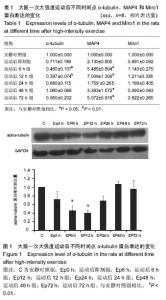
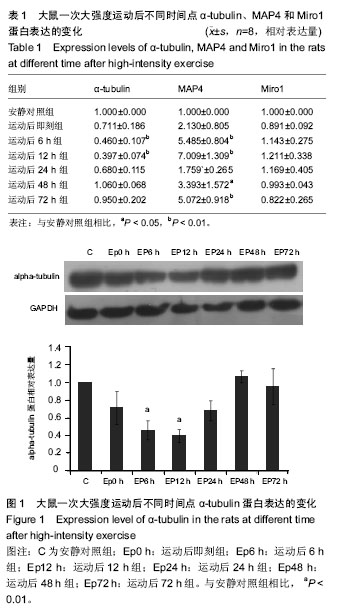
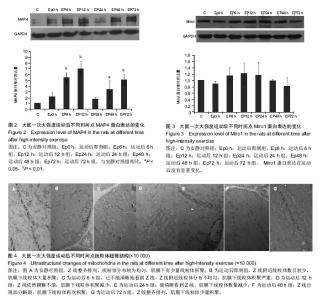
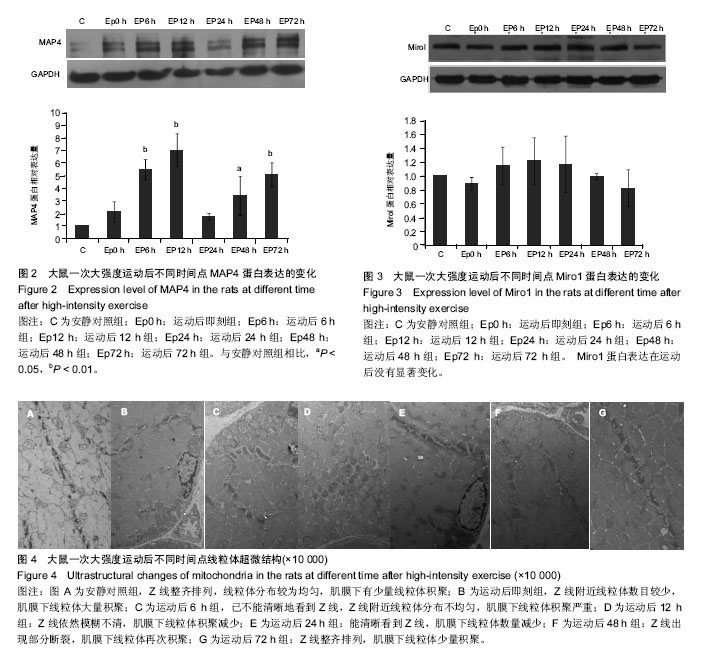
| [1] Guzun R,Varikmaa MK,Granillo MG,et al.Mitochondria-cytoskeleton interaction: Distribution of β-tubulin in cardiomyocytes and HL-1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1807: 458-469.[2] Cai Q, Sheng ZH. Mitochondrial transport and docking in axons. Exp Neurol. 2009;218(2): 257-267.[3] Maldonado EN, Patnaik J, Mullins MR, et al. Free tubulin modulates mitochondrial membrane potential in cancer cells. Cancer Res.2010;70:10192-10201.[4] Otera H, Mihara K. Molecular mechanisms and physiologic functions of mitochondrial dynamics. J Biochem. 2011; 149(3): 241-251.[5] Hu JY, Chu ZG, Han J, et al. The p38/MAPK pathway regulates microtubule polymerization through phosphorylation of MAP4 and Op18 in hypoxic cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010; 67: 321-323.[6] Nogales E. Structural insight into microtubule function.Annu Rev BiophysBiomolStruct. 2001; 30: 397-420.[7] Wang Zai, Cui Ju, Wong WaiMan, et al. Kif5b controls the localization of myofibril components for their assembly and linkage to the myotendinous junctions. Development. 2013; 140: 617-626.[8] Fransson Å, Ruusala A, Aspenström P. A tyical Rho GTPases have roles in mitochondrial homestasis and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 6495-6502.[9] Glater EE, Megeath LJ, Stowers RS, et al. Axonal transport of mitochondria respires Milton to recruit kinesin heavy chain and is light chain independent. J Cell Biol. 2006;173(4): 545-557.[10] Fransson Å, Ruusala A, Aspenström P. The atypical Rho GTPases Miro-1 and Miro-2 have essential roles in mitochondrial trafficking. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344(2): 500-510.[11] Wang X, Winter D, Ashrafi G, et al. PINK1 and parkin marget Miro for phosphorylation and degradation to arrest mitochondrial motility. Cell. 2011;147(11): 893-906.[12] 刘晓然,李俊平,王蕴红,等.大负荷运动及针刺干预对骨骼肌微管蛋白的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(33): 4949-4956.[13] 周丽娟, 韩磊, 李力. 细胞骨架与人滋养细胞迁移关系的研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2015, 40(7): 599-602.[14] Boudriau S, Vincent M, Cote CH, et al. Cytoskeletal structure of skeletal muscle: identification of an intricate exosarcomeric microtubule lattice in slow- and fast- twitch muscle fibers. J histochem & cytochem.1993; 41(7): 1013-1021.[15] Heins DC. Ischemia induces early changes to cytoskeletal and contractile proteins in diseased human myocardium. J Thorac Cardiovas Surg.1995; 110(1): 89.[16] Sakurai T, Fujita Y, Ohto E, et al. The decrease of the cytoskeleton tubulin follows the decrease of the associating molecular chaperone αB-crystallin in unloaded soleus muscle atrophy without stretch. FASEB J. 2005; 19(9):1199-1201.[17] 张庆, 张慧琳. MAP4K1与其接头蛋白的相互作用[J]. 中南大学学报:医学版, 2015,40(3): 326-335.[18] Cheng GM, Takahashi M, Shunmugavel A, et al. Basis for MAP4dephosporylation-related microtubule network densification in pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy. J Bio Chem.2010;49(285):38125-38140.[19] 褚志刚. 微管相关蛋白4在缺氧心肌细胞线粒体通透性转换孔开放和凋亡中的作用及机制研究[D]. 第三军医大学博士学位论文, 2010.[20] 金其贯,刘霞,李淑艳,等. 反复离心运动对大鼠骨骼肌损伤和蛋白质降解机制的影响[J].体育科学, 2010, 30(6): 76-80.[21] 于滢. 一次大负荷运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体分布和功能影响及针刺干预作用[D]. 北京体育大学博士学位论文,2015.[22] Gamboa JL, Andrade FH. Mitochondrial content and distribution changes specific to mouse diaphragm after chronic normobaric hypoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 ;298(3):R575-583. [23] 于晓伟,解玉珍,顾博雅等. 有氧运动调节驱动蛋白改善AD模型皮层线粒体轴突转运[J].北京体育大学学报,2016,39(6): 63-68.[24] Morlino G, Barreiro O, Baixauli F, et al. Miro-1 links mitochondria and microtubule dynein motors to control lymphocyte migration and polarity. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34(8): 1412-1426.[25] Korobova F, Gauvin TJ, Higgs HN. A role for myosin 2mammalian mitochondrial fission. Curr Biol.2014;17(24): 409-414.[26] Glater EE, Megeath LJ, Stowers RS, et al. Axonal transport of mitochondria requires milton to recruit kinesin heavy chain and is light chain independent. J Cell Biol. 2006; 173(4):545-57.[27] Leidel CP. Measuring molecular motor forces to probe transport regulation in vivo. 2013;103(3):492-500.[28] 刘慧君,翟克敏,赵斐, . 线粒体移动相关基因 miro1 在急性运动中的表达特征[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2010 (2): 173-176.[29] Macaskill AF, Rinholm JE, Twelvetrees AE, et al. Miro1 is a calcium sensor for glutamate receptor-dependent localization of mitochondria at synapses. Neuron. 2009;61(4):541-555. |