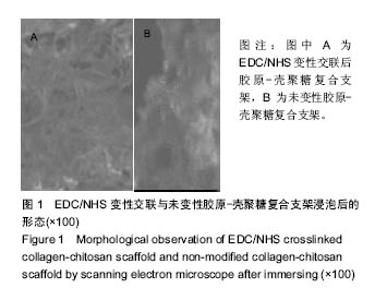
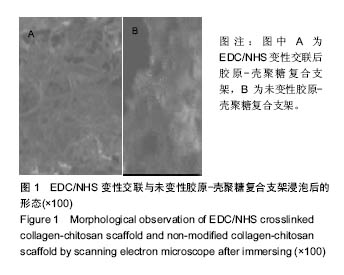
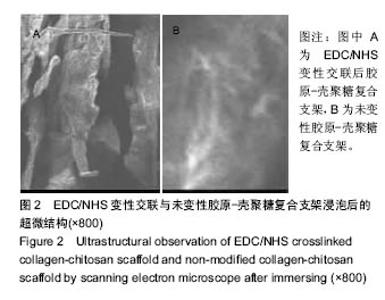
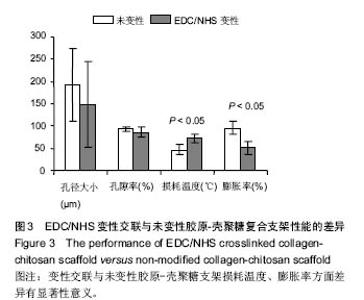
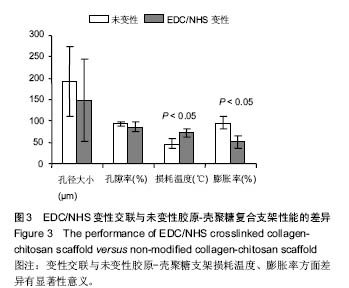
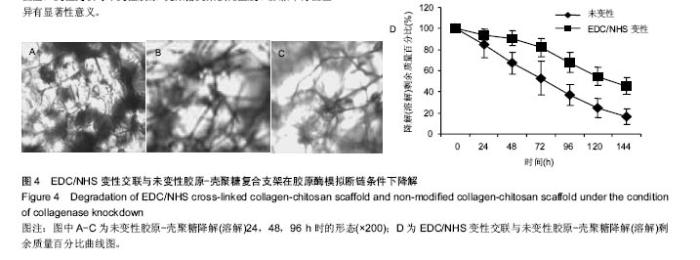
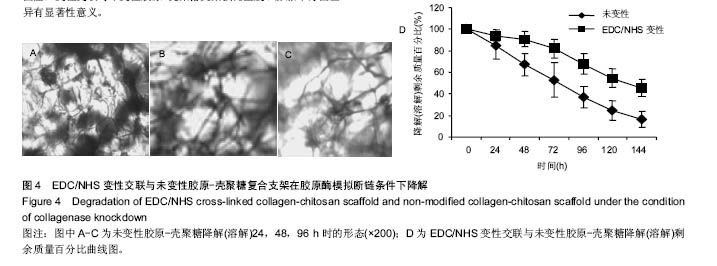
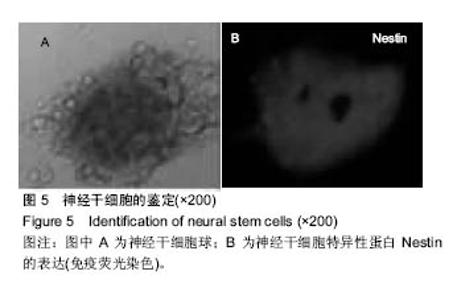
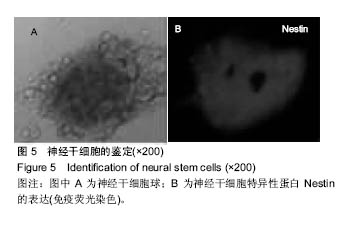
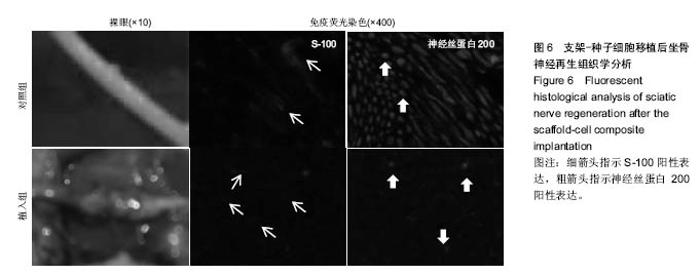
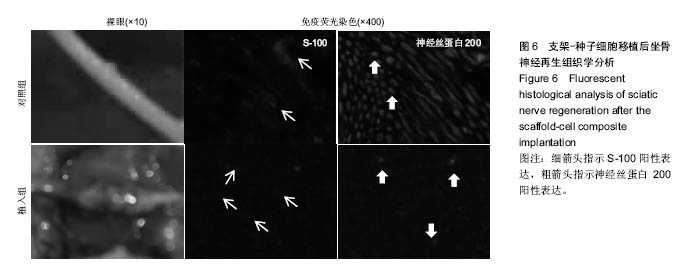
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (18): 2913-2919.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.18.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
A novel tissue-engineered crosslinked collagen-chitosan scaffold and its biocompatibility with nerve cells
- 1First Clinical College, 2Institute of Anesthesiology, 4Basic Medical Institute, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; 3Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Taihe Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2017-02-21Online:2017-06-28Published:2017-07-07 -
Contact:Zhang Guo-hui, First Clinical College, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Lu Jiang, M.D., Lecturer, First Clinical College, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; Institute of Anesthesiology, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Taihe Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Education Ministry of China in 2012, No. 201210929004; the National College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Education Ministry of China in 2016, No. 201610929005; the Scientific and Technological Project of Shiyan City of Hubei Province, No. 14Y13; the Educational Scientific Foundation of Hubei University of Medicine in 2016, No. 2016027; the Natural Science Research Project of Hubei University of Medicine, No. 2011QDZR-1, 2011QDZR-2; Fund of Disciplines Construction of Hubei University of Medicine in 2015, No. 2015; and the Scientific Foundation of Affiliated Taihe Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine in 2016, No. 2016JJXM001
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Jiang, Chen Xuan-li, Tang He-xin, She Na, Zhu Yao, Li Si-xing, Wang Tian-ying, Zhang Guo-hui.
A novel tissue-engineered crosslinked collagen-chitosan scaffold and its biocompatibility with nerve cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(18): 2913-2919.
share this article
| [1]Grinsell D, Keating CP. Peripheral nerve reconstruction after injury: a review of clinical and experimental therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:698256. [2]Panagopoulos GN, Megaloikonomos PD, Mavrogenis AF. The Present and Future for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Orthopedics. 2017;40(1):e141-e156. [3]Faroni A, Mobasseri SA, Kingham PJ, et al. Peripheral nerve regeneration: experimental strategies and future perspectives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;82-83:160-167.[4]Allodi I, Udina E, Navarro X. Specificity of peripheral nerve regeneration: interactions at the axon level. Prog Neurobiol. 2012;98(1):16-37. [5]Jiang L, Jones S, Jia X. Stem Cell Transplantation for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Current Options and Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1). pii: E94. [6]Monaco G, Cholas R, Salvatore L, et al. Sterilization of collagen scaffolds designed for peripheral nerve regeneration: Effect on microstructure, degradation and cellular colonization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;71:335-344.[7]Kanetis L, Exarchou V, Charalambous Z, et al. Edible coating composed of chitosan and Salvia fruticosa Mill. extract for the control of grey mould of table grapes. J Sci Food Agric. 2017; 97(2):452-460.[8]Gratzer PF, Santerre JP, Lee JM. The effect of chemical modification of amino acid side-chains on collagen degradation by enzymes. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007;81(1):1-11.[9]Minardi S, Taraballi F, Wang X, et al. Biomimetic collagen/elastin meshes for ventral hernia repair in a rat model. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:165-177.[10]Jithendra P, Rajam AM, Kalaivani T, et al. Preparation and characterization of aloe vera blended collagen-chitosan composite scaffold for tissue engineering applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(15):7291-7298. [11]Grover CN, Cameron RE, Best SM. Investigating the morphological, mechanical and degradation properties of scaffolds comprising collagen, gelatin and elastin for use in soft tissue engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;10:62-74. [12]Davidenko N, Schuster CF, Bax DV, et al. Control of crosslinking for tailoring collagen-based scaffolds stability and mechanics. Acta Biomater. 2015;25:131-142.[13]Kumari S, Kumar Annamareddy SH, Abanti S, et al. Physicochemical properties and characterization of chitosan synthesized from fish scales, crab and shrimp shells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. in press.[14]Varun TK, Senani S, Jayapal N, et al. Extraction of chitosan and its oligomers from shrimp shell waste, their characterization and antimicrobial effect. Vet World. 2017;10(2):170-175.[15]Marei NH, El-Mazny W, El-Shaer A, et al. Enhanced wound healing activity of desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria) vs. shrimp (Penaeus monodon) chitosan based scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;97:23-33. [16]Zhang H, Yun S, Song L, et al. The preparation and characterization of chitin and chitosan under large-scale submerged fermentation level using shrimp by-products as substrate. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;96:334-339. [17]Wrobel S, Serra SC, Ribeiro-Samy S, et al. In vitro evaluation of cell-seeded chitosan films for peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(17-18):2339-2349. [18]Han F, Dong Y, Su Z, et al. Preparation, characteristics and assessment of a novel gelatin-chitosan sponge scaffold as skin tissue engineering material. Int J Pharm. 2014;476(1-2): 124-133. [19]Mututuvari TM, Harkins AL, Tran CD. Facile synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of cellulose-chitosan-hydroxyapatite composite material: a potential material for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(11):3266-3277.[20]Yin A, Zhang K, McClure MJ, et al. Electrospinning collagen/chitosan/poly(L-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone) to form a vascular graft: mechanical and biological characterization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(5):1292-1301.[21]Su JY, Chen SH, Chen YP, et al. Evaluation of Magnetic Nanoparticle-Labeled Chondrocytes Cultivated on a Type II Collagen-Chitosan/Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic) Acid Biphasic Scaffold. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1). pii: E87. [22]Zhang ML, Cheng J, Xiao YC, et al. Raloxifene microsphere-embedded collagen/chitosan/β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold for effective bone tissue engineering. Int J Pharm. 2017;518(1-2):80-85.[23]Muthukumar T, Aravinthan A, Sharmila J, et al. Collagen/chitosan porous bone tissue engineering composite scaffold incorporated with Ginseng compound K. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;152:566-574.[24]Fan X, Chen K, He X, et al. Nano-TiO2/collagen-chitosan porous scaffold for wound repairing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;91:15-22.[25]Yan F, Yue W, Zhang YL, et al. Chitosan-collagen porous scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(9):1421-1426. [26]Haaparanta AM, Järvinen E, Cengiz IF, et al. Preparation and characterization of collagen/PLA, chitosan/PLA, and collagen/chitosan/PLA hybrid scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(4):1129-1136.[27]Han J, Zhou Z, Yin R, et al. Alginate-chitosan/hydroxyapatite polyelectrolyte complex porous scaffolds: preparation and characterization. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;46(2):199-205.[28]Mathews S, Bhonde R, Gupta PK, et al. Novel biomimetic tripolymer scaffolds consisting of chitosan, collagen type 1, and hyaluronic acid for bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells-based bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(8):1825-1834.[29]Pati F, Adhikari B, Dhara S. Collagen intermingled chitosan-tripolyphosphate nano/micro fibrous scaffolds for tissue-engineering application. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012;23(15):1923-1938. [30]Wang A, Ao Q, Cao W, et al. Porous chitosan tubular scaffolds with knitted outer wall and controllable inner structure for nerve tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(1):36-46.[31]Wang X, Li Q, Hu X, et al. Fabrication and characterization of poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) knitted mesh-reinforced collagen-chitosan hybrid scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;8:204-215.[32]Bi L, Cao Z, Hu Y, et al. Effects of different cross-linking conditions on the properties of genipin-cross-linked chitosan/collagen scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(1):51-62. [33]Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, et al. Ex vivo expansion of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in spinner flasks. Biotechnol J. 2009;4(8):1198-1209. [34]Adekogbe I, Ghanem A. Fabrication and characterization of DTBP-crosslinked chitosan scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(35):7241-7250.[35]Ma F, Zhu T, Xu F, et al. Neural stem/progenitor cells on collagen with anchored basic fibroblast growth factor as potential natural nerve conduits for facial nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:188-197.[36]Li Q, Lu J, Wang X. Propofol and remifentanil at moderate and high concentrations affect proliferation and differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(22):2002-2007. [37]Lu J, Li D, Lu K. Distribution and localization of fibroblast growth factor-8 in rat brain and nerve cells during neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(19):1455-1462. [38]Lu J, Lu K, Li D. Changes in expression and secretion patterns of fibroblast growth factor 8 and Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway molecules during murine neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(22):1688-1694.[39]Kleiderman S, Gutbier S, Ugur Tufekci K, et al. Conversion of Nonproliferating Astrocytes into Neurogenic Neural Stem Cells: Control by FGF2 and Interferon-γ. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(12):2861-2874.[40]Porseva VV, Shilkin VV, Korzina MB, et al. Peculiarities of age changes of NF200(+)-neurons in the sensory ganglia of different segmental levels after chemical deafferentation. Morfologiia. 2012;142(4):37-42.[41]Johnson MD, Glick AD, Davis BW. Immunohistochemical evaluation of Leu-7, myelin basic-protein, S100-protein, glial-fibrillary acidic-protein, and LN3 immunoreactivity in nerve sheath tumors and sarcomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988;112(2):155-160.[42]Tiainen H, Lyngstadaas SP, Ellingsen JE, et al. Ultra-porous titanium oxide scaffold with high compressive strength. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(10):2783-2792. [43]Wang Y, Wang X, Shang J, et al. Repairing the ruptured annular fibrosus by using type I collagen combined with citric acid, EDC and NHS: an in vivo study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3): 884-893.[44]Liu EY, Jung S, Yi H. Improved Protein Conjugation with Uniform, Macroporous Poly(Acrylamide-co-Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel Microspheres via EDC/NHS Chemistry. Langmuir. 2016. in press.[45]Hua J, Li Z, Xia W, et al. Preparation and properties of EDC/NHS mediated crosslinking poly (gamma-glutamic acid)/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:879-892. [46]Raghav R, Srivastava S. Immobilization strategy for enhancing sensitivity of immunosensors: L-Asparagine-AuNPs as a promising alternative of EDC-NHS activated citrate-AuNPs for antibody immobilization. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;78:396-403. [47]Park C, Vo CL, Kang T, et al. New method and characterization of self-assembled gelatin-oleic nanoparticles using a desolvation method via carbodiimide/ N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) reaction. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;89:365-373. [48]Shepherd DV, Shepherd JH, Ghose S, et al. The process of EDC-NHS Cross-linking of reconstituted collagen fibres increases collagen fibrillar order and alignment. APL Mater. 2015;3(1). pii: 014902.[49]Krishnamoorthy G, Selvakumar R, Sastry TP, et al. Experimental and theoretical studies on Gallic acid assisted EDC/NHS initiated crosslinked collagen scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;43:164-171. [50]Hao Z, Song Z, Huang J, et al. The scaffold microenvironment for stem cell based bone tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2017. in press.[51]Sadtler K, Allen BW, Estrellas K, et al. The Scaffold Immune Microenvironment: Biomaterial-Mediated Immune Polarization in Traumatic and Nontraumatic Applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016. in press.[52]Peng CH, Chuang JH, Wang ML, et al. Laminin modification subretinal bio-scaffold remodels retinal pigment epithelium-driven microenvironment in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2016;7(40):64631-64648. [53]Sadtler K, Estrellas K, Allen BW, et al. Developing a pro-regenerative biomaterial scaffold microenvironment requires T helper 2 cells. Science. 2016;352(6283):366-370.[54]Badylak SF. Tissue regeneration. A scaffold immune microenvironment. Science. 2016;352(6283):298.[55]Kim J, Ma T. Perfusion regulation of hMSC microenvironment and osteogenic differentiation in 3D scaffold. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012;109(1):252-261.[56]Vrana NE, Builles N, Kocak H, et al. EDC/NHS cross-linked collagen foams as scaffolds for artificial corneal stroma. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18(12):1527-1545.[57]Chang JY, Lin JH, Yao CH, et al. In vivo evaluation of a biodegradable EDC/NHS-cross-linked gelatin peripheral nerve guide conduit material. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7(4): 500-507.[58]Krishnamoorthy G, Sehgal PK, Mandal AB, et al. Novel collagen scaffolds prepared by using unnatural D-amino acids assisted EDC/NHS crosslinking. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(3):344-364. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [5] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [6] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [8] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [9] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [12] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [13] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [14] | Wang Kun, He Benxiang. Asperosaponin VI therapy for Achilles tendinopathy in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 211-217. |
| [15] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||