Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3589-3594.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
3D bioprinting of tissues and organs and its application in oral medicine
- Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, College of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China
-
Received:2017-03-09Online:2017-08-08Published:2017-09-01 -
Contact:Wang Xu-dong, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, College of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China -
About author:Lin Yu-heng, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, College of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271122, 81570947; Shanghai Summit & Plateau Disciplines; and the ?Program for Innovation Research Teams of the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Yu-heng, Wang Xu-dong, Shen Guo-fang.
share this article
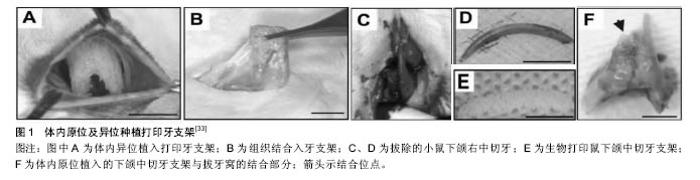
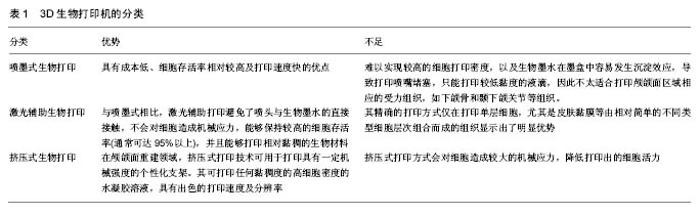
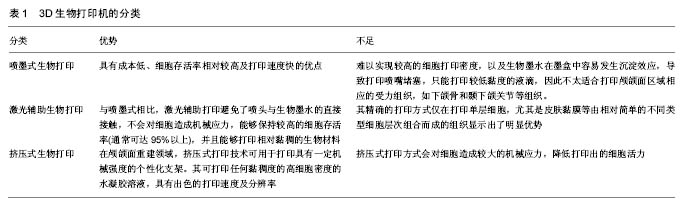
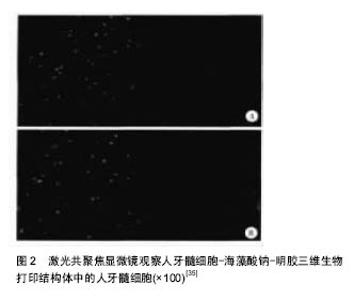
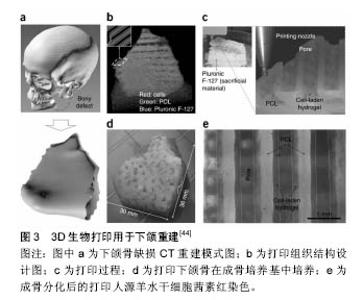
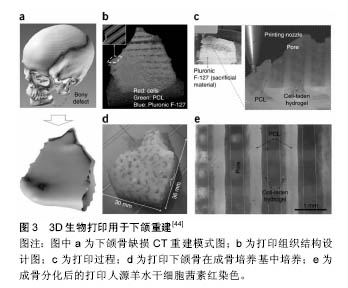
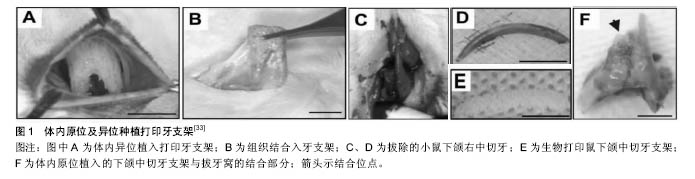
2.1.1 喷墨式生物打印 首先出现的生物细胞打印技术是喷墨式生物打印,它具有成本低、细胞存活率相对较高及打印速度快的优点[17]。但另一方面,其难以实现较高的细胞打印密度,以及生物墨水在墨盒中容易发生沉淀效应[18],导致打印喷嘴堵塞,只能打印较低黏度的液滴,因此不太适合打印颅颌面区域相应的受力组织,如下颌骨和颞下颌关节等组织。而喷墨式打印更为可能应用在一些非受力组织,包括腱膜、耳鼻软骨或者受外伤影响的面部肌肉,如口轮匝肌、眼轮匝肌、降口角肌等[19]。 2.1.2 激光辅助生物打印 与喷墨式相比,激光辅助打印避免了喷头与生物墨水的直接接触,不会对细胞造成机械应力,能够保持较高的细胞存活率(通常可达95%以上[20]),并且能够打印相对黏稠的生物材料。其精确的打印方式在打印单层细胞,尤其是皮肤黏膜等由相对简单的不同类型细胞层次组合而成的组织显示出了明显优势,在打印口腔黏膜、面部肌肉、表皮基底膜、血管内皮细胞等方面具有广阔的应用前景。 2.1.3 挤压式生物打印 挤压式生物打印机是在喷墨式的基础上改良而来。在颅颌面重建领域,挤压式打印技术可用于打印具有一定机械强度的个性化支架。其可打印任何黏稠度的高细胞密度的水凝胶溶液,具有出色的打印速度及分辨率。但挤压式打印方式会对细胞造成较大的机械应力,降低打印出的细胞活力。目前,已有部分研究打印骨或软骨组织[21],并获得了一定的机械强度,这也表明了其应用于口腔颅颌面相关的骨组织重建方面的潜力。 2.2 3D生物打印在不同组织与器官中的应用 2.2.1 3D生物打印简单组织 在生物打印领域,如何打印组织的血管网络,是生物打印功能器官面临的主要问题之一。由于血管能够运输营养和氧气,并且能够带走组织代谢物,因此其对于打印复杂的组织与器官尤为重要。Skardal等[9]较早地利用负载细胞的水凝胶打印出了血管结构,而为了减少血管的管道尺寸以便将其整合进入打印组织,研究者开始使用牺牲性材料并取得了一定的成果。Kolesky等[8]使用普郎尼克F127(Pluronic F127)自牺牲材料,打印出直径为45 μm的管道,通过紫外照射GelMA基质使其交联,降低环境温度,使牺牲性材料液化,使得所打印出的血管具可灌注特性。而在此之前,Bertassoni等[22]通过将含有悬浮细胞的凝胶打印于成型的碳水化合物结构周围,交联后再将碳水化合物溶解形成中空管道,进而灌注人脐静脉内皮细胞HUVECs以形成单层内皮。类似的利用牺牲性材料的技术,不仅能够简化生物打印组织的成血管模式,而且对打印复杂的大型器官具有极大的意义。 除了对于打印血管的探索,研究人员还尝试将生物打印应用于神经组织。复杂器官往往需要将其与神经系统进行整合,以完善其相应的生物学功能。Owens等[23]将小鼠骨髓干细胞和许旺细胞接种于直径500 μm的管道中,利用生物打印机将其打印形成由骨髓干细胞包绕的许旺细胞神经管。随后,Lorber等[24]将大鼠视网膜神经节细胞和神经胶质应用于喷墨打印系统,进一步证明了生物打印神经系统的可行性。 在对打印脂肪组织的早期探索中,脂肪来源干细胞和明胶/藻酸盐水凝胶被用于打印成三维立体结构,所打印出的脂肪来源干细胞依然能够增殖和分化,当向其中添加成纤维生长因子之后,位于支架壁上的细胞分化为内皮样细胞,而嵌入在水凝胶中的细胞则分化为脂肪样细胞[25]。Pati等[26]则将人类脂肪基质作为生物墨水打印脂肪组织。 2.2.2 3D生物打印复杂组织 自观察到组织工程中肝脏实质细胞的分化后[27],3D生物打印随后也被应用于打印肝脏样微结构当中。虽然打印具有生物活性的肝脏结构仍处于早期,但研究者已经就实现肝脏结构的部分功能进行了一系列的工作[10,28]。Chang等[11]将HepG2肝癌细胞、生长因子及支架材料封装于藻酸盐中,通过微挤压生物打印技术打印肝脏结构,并利用这些微型肝脏结构模拟体内生理条件,进行药物的代谢研究。其后,作为较早生物打印公司之一的Organovo公司,完成了具有高细胞存活率和高细胞密度的三维血管化肝脏组织生物打印[29]。 3D生物打印的兴起同样为再造功能性心脏提供了一种极具潜力的方式。Duan等[30]将人主动脉血管间质细胞与丙烯酸甲酯透明质酸和GelMA的混合凝胶作为生物墨水,用于打印心脏瓣膜管道,在7 d的静态培养后细胞存活率在90%以上。在此之前,他们分别利用主动脉瓣根部窦平滑肌细胞和主动脉瓣小叶间质细胞成功打印出主动脉瓣,细胞7 d存活率分别为81.4%和83.2%[31]。在另一项较早的研究中,Gaetani等[14]以心肌祖细胞和藻酸盐水凝胶为墨水打印体外心脏样组织,观察到打印后的心脏祖细胞早期表达了Nkx2.5、Gata-4、Mef-2c等心脏转录因子。 2.3 3D生物打印在口腔及颅颌面修复中的研究进展 2.3.1 牙周及牙体组织 牙周组织作为牙体的支持组织,极易遭受口腔致病菌的破坏。致病菌与宿主发生作用,能够导致牙周组织的丧失,造成牙齿松动甚至脱落。近年来,3D生物打印研究的兴起,为牙周组织再生提供了可行研究途径。虽然目前缺乏直接利用细胞作为原料打印牙周组织的研究,但Green等[32]提出可借鉴激光辅助打印皮肤的原理,将含有成纤维细胞和角质形成细胞的溶液作为生物墨水逐层打印。在打印牙周组织的初始阶段,需再生相关的正常解剖结构,如马拉瑟上皮剩余、血管内外膜及相应的纤维等。而在此之中,关键部分在于形成具有物质交换功能的组织表面,与对应牙体解剖结构形成生物学连接,实现分子跨膜运输的自主调节。 由于在牙体形成过程当中,外胚层与外胚间充质细胞的相互诱导发挥了重要作用。因此,对于牙体再生而言,其关键部分在于需要对再生组织细胞聚集进行精准控制,以模拟牙体组织发育早期上皮间充质交界处的诱导过程。由于3D生物打印技术能够精确地将细胞打印于预先设计的坐标上,构成具有丰富层次细胞的组织,使得其在牙体组织再生领域具有广阔的应用潜力。研究表明,多种细胞类型均具有牙源性潜力,如牙髓干细胞等可作为牙体再生的细胞来源。Kim等[33]以多聚己内酯与 羟基磷灰石的复合墨水为原料,分别在体内与体外对牙体的正常解剖结构进行了还原,证明了以生物支架的方式实现牙体再生的可能性(图1)。但支架材料往往存在不同程度的生物相容性欠佳、细胞与基质间相互作用被阻断、生长因子存留性差等缺点,因此可使用水凝胶包裹细胞以维持其活性。水凝胶是由亲水性聚合物组成,其含水量可达99%,具有良好的生物相容性和可降解性,有利于可溶性因子的转运,其作为人工细胞外基质材料,已被广泛应用于生物打印领域[34]。北大薛世华等[35]利用人牙髓细胞和海藻酸钠-明胶水溶液组成共混物作为生物墨水,共混物中海藻酸钠的终质量浓度为20 g/L,人牙髓细胞浓度为1×109 L-1,并且观察到打印后的细胞存活率为(87±2)% (图2)。尽管所构建牙髓组织结构尺寸与自然牙体还有一定差别,但已从一定程度上证明了将生物打印技术应用于牙体再生的可行性。 2.3.2 颅颌面组织 迄今为止,生物打印领域多数的报道集中于研究打印骨、软骨和皮肤。而颅颌面区域的疾病或者创伤所导致的组织缺损,又常常累及这些组织。因此,上述组织的生物打印研究,对于临床上颅颌面部缺损的个性化修复具有重要意义。 熔融沉积制造作为3D打印技术的一种,通过高温将材料融化为液态,以打印喷头将材料挤出且固化后形成三维立体模型,尤其适合于受力及负荷较大如骨或软骨等部位的支架生物打印[36-37]。Goh等[38]通过熔融沉积聚己内酯以保存牙槽嵴位点,而Reichert等[39]利用聚己内酯制造含有20%磷酸三钙微粒的柱形支架,并与重组人骨形态发生蛋白7相结合,以促进骨形成。颅颌面相关的骨缺损可借鉴此种生物打印模式进行个性化修复。目前,生物打印骨和软骨组织的细胞主要有人类间充质干细胞[40]、人脐静脉内皮细胞[41]、鼠成骨细胞[42]、人骨髓基质细胞等[43]。Kang等[44]利用人羊水来源干细胞打印出了个性化的下颌骨缺损模型,并证明打印过程不会影响细胞的活力(图3)。Pati等陆续以人羊水干细胞和兔耳软骨细胞分别完成了对颅顶骨缺损和耳软骨的打印。此外,对于原位的组织生物打印,Keriquel等[42]使用激光辅助打印应用于鼠颅骨模型。而Skardal等[45]同样以激光生物打印技术修复了小鼠背部皮肤缺损,可为原位打印颅颌面皮肤组织的研究提供相关参考。 "
| [1]Rasperini G,Pilipchuk SP,Flanagan CL,et al.3d-printed bioresorbable scaffold for periodontal repair.J Dent Res. 2015;94(9 Suppl):153S-157S.[2]Sun Y,Luebbers HT,Agbaje JO,et al.Accuracy of a dedicated bone-supported surgical template for dental implant placement with direct visual control.J Healthc Eng.2015; 6(4):779-790.[3]Murphy SV,Atala A.3d bioprinting of tissues and organs.Nat Biotechnol.2014;32(8):773-785.[4]Mironov V,Reis N,Derby B.Review: Bioprinting: A beginning. Tissue Eng.2006;12(4):631-634.[5]Koch L,Kuhn S,Sorg H,et al.Laser printing of skin cells and human stem cells . Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2010; 16(5): 847-854.[6]Michael S,Sorg H,Peck CT,et al.Tissue engineered skin substitutes created by laser-assisted bioprinting form skin-like structures in the dorsal skin fold chamber in mice.PloS One. 2013;8(3):e57741.[7]Lee V,Singh G,Trasatti JP,et al.Design and fabrication of human skin by three-dimensional bioprinting.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2014;20(6):473-484.[8]Kolesky DB,Truby RL,Gladman AS,et al.3d bioprinting of vascularized, heterogeneous cell-laden tissue constructs.Adv Mat.2014;26(19):3124-3130.[9]Skardal A,Zhang J,Prestwich GD.Bioprinting vessel-like constructs using hyaluronan hydrogels crosslinked with tetrahedral polyethylene glycol tetracrylates. Biomaterials. 2010;31(24):6173-6181.[10]KhatiwalaC, Law R,Shepherd B,et al.3d cell bioprinting for regenerative medicine research and therapies.Gene Ther Regulat.2013;7(1):1100030.[11]Chang R,Emami K,Wu H,et al.Biofabrication of a three-dimensional liver micro-organ as an in vitro drug metabolism model.Biofabrication.2010;2(4):045004-045004.[12]Gao G,Yonezawa T,Hubbell K,et al.Inkjet-bioprinted acrylated peptides and peg hydrogel with human mesenchymal stem cells promote robust bone and cartilage formation with minimal printhead clogging.Biotechnol J. 2015;10(10): 1568-1577.[13]Duarte Campos DF,Blaeser A,Korsten A,et al.The stiffness and structure of three-dimensional printed hydrogels direct the differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells toward adipogenic and osteogenic lineages.Tissue EngA. 2015; 21(3-4):740-756.[14]Gaetani R,Doevendans PA,Metz CHG,et al.Cardiac tissue engineering using tissue printing technology and human cardiac progenitor cells.Biomaterials.2012;33(6):1782-1790.[15]Lee JS,Hong JM,Jung JW,et al.3d printing of composite tissue with complex shape applied to ear regeneration. Biofabrication. 2014;6(2):024103-024103.[16]Pati F,Ha DH,Jang J,et al.Biomimetic 3d tissue printing for soft tissue regeneration.Biomaterials.2015;62:164-175.[17]Cui X,Gao G,Qiu Y.Accelerated myotube formation using bioprinting technology for biosensor applications.Biotechnol Lett.2013;35(3):315-321.[18][18]Pepper ME,Seshadri V,Burg TC,et al.Characterizing the effects of cell settling on bioprinter output.Biofabrication. 2012;4(1):11001-11006(11006).[19]Visscher DO,Farre-Guasch E,Helder MN,et al.Advances in bioprinting technologies for craniofacial reconstruction.Trends Biotechnol.2016;34(9):700-710.[20]Mandrycky C,Wang Z,Kim K,et al.3d bioprinting for engineering complex tissues.Biotechnol Adv.2016;34(4): 422-434.[21]Sawkins MJ,Mistry P,Brown BN,et al.Cell and protein compatible 3d bioprinting of mechanically strong constructs for bone repair.Biofabrication.2015;7(3):035004.[22]Bertassoni LE,Cecconi M,Manoharan V,et al.Hydrogel bioprinted microchannel networks for vascularization of tissue engineering constructs.Lab Chip. 2014;14(13):2202-2211.[23]Owens CM Marga F,Forgacs G,et al.Biofabrication and testing of a fully cellular nerve graft.Biofabrication.2013;5(4):380-387.[24]Lorber B,Hsiao WK,Hutchings IM,et al.Adult rat retinal ganglion cells and glia can be printed by piezoelectric inkjet printing.Biofabrication.2014;6(1):152-163.[25]Yao R,Zhang R,Yan Y,et al.In vitro angiogenesis of 3d tissue engineered adipose tissue.J Bioact Compat Polym.2009; 24(1):5-24.[26]Pati F,Jang J,Ha DH,et al.Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink.Nat Commun.2014;5:3935-3935.[27]Lee JS,Cho SW.Liver tissue engineering: Recent advances in the development of a bio-artificial liver.Biotechnol Bioproc Eng.2012;17(3):427-438.[28]Cui X,Boland T.Human microvasculature fabrication using thermal inkjet printing technology.Biomaterials. 2009;30(31): 6221-6227.[29]Nguyen D,Robbins J,Crogangrundy C,et al.Functional characterization of three-dimensional (3d) human liver tissues generated by an automated bioprinting platform.Faseb J.2015.[30]Duan B,Kapetanovic E,Hockaday LA,et al.Three-dimensional printed trileaflet valve conduits using biological hydrogels and human valve interstitial cells.Acta Biomaterialia. 2014;10(5): 1836-1846.[31]Duan B,Hockaday LA,Kang KH,et al.3d bioprinting of heterogeneous aortic valve conduits with alginate/gelatin hydrogels.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(5):1255-1264.[32]Green DW,Lee JS,Jung HS.Small-scale fabrication of biomimetic structures for periodontal regeneration.Front Physiol.2016;7:6. [33]Kim K,Lee CH,Kim BK,et al.Anatomically shaped tooth and periodontal regeneration by cell homing.J Dent Res.2010; 89(8):842-847.[34]Li CC,Kharaziha M,Min C,et al.Microfabrication of cell-laden hydrogels for engineering mineralized and load bearing tissues.Adv Exp Med Biol.2015;881:15-31.[35]薛世华,吕培军,王勇,等.人牙髓细胞共混物三维生物打印技术[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2013,45(1):105-108.[36]Obregon F,Vaquette C,Ivanovski S,et al.Three-dimensional bioprinting for regenerative dentistry and craniofacial tissue engineering.J Dent Res.2015;94(9 Suppl):143S-152S.[37]Reichert JC,Wullschleger ME,Cipitria A,et al.Custom-made composite scaffolds for segmental defect repair in long bones.Int Orthop.2011;35(8):1229-1236.[38]Goh BT,Teh LY,Tan DB,et al.Novel 3d polycaprolactone scaffold for ridge preservation - a pilot randomised controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Implants Res.2015;26(3):271-277.[39]Reichert JC,Cipitria A,Epari DR,et al.A tissue engineering solution for segmental defect regeneration in load-bearing long bones.Sci Translat Med.2012;4(141):1251-1255.[40]Gurkan UA,El AR,Yildiz SE,et al.Engineering anisotropic biomimetic fibrocartilage microenvironment by bioprinting mesenchymal stem cells in nanoliter gel droplets.Mol Pharm.2014;11(7):2151-2159.[41]Gauvin R,Chen YC,Jin WL,et al.Microfabrication of complex porous tissue engineering scaffolds using 3d projection stereolithography.Biomaterials. 2012;33(15):3824-3834.[42]Keriquel V,Guillemot F,Arnault I,et al.In vivo bioprinting for computer- and robotic-assisted medical intervention: Preliminary study in mice.Biofabrication.2010;2(1):1206-1206.[43]Catros S,Fricain JC,Guillotin B,et al.Laser-assisted bioprinting for creating on-demand patterns of human osteoprogenitor cells and nano-hydroxyapatite. Biofabrication.2011;3(2): 25001-25011(25011).[44]Kang HW,Lee SJ,Ko IK,et al.A 3d bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity.Nat Biotechnol.2016;34(3):312-319.[45]Skardal A,Mack D,Kapetanovic E,et al.Bioprinted amniotic fluid-derived stem cells accelerate healing of large skin wounds.Stem Cells TranslatMed.2012;1(11):792-802.[46]顾奇,郝捷,陆阳杰,等.生物三维打印的研究进展[J].中国科学:生命科学, 2015,45(5):439-449. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||