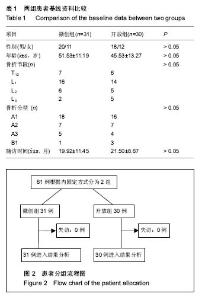
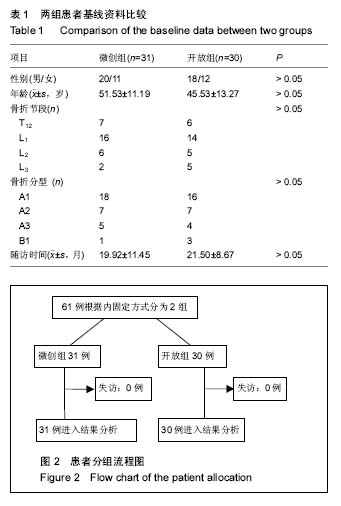
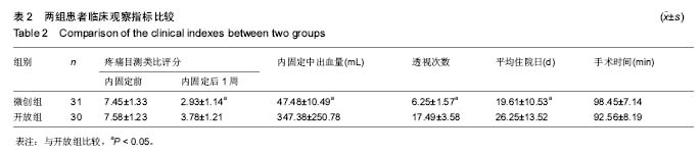
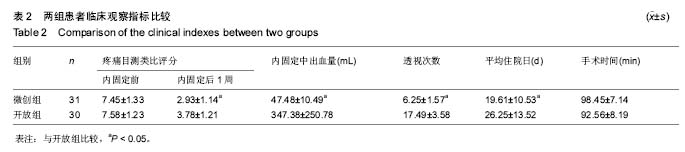
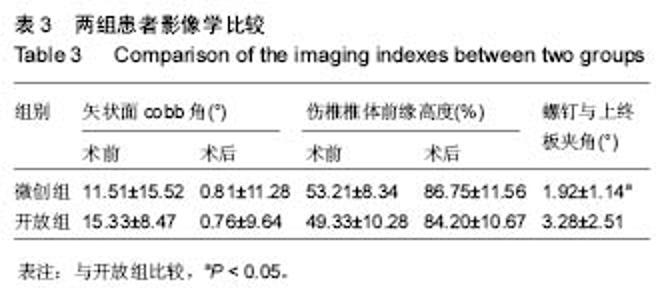
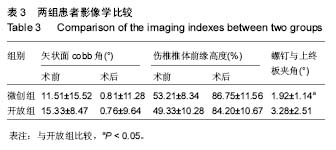
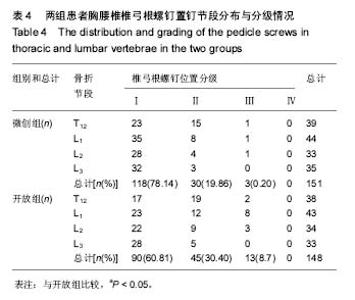
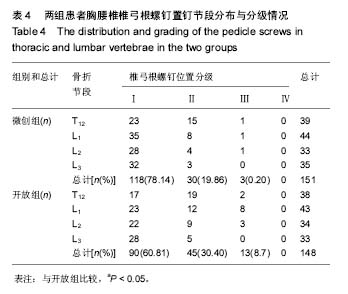
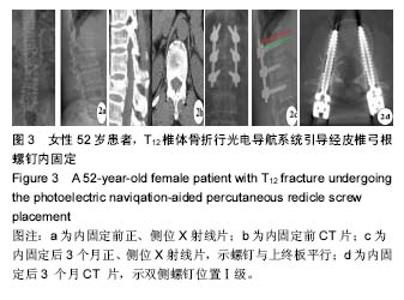
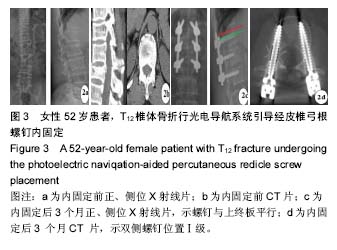
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (23): 3718-3723.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.23.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Photoelectric navigation-aided percutaneous pedicle screw placement versus traditional open posterior pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures
Zhong Ze-li, Wan Sheng-yu, Tan Lun, Lin Xu, Wu Chao
- Department of Orthopedics, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2017-08-18Published:2017-09-01 -
Contact:Wan Sheng-yu, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhong Ze-li, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Program of Zigong City in 2016, No. 2016SFO1
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhong Ze-li, Wan Sheng-yu, Tan Lun, Lin Xu, Wu Chao. Photoelectric navigation-aided percutaneous pedicle screw placement versus traditional open posterior pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(23): 3718-3723.
share this article
| [1] Wang HW, zhang Y, Xiang Q, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal fracture: experience form medical university affiliated hospitals in Chongqing, china, 2001-2010.J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(5):459-468.[2] Verlaan JJ, Diekerhof CH, Buskens E,et al.Surgical treatment fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine:a systemic review of the literature on techniques, complications, and outcome. Spine.2004;29(7):803-814.[3] Hanug TJ, Hsu RW, Li YY,et al.Loss systemic cytokine response in patients fo1lowing microendoscopic Versus “open” lumbar discectomy.J Orthop Res.2005;23(2): 406-411.[4] Mathews HH, Long BH.Minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of intervertebral disk herniation.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2002;10(2):80-85.[5] Kim BG, Dan JM, Shin DE. Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(1):133-146.[6] Phan K, Rao PJ, Mobbs RJ. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: Systematic review and meta -analysis of comparative studies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2015;135: 85-92.[7] Dahdaleh NS,Smith ZA,Hitchon PW. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures.Neurosurg Clin NAm.2014;25(2):337-346.[8] Lyu J,Chen K,Tang Z,et al.A comparison of three different surgical procedures in the treatment of type A thoracolumbar fractures:a randomized controlled trial Int Orthop. 2016;40: 1233-1238[9] Pishnamaz M, Oikonomidis S, Knobe M, et al.Open versus percutaneous stabilization of thoracolumbar spine fractures: a short-term functional and radiological follow-up. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2015;82(4):274-281.[10] 程杭清,李国庆,孙韶华,等.小切口经肌间隙与微创经皮入路治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折的临床对比研究[J]. 中国骨伤杂志, 2015, 28(11):1108-1112[11] Zhang W, Li H, Zhou Y,et al.Minimally Invasive Posterior Decompression Combined With Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures With Neurological Deficits: A Prospective Randomized Study Versus Traditional Open Posterior Surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 19:B23-B29.[12] Magerl F,Aebi M,Gertzbein SD, et al. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries.Eur Spine J. 1994;3(4):184-201.[13] Farey JP,Weidenbaum M,Glassman S.Sagittal index in the management of thracolumbar burst fractures.Spine. 1990; 5(9):958-965.[14] Ringel F, Stoffel M,Stuer C,et al.Minimally invasive transmuscular pedicle screw fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine.Neurosurgery.2006;59(Suppl4): ONS361-367.[15] Macnab I. Cuthbert H. Godfrey CM. The incidence of denervation of the sacrospinales muscles following spinal surgery.Spine.1977;2(4):293-299.[16] Sihvonen T, Herno A,Paljarvi L,et al. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muselesin postoperative failed back syndrome, Spine.1993;18(5):575-581.[17] Mathews HH, Long BH. Endoscopy assisted percutaneous anterior interbody fusion with subcutaneous suprafascial internal fixation: evolution of technique and surgical considerations.Orthop Int.1995; 3: 496-500.[18] Foley KT, Gupta SK, Justis JR. 802 pereutaneous pedicle serew-rod fixation of the lumbar spine. Neurosurg Focus. 2001;10(4): E10.[19] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.附加伤椎固定的微创经皮椎弓根螺钉(Sextant)治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2010,12(2): 18-22.[20] 李长青,罗刚,周跃,等.新型微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志, 2009, 25(6): 522-525.[21] 李长青,罗刚,周跃,等.微创三节段经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定选择性治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].第三军医大学学报,2009,31(22):2284-2287.[22] Weinstein JN, Rydevik BL, Orausching W, et al.Anatomical and technical considerations of pedicle screw fixation. Clin Orthop RelatRes.1992; (284):34-36.[23] Castro WH, Halm H, Jerosch J, et al. Accuracy 0f pedicle screw placement in lumbar ventebrae.Spine.1996;21(11): 1320-1324.[24] Haaker RG,Eickhoff U,Schopphoff E,et al.Verification of position of pedicle screws in lumbar 8pinal fusion. Eur Spine J.1997;6(2):125-128.[25] Raley DA,Mobbs RJ.Retrospective computed tomography scan analysis of percutaneously inserted pedicle screws for posterior transpedicular stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine:accuracy and complication rates. Spine.2012; 37(12):1092-1100.[26] Wiesner L. Kothe R.Ruther W.Anatomic evaluation of two different techniques for the percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine. Spine.1999;24(15):1599-1603.[27] Wiesner L,Kothe R,Schulitz KP,et al. Clinical evaluation and computed tomography scan analysis of screw tracts after percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine. Spine.2000;25(5):615-621.[28] Schizas C,Michel J,Kosmopoulos V,et al.Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw insertion in percutaneous posterior tran8pedicular stabilization. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(5):613-617.[29] Chapman TM, Blizzard DJ, Sheets C, Brown CR. CT accuracy of percutaneous versus open pedicle screwtechniques: a series of 1609 screws Eur Spine J. 2016, 25:1781-1786.[30] 夏天,董双海,王雷,等.胸腰椎经皮椎弓根螺钉置钉的准确性分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(9): 794-797.[31] 叶斌,孟祥龙,刘玉增,等.徒手置钉技术在脊柱畸形矫正中的准确性与安全性研究[J]. 2014,12(1):25-34.[32] Park DK, Thomas AO, St Clair S, et al. Percutaneous lumbar and thoracic pedicle screws: a trauma experience. J Spinal Disord Tech.2012; 27(3): 154-161.[33] Parker SL,Amin AG,Santiago-Dieppa D,et al.Incidence and clinical significance of vascular encroachment resulting from free—hand placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic and lumbarspine:analysis of 68 16 consecutive screws.Spine. 2014;38:683-687. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [4] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [5] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [7] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [8] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [9] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [10] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [11] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [12] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [13] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||