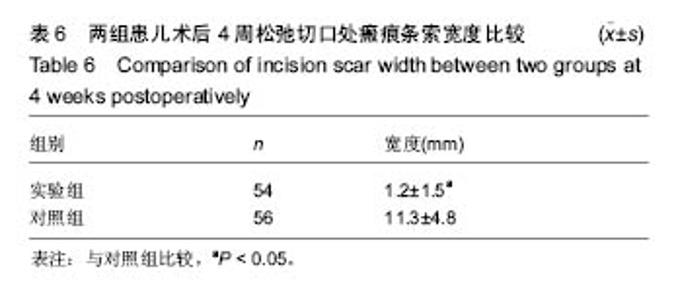
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (18): 2900-2905.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.18.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical use of gelatin sponge in palatorrhaphy
- Department of Stomatology, Hainan Provincial People’s Hospital, Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China
-
Received:2017-01-14Online:2017-06-28Published:2017-07-07 -
About author:Hu Guang-wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Hainan Provincial People’s Hospital, Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Guang-wei, Liao Tian-an, Wang Tao, Wang Hong.
share this article

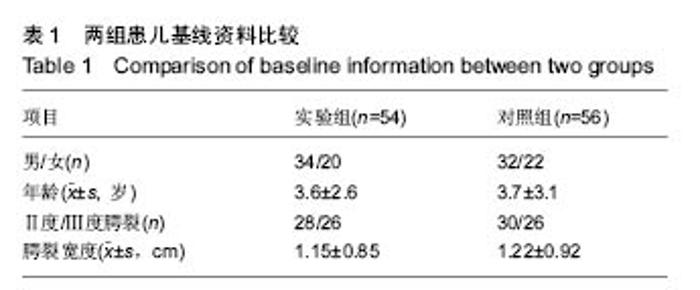
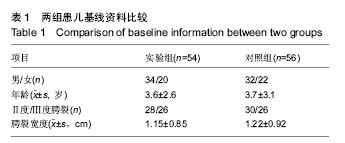
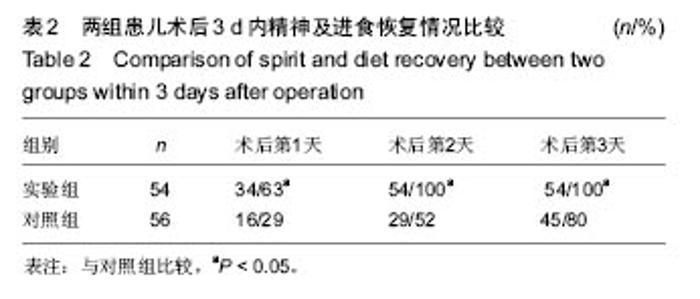
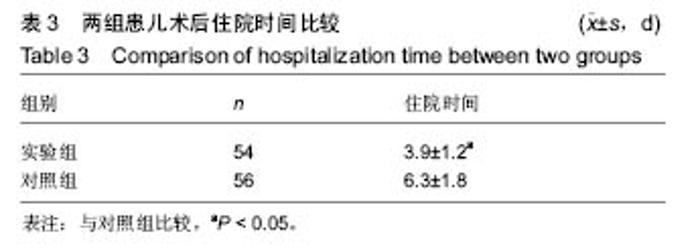
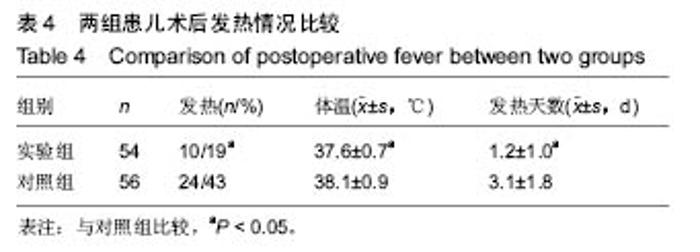
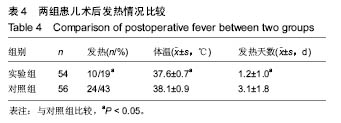
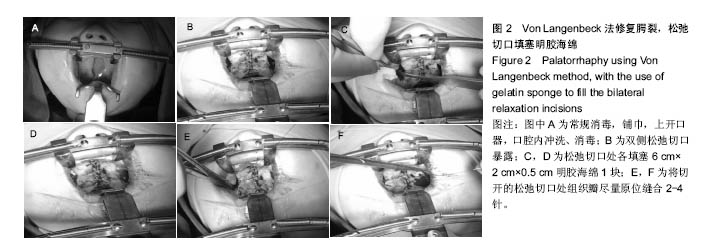
2.7 典型病例 病例1:患者女,1岁3个月,发现腭部裂开1年余于2015年5月入院。患儿出生后即被发现上腭部裂开,进食时常从鼻孔流出,开始学讲话后,一直语音不清,鼻音明显。门诊以“腭裂”收入口腔科。既往史:无特殊。患儿足月医院顺产,人工喂养,发育及智力同周围同龄幼儿,按社会正常接种计划预防接种。无特殊家族史。患儿近2周内无咳嗽、发热症状。体查:体温36.8 ℃,脉搏90次/min,呼吸20次/min,体质量12 kg。营养发育正常,双侧颌面部对称,颞下颌关节区无压痛。上唇未见裂开。张口度为3横指,张口型正常。口内见腭部自悬雍垂裂开至硬腭中份处,裂隙宽约1.4 cm。腭裂语音明显。双侧扁桃体肿大Ⅰ度。实验室检查:血常规:中性粒细胞百分率 20.3%、淋巴细胞百分率 67.9%、淋巴细胞绝对值6.63×109 L-1、单核细胞绝对值0.77×109 L-1、红细胞4.86×1012 L-1、平均红细胞体积78.2 fL、平均红细胞血红蛋白含量26.3 pg、血小板计数 398×109 L-1、血小板平均体积9.0 fL、血小板容积比 0.361%;血生化:同型半胱胺酸3.9 μmol/L、糖化血清蛋白120 μmol/L、D-3羟丁酸 0.43 mmol/L、肌酐25.0 μmol/L、总蛋白64.8 g/L、谷草转氨酶 48.0 U/L、α羟丁酸脱氢酶 219.6 U/L、磷酸肌酸激酶同工酶29.9 U/L;输血4项:乙肝表面抗体定量 14.837 mIU/mL。心电图:窦性心动过速(哭闹时)。胸片提示:双肺纹理增强。患儿完善相关检查后,遂行全麻手术,采用Von Langenbeck法修复腭裂。手术步骤:全麻插管后,面部常规消毒,铺巾,上开口器,口腔内冲洗、消毒(图2A);沿双侧硬腭的龈缘下方2 mm切开黏膜,深达骨膜深层,向后直到上颌结节,再弯向外侧,向外向后延伸切口,切开两侧裂隙缘,显露软腭肌肉,前端横过硬腭转向腭部中份,与裂缘切口重叠,切开前用肾上腺素盐水注射切口区,避免较多出血;切开硬腭后在骨膜下分离黏膜骨膜瓣,分离至硬腭骨后缘时保护腭大血管神经束,形成黏膜骨膜瓣;在腭大孔穿出的腭大血管神经周围钝性分离其外周组织,保护血管神经束。显露翼钩和腭帆张肌,稍加钝性分离,拨断翼钩,使黏膜骨膜瓣向内松解;在裂隙缘切口剥离出软腭的鼻侧黏膜瓣,在软硬腭交界处剪断腭键膜附着;缝合悬雍垂及鼻腔侧黏膜,然后缝合肌层,最后缝合口腔侧的软硬腭的黏膜层。双侧松弛切口暴露(图2B),最宽处约1.2 cm,于松弛切口处各填塞6 cm×2 cm×0.5 cm明胶海绵1块(图2C,D),利用软腭组织瓣的弹性将切开的松弛切口处组织瓣尽量原位缝合2-4针(图2E,F),从而消除了骨裸露创面,腭部瘢痕条索的形成,并避免了明胶海绵脱落的风险。患儿术后第1天体温平稳,6 h后精神逐渐恢复,并开始进流质饮食,未出现恶心症状,口腔内未见活动性渗血。1 d后精神基本恢复正常,进食增加,下床自由活动,给予抗炎2 d,于术后第3天安全出院。 "
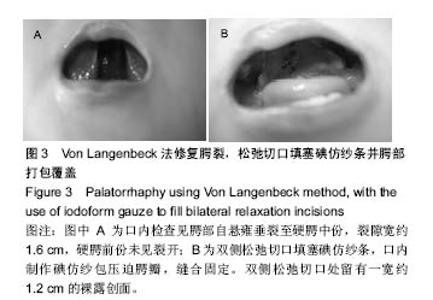
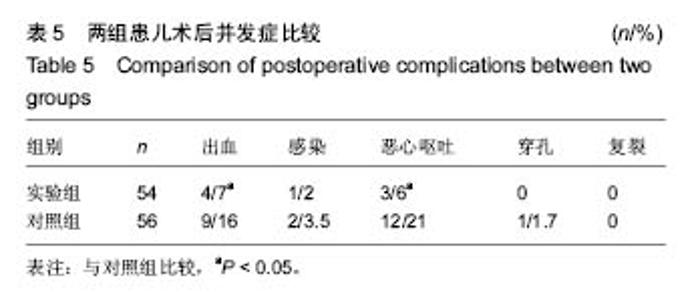
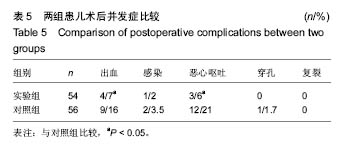
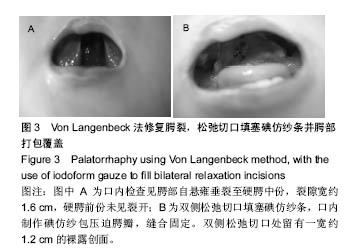
病例2:患者女,1岁6个月,发现腭部裂开1年余于2010年8月入院。患儿出生后即被发现上腭部裂开,进食时常从鼻孔流出,开始学讲话后,一直语音不清。门诊以“腭裂”收入口腔科。无特殊既往史、个人史、家族史。患儿近2周内无咳嗽、发热症状。体查:体温36.5 ℃,脉搏78次/min,呼吸20次/min,体质量13 kg。口内检查见腭部自悬雍垂裂至硬腭中份,裂隙宽约1.6 cm,硬腭前份未见裂开(图3A)。腭裂语音明显。舌颊黏膜未见明显异常。双侧扁桃体肿大Ⅰ度。实验室检查:血常规:白细胞10.49×109 L-1、中性粒细胞百分率28.5%、淋巴细胞百分率55.5%、淋巴细胞绝对值5.82×109 L-1、单核细胞绝对值0.90×109 L-1、嗜酸性粒细胞绝对值0.76×109 L-1、红细胞4.85×1012 L-1、血小板计数391×109 L-1、大型血小板比率0.106、血小板平均体积8.4 fL、血小板体积分布宽度8.5%、血小板容积比0.330%;血生化:钠135.1 mmol/L、总二氧化碳21.1 mmol/L、肌酐20.0 μmol/L、视黄醇结合蛋白22.72 mg/L、胱抑素C 0.54 mg/L、总胆汁酸35.40 μmol/L、谷草转氨酶36.7 U/L、前白蛋白163.00 mg/L、α羟丁酸脱氢酶239.9 U/L;输血4项:乙肝E抗体定量0.070 PEI U/mL、乙型肝炎病毒前S1抗原阴性(-)S/CO值;凝血4项:活化部分凝血活酶时间41.1 s;胸片、心电图正常。患儿完善相关检查后,遂行全麻手术,采用Von Langenbeck法修复腭裂(手术步骤同病例1)。于双侧松弛切口填塞碘仿纱条,口内制作碘仿纱包压迫腭瓣,缝合固定。患儿术后3 d出现发热,最高达38.9 ℃,精神较差,于第2天开始进极少许流质饮食,伴有恶心,口内分泌物多,口腔内卫生较差,且难以清洗。患儿拆除口内腭部碘仿纱包后,进食量才明显增加,精神逐渐好转。患儿于术后第5天拔除松弛切口碘仿纱条时,出现活动性渗血,患儿非常紧张,哭闹明显,极不配合,给予局部压迫止血,并给予全身止血药物后渗血症状逐渐消失。双侧松弛切口处留有一宽约 1.2 cm的裸露创面(图3B),延长了伤口愈合时间,患儿于术后第7天安全出院。"
| [1]邱蔚六.口腔颌面外科学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008: 414.[2]Zhang M, Zhang X, Zheng C. Application of buccal fat pads in pack palate relaxing incisions on maxillary growth: a clinical study. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(2):2689-2692.[3]Barnard J, Millner R. A review of topical hemostatic agents for use in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88(4):1377-1383.[4]王勇,陆伟.体内可吸收止血材料研究及临床应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2009,26(4):922-926.[5]吴冰,叶茂昌,李志来,等.腭裂松弛切口碘仿纱条填塞的临床观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2003,19(10):607-608.[6]王力敏,殷卫红,刘楠.腭裂手术的回顾与体会[J].口腔医学, 2001, 9(3):135-136.[7]阳爱民,陈红.腭裂松弛切口处理方法的探讨[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2004,18(3):281-282.[8]傅豫川.唇腭裂整复术的现代概念[J].口腔医学研究, 2002,18(4): 217-221.[9]董智.吸收明胶海绵中明胶交联度的测定[J].药物分析杂志, 2010,30(3):511-512.[10]Kobatake K, Mita K, Kato M. Effect on hemostasis of an absorbable hemostatic gelatin sponge after transrectal prostate needle biopsy. Int Braz J Urol. 2015;41(2):337-343.[11]Donaldson MR, Weber LA. Gelatin sponge to decrease pedicle bleeding after paramedian forehead flap. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41(4):532-533. [12]Toda A, Sawada K, Osuga K, et al. Efficacies of uterine artery embolization for symptomatic uterine fibroids using gelatin sponge: a single-center experience and literature review. Int J Womens Health. 2016;8:397-404.[13]Karim AB, Lindsey S, Bovino B, et al.Oral Surgical Procedures Performed Safely in Patients With Head and Neck Arteriovenous Malformations: A Retrospective Case Series of 12 Patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(2):255.e1-8.[14]Shimohira M, Nagai K, Hashizume T, et al. Preoperative transarterial embolization using gelatin sponge for hypervascular bone and soft tissue tumors in the pelvis or extremities. Acta Radiol. 2016;57(4):457-462.[15]Toda A, Sawada K, Osuga K, et al. Efficacies of uterine artery embolization for symptomatic uterine fibroids using gelatin sponge: a single-center experience and literature review. Int J Womens Health. 2016;8:397-404.[16]Dong Y, Liu W, Lei Y, et al. Effect of gelatin sponge with colloid silver on bone healing in infected cranial defects. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 1):371-377.[17]Liang J, Liu H, Huang X, et al. Using tranexamic acid soaked absorbable gelatin sponge following complex posterior lumbar spine surgery: A randomized control trial. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;147:110-114.[18]Li Y, Yao M, Wang X, et al. Effects of gelatin sponge combined with moist wound-healing nursing intervention in the treatment of phase III bedsore. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(6):2213-2216.[19]Igai H, Yamamoto Y, Chang SS, et al. Tracheal cartilage regeneration by slow release of basic fibroblast growth factor from a gelatin sponge. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 134(1):170-175.[20]刘宿,牛金柱,葛衡江,等.三种止血材料止血活性的体外实验研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(12):732-735.[21]黄旭,石冰,宋庆高,等.硬腭裸露骨面对上颌骨及牙弓生长发育的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2005,40(3):207-209.[22]Liao YF, Lee YH, Wang R, et al. Vomer flap for hard palate repair is related to favorable maxillary growth in unilateral cleft lip and palate. Clin Oral Investig. 2014;18(4):1269-1276.[23]Mohan S, Kankariya H, Harjani B. The use of the buccal fat pad for reconstruction of oral defects: review of the literature and report of cases. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11(2):128-131.[24]Gregory.R.D.Evans.整形外科手术学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001:429-439.[25]Sommerlad BC. A technique for cleft palate repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112(6):1542-1548.[26]张红闯,万延俊,张扬,等. Sommerlad腭帆提肌重建联合带蒂颊脂垫瓣在完全性腭裂修复中的应用[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志,2015,11(4):252-254.[27]刘慧,龚忠诚,扈梅,等. 腭裂松弛切口不同处理方法的临床观察比较[J].新疆医科大学学报,2013,36(9):1297-1300.[28]廖圣恺,徐涛,高廷益,等. 腭裂术后松弛切口两种不同处理方法临床效果比较[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(1):35-37.[29]王洪涛,孙莲芬,张祖斌. 腭裂创面不同处理方法的比较[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2007,23(10):614-615.[30]Cenni E, Ciapetti G, Stea S, et al. Biocompatibility and performance in vitro of a hemostatic gelatin sponge. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2000;11(7):685-699.[31]何平. 三种鼻腔填塞物在老年鼻出血患者中的应用[J]. 西部医学,2011,23(8):1522-1523.[32]池朝玲,张军,庞晓纲,等. 腭裂术后松弛切口不同处理方法的观察[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志,2008,22(3):242-243.[33]刘军平,孙明亮,杜语, 等. 腭裂术后松弛切口两种不同处理方法的比较[J]. 西部医学,2008,20(2):368-369.[34]丰景,胡升.腭裂松弛切口填塞明胶海绵80例的临床观察[J].口腔医学,2007,27(10):556-558. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||