图5A,B)。其中,miR-26a/PEI组矿化结节密度高于miR-218/PEI组。定量分析结果显示, 50 nmol/L miR-218/PEI组、50 nmol/L miR-26a/PEI组、25 nmol/L miR-218+25 nmol/L miR-26a/PEI组和50 nmol/L miR-218+50 nmol/L miR-26a /PEI组细胞中钙化结节含量明显高于空白对照组(P < 0.01),其中50 nmol/L miR-26a/PEI组钙化结节含量高于50 nmol/L miR-218/PEI组,提示miR-26a成骨能力优于miR-218 (P < 0.01;图5C)。"
| [1] 刘继中,王臻,胡蕴玉.异体骨关节移植修复肢体大段骨缺损的术后并发症[J].中华外科杂志,2000,38(5):332-335.[2] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999; 284(5417):1168-1170.[3] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [4] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215-233. [5] Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351-379. [6] Bentwich I. A postulated role for microRNA in cellular differentiation. FASEB J. 2005;19(8):875-879.[7] Ma Y, Qin H, Cui Y. MiR-34a targets GAS1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/Bad pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(4):958-963.[8] Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Shi M, et al. Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(10):2495-2505. [9] Hassan MQ, Maeda Y, Taipaleenmaki H, et al. miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(50):42084-42092. [10] Su X, Liao L, Shuai Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1851. [11] Wang QF, Huang Y, He GC, et al. Osteoblast differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells by polyethylenimine- mediated BMP-2 gene transfection in vitro. Genet Mol Res. 2017;16(1). [12] Wang X, Niu D, Hu C, et al. Polyethyleneimine-Based Nanocarriers for Gene Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(42):6140-6156.[13] Wang M, Guo Y, Yu M, et al. Photoluminescent and biodegradable polycitrate-polyethylene glycol- polyethyleneimine polymers as highly biocompatible and efficient vectors for bioimaging-guided siRNA and miRNA delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:69-80. [14] Liu L, Zheng M, Librizzi D, et al. Efficient and Tumor Targeted siRNA Delivery by Polyethylenimine-graft-polycaprolactone- block-poly(ethylene glycol)-folate (PEI-PCL-PEG-Fol). Mol Pharm. 2016;13(1): 134-143. [15] Boussif O, Lezoualc'h F, Zanta MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(16): 7297-7301.[16] Wang X, Niu D, Hu C, et al. Polyethyleneimine-Based Nanocarriers for Gene Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(42):6140-6156.[17] Liang G, Li Y, Feng W, et al. Polyethyleneimine-coated quantum dots for miRNA delivery and its enhanced suppression in HepG2 cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:6079-6088. [18] Parmar MB, Arteaga Ballesteros BE, Fu T, et al. Multiple siRNA delivery against cell cycle and anti-apoptosis proteins using lipid-substituted polyethylenimine in triple-negative breast cancer and nonmalignant cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(12):3031-3044. [19] Neu M, Fischer D, Kissel T. Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly(ethylene imine) and its derivatives. J Gene Med. 2005;7(8):992-1009.[20] Qi H, Aguiar DJ, Williams SM, et al. Identification of genes responsible for osteoblast differentiation from human mesodermal progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(6):3305-3310. [21] Garg P, Mazur MM1, Buck AC1, et al. Prospective Review of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Osteoblasts. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):13-19. [22] Fu X, Jin L, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA-26a targets ten eleven translocation enzymes and is regulated during pancreatic cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(44): 17892-17897.[23] Li H, Xie H, Liu W, et al. A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(12): 3666-3677. [24] Hu R, Liu W, Li H, et al. A Runx2/miR-3960/miR-2861 regulatory feedback loop during mouse osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(14):12328-12339. [25] Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, et al. Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(23):15676-15684. [26] Li T, Li H, Wang Y, et al. microRNA-23a inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting LRP5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016; 72:55-62.[27] Tian F, Ji XL, Xiao WA, et al. CXCL13 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inhibiting miR-23a Expression. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:632305.[28] Cao Y, LV Q, LV C. MicroRNA-153 suppresses the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by targeting bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(3):760-766. [29] Zuo B, Zhu J, Li J, et al. microRNA-103a functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit bone formation through targeting Runx2. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):330-345. [30] Karbiener M, Pisani DF, Frontini A, et al. MicroRNA-26 family is required for human adipogenesis and drives characteristics of brown adipocytes. Stem Cells. 2014;32(6):1578-1590. [31] Hu F, Sun B, Xu P, et al. MiR-218 Induces Neuronal Differentiation of ASCs in a Temporally Sequential Manner with Fibroblast Growth Factor by Regulation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39427.[32] Qu B, Xia X, Yan M, et al. miR-218 is involved in the negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by partial suppression of p38MAPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling: Potential role for osteopenic diseases. Exp Cell Res. 2015; 338(1):89-96. [33] Taipaleenmäki H, Farina NH, van Wijnen AJ, et al. Antagonizing miR-218-5p attenuates Wnt signaling and reduces metastatic bone disease of triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):79032-79046. [34] Sun F, Ma Y, Cai Z, et al. MiR-218 promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cell through activation of Wnt signaling by targeting SFRP2. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016;9(10):10188-10196.[35] Zhang WB, Zhong WJ, Wang L. A signal-amplification circuit between miR-218 and Wnt/β-catenin signal promotes human adipose tissue-derived stem cells osteogenic differentiation. Bone. 2014;58:59-66. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [6] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [7] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [8] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [11] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [15] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||