Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (5): 760-765.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.05.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Endometrial stromal stem cells: in vitro isolation, culture and biological features
Bi Yu-hu, Teng Jun-ru
- Third People’s Hospital of Jinan City, Jinan 250132, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2017-02-18Published:2017-03-20 -
About author:Bi Yu-hu, Attending physician, Third People’s Hospital of Jinan City, Jinan 250132, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bi Yu-hu, Teng Jun-ru. Endometrial stromal stem cells: in vitro isolation, culture and biological features[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(5): 760-765.
share this article
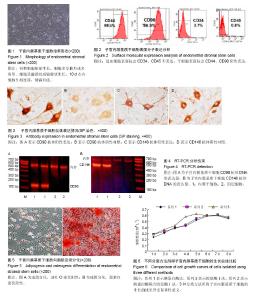
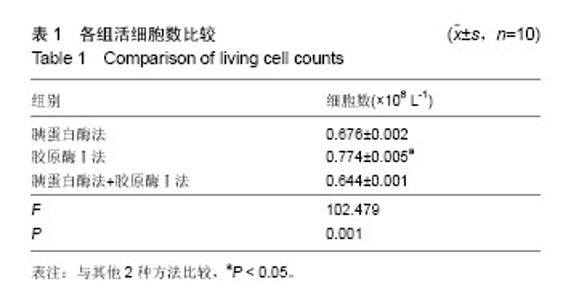
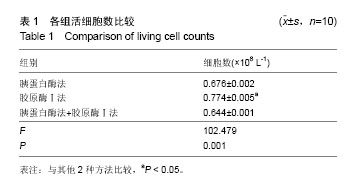
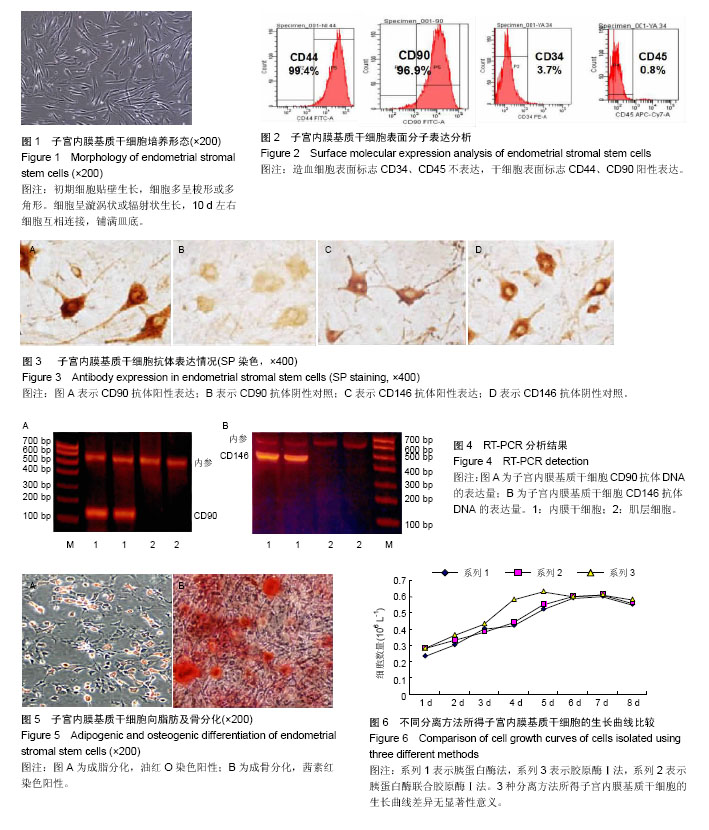
2.1 子宫内膜基质干细胞生长情况 接种24-48 h后即可看到少量贴壁细胞,细胞形态不均一。培养三至四天细胞逐渐汇合形成大小不一的细胞集落,7 d时细胞集落明显增大,细胞多呈梭形或多角形。细胞呈漩涡状或辐射状生长,10 d左右细胞互相连接,铺满皿底(图1)。传代培养细胞生长方式与原代细胞相似,第2代细胞呈均一的成纤维状,融合后呈典型的极性。3种方法培养比较:胰蛋白酶法消化时间短,活细胞数量较少,贴壁时间较长,杂质多,胶原酶Ⅰ法消化时间长,但活细胞数量较多,贴壁时间较短,杂质少,胰蛋白酶联合胶原酶Ⅰ法介于两者之间。可见胶原酶Ⅰ法分离培养子宫内膜基质干细胞具有一定优势。 2.2 子宫内膜基质干细胞鉴定 2.2.1 流式细胞仪分析 流式细胞仪检测发现子宫内膜基质干细胞阳性表达干细胞表面标志CD44、CD90,不表达造血细胞表面标志CD34、CD45(图2)。 2.2.2 免疫组化分析 显微镜观察结果显示,CD90和CD146抗体主要表现为细胞核染色,部分为胞浆染色。染色阳性结果呈现淡黄色至深棕色,显色强度不明显为阴性(图3)。 2.2.3 RT-PCR分析结果 在紫外线投射仪下观察电泳情况,分别比较目的基因CD90和CD146 mRNA的表达量[12],标本选取子宫内膜与子宫肌层交界部位,以相近的子宫肌层组织作为对照,目的基因CD90、CD146在子宫肌层不表达,但是CD90的DNA在150 bp左右、基因CD146的DNA在500 bp左右高表达(图4)。 2.2.4 成骨成脂分化能力 子宫内膜基质干细胞成脂诱导2周进行油红O染色,可见红色脂滴(图5A);成骨诱导2周进行茜素红染色,可见钙盐被染为红色(图5B)。 2.3 不同分离方法下子宫内膜基质干细胞的生长曲线 3种分离方法所得单细胞悬液经细胞培养后,通过采用细胞计数法对第2代细胞进行计数,所得生长曲线均表现为S型,存在一定的滞留期、对数期和平台期,各组比较差异无显著性意义(图6)。 2.4 不同分离方法获得活细胞数比较 3种方法所获得活细胞数比较差异有显著性意义。胶原酶Ⅰ法所获得的活细胞数显著高于胰蛋白酶法和胰蛋白酶联合胶原酶Ⅰ法(P < 0.05,表1)。"
| [1] 高红艳,陈继明,何援利,等.人子宫内膜基质细胞的分离纯化和体外培养方法研究[J].重庆医学,2014,10(34):4634-4636.[2] Deane JA, Gualano RC, Gargett CE, et al. Regenerating endometrium from stem/progenitor cells: Is it abnormal in endometriosis, Asherman's syndrome and infertility? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;25(3):193-200. [3] Ding L,Li X,Sun H, et al.Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on collagen scaffolds for the functional regeneration of injured rat uterus.Biomaterials. 2014;35(18):4888-4900.[4] Indumathi S,Harikrishnan R,Rajkumar JS,et al.Prospective biomarkers of stem cells of human endometrium and fallopian tube compared with bone marrow. Cell Tissue Res. 2013; 352(3):537-549.[5] Jing Z,Qiong Z,Yonggang W, et al. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve regeneration of thin endometrium in rat. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(2):587-594.[6] Cervelló I, Mas A, Gil-Sanchis C, et al. Somatic stem cells in the human endometrium.Semin Reprod Med. 2013;31(1): 69-76.[7] Yang XY, Wang W, Li X, et al.In vitro hepatic differentiation of human endometrial stromal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 2014;50(2):162-170.[8] 张继雯.人类子宫内膜肿瘤干细胞的研究进展[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2013,40(4):327-330.[9] Gil-Sanchis C, Cervelló I, Mas A, et al. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5) as a putative human endometrial stem cell marker. Mol Hum Reprod. 2013;19(7/8):407-414.[10] Apostolou G, Apostolou N, Biteli M, et al. Utility of Ki-67, p53, Bcl-2, and Cox-2 biomarkers for low-grade endometrial cancer and disordered proliferative/benign hyperplastic endometrium by imprint cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2014;42(2):134-142.[11] Chen YZ,Wang JH, Yan J, et al. Increased expression of the adult stem cell marker Musashi-1 in the ectopic endometrium of adenomyosis does not correlate with serum estradiol and progesterone levels. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014; 173:88-93.[12] Bures N, Nelson G, Duan Q, et al. Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the endometrium: Clinicopathologic and molecular characteristics. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2013;32(6): 566-575.[13] Mingels MJ, Geels YP, Pijnenborg JM, et al. Histopathologic assessment of the entire endometrium in asymptomatic women. Human Pathol.2013;44(10):2293-2301.[14] 朱明,肖南,黄宏,等.间充质干细胞治疗皮肤创伤的研究进展[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2015,3(6):911-918.[15] 郭珊珊,沈志森,陆达锴,等.干细胞向骨骼肌细胞的诱导分化及其在治疗骨骼肌病变中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2015, 4(1):124-131.[16] Ayd?n A, Duruksu G, Erman G, et al. Neurogenic differentiation capacity of subacromial bursal tissue - Derived stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(1):151-158.[17] Baulcha JE.干细胞释放的微囊泡有望更安全地治疗大脑放射损伤[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2016,11(3):22-23.[18] 于文竹.人胚胎干细胞向子宫内膜上皮样细胞诱导分化的相关研究[D].郑州大学, 2014. [19] Bae D, Moon SH, Park BG, et al. Nanotopographical control for maintaining undifferentiated human embryonic stem cell colonies in feeder free conditions.Biomaterials. 2014;35(3):916-928.[20] Wu JC, Tzanakakis ES. Deconstructing stem cell population heterogeneity: Single-cell analysis and modeling approaches. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(7):1047-1062.[21] Arefeh G, Hossein H, Abbas P, et al. Galactosylated collagen matrix enhanced in vitro maturation of human embryonic stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Biotechnol Lett.2014; 36(5): 1095-1106.[22] Sanjuan-Pla A, Macaulay IC, Jensen CT, et al. Platelet-biased stem cells reside at the apex of the haematopoietic stem-cell hierarchy.Nature. 2013;502(7470):232-236.[23] Kajihara T, Brosens J, Ishihara O, et al.The role of FOXO1 in the decidual transformation of the endometrium and early pregnancy. Med Mol Morphol. 2013;46(2):61-68.[24] Parra-Herran CE, Yuan L, Nucci MR, et al. Targeted development of specific biomarkers of endometrial stromal cell differentiation using bioinformatics: The IFITM1 model. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(4):569-579.[25] Li J, Hansen KC, Zhang Y, et al. Rejuvenation of chondrogenic potential in a young stem cell microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2014;35(2):642-653.[26] Emmert MY, Wolint P, Wickboldt N, et al. Human stem cell-based three-dimensional microtissues for advanced cardiac cell therapies.Biomaterials. 2013;34(27):6339-6354.[27] Samborski A, Graf A, Krebs S, et al.Transcriptome changes in the porcine endometrium during the preattachment phase. Biol Reprod. 2013;89(6):134-134.[28] Parra-Herran CE, Monte NM, Mutter GL. Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia with secretory differentiation: Diagnostic features and underlying mechanisms. Mod Pathol. 2013;26(6):868-873.[29] Thiruchelvam U, Dransfield I, Saunders PT, et al. The importance of the macrophage within the human endometrium. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;93(2):217-225.[30] 周华,宋丽娜,张敏.人子宫内膜干细胞体外分离、培养及鉴定[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2014,17(8):1907-1908.[31] Sakr S, Naqvi H, Komm B, et al. Endometriosis impairs bone marrow-derived stem cell recruitment to the uterus whereas bazedoxifene treatment leads to endometriosis regression and improved uterine stem cell engraftment. Endocrinology. 2014;155(4):1489-1497.[32] 陈岩,李栋,张哲,等. 人脐带间充质干细胞对大鼠子宫内膜异位症病灶神经纤维的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2013,51(3): 48-51.[33] Osuga Y, Koga K, Tsutsumi O, et al. Stem cell factor (SCF) concentrations in peritoneal fluid of women with or without endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2000;44(4):231-235. [34] León M, Vaccaro H, Alcázar JL, et al. Extended transvaginal sonography in deep infiltrating endometriosis: Use of bowel preparation and an acoustic window with intravaginal gel: Preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33(2):315-321.[35] 蒋智.人子宫内膜干细胞通过旁分泌作用保护心肌并促进心肌再生改善大鼠心梗后心功能[D].浙江大学, 2013.[36] Jeschke U, Hutter S, Heublein S, et al. Expression and function of galectins in the endometrium and at the human feto-maternal interface. Placenta. 2013;34(10):863-872.[37] 严琰,东健沣,桑运霞,等.经血源子宫内膜干细胞培养、鉴定及体外分化潜能的研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2014,22(7):892- 899.[38] 张倩媚,马颖.子宫内膜干细胞体外诱导及定性分化的研究[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2013, 42(7):770-771.[39] Adammek M, Greve B, Kässens N, et al. MicroRNA miR-145 inhibits proliferation, invasiveness, and stem cell phenotype of an in vitro endometriosis model by targeting multiple cytoskeletal elements and pluripotency factors. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(5):1346-1355. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [8] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [9] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [10] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [11] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [12] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [13] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [14] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [15] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||