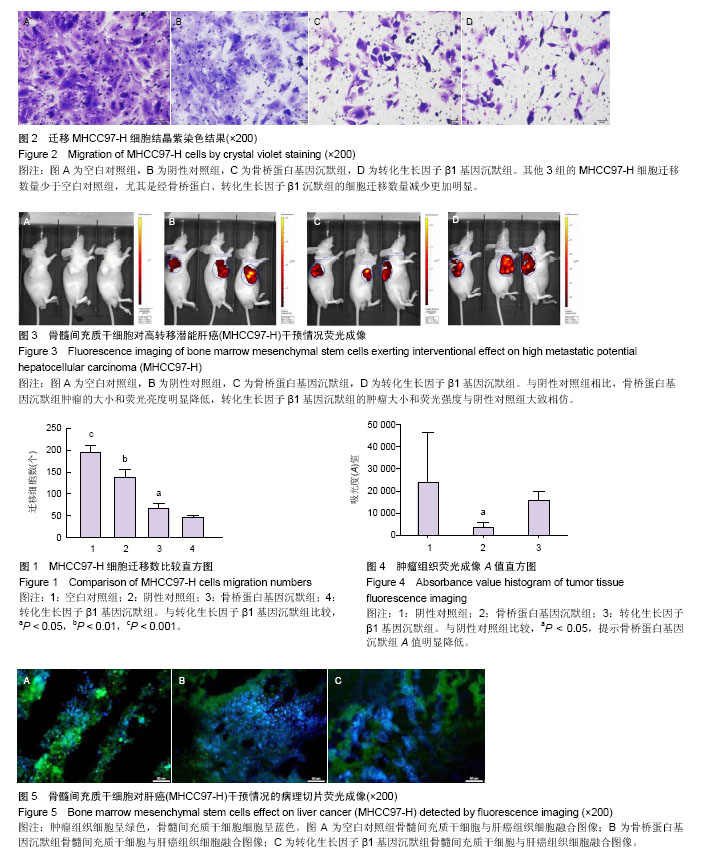
| [1] 郭晓钟,刘旭,王迪,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植对不同病因肝硬化的疗效研究[J]. 中华消化杂志,2011,31(1):53-54.[2] Vainshtein JM, Kabarriti R, Mehta KJ, et al. Bone marrow-derived stromal cell therapy in cirrhosis: clinical evidence, cellular mechanisms, and implications for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014,89(4):786-803. [3] 李天然,卢光明,宋斌,等. hMSC对高低转移潜能肝癌细胞影响的实验研究[J].胃肠病学与肝病学杂志,2014,23(9):1056-1060.[4] Li G, Zhang H, Zhao Q, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor angiogenesis via the action of transforming growth factor β1. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(2): 1089-1094.[5] Liu GK,Fan XY,Tang M, et al. Osteopontin induces autophagy to promote chemo-resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;383(2): 171-182.[6] 舒宏,康晓楠,刘银坤.肝癌转移、复发预测的蛋白质分子标志物[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2010,18(13):1350-1355.[7] 徐冰,姚明. 国内肝癌转移动物模型研究概况[J].中国医学工程, 2012,20(5):184-187.[8] 汤钊猷. 转移复发一肝癌研究的重中之重[J].中华消化外科杂志, 2007,6(1):2.[9] Tian MM, Cheng H, Wang ZQ, et al. Phosphoproteomic Analysis of the Highly-Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line, MHCC97-H. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(2): 4209-4225. [10] Lin WF, Zhong MF, Liang SF,et al. Emodin inhibits migration and invasion of MHCC-97H human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp Ther Med. 2016;l(12):3369-3374.[11] Wang G,Chen S,Zhao C,et al. Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles of OPN signalling pathway in four kinds of liver diseases. J of Genet. 2016;95(3):741-750.[12] Wang G, Li, X, Chen S, et al. Expression profiles uncover the correlation of OPN signaling pathways with rat liver regeneration at cellular level. Cell Biol Int.2015;39(11): 1329-1340.[13] 李天然,蔡立杰,赵绍宏,等.骨桥蛋白转染骨髓间充质干细胞对高转移潜能肝癌细胞的影响[J].胃肠病学与肝病学杂志,2015, 24(9):1057-1061.[14] 李天然,杜湘珂,宋斌,等. 转化生长因子β1转染hMSC对MHCC97-H影响的实验研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2013, 22(7):615-619.[15] 刘昆鹏,张炳远,卢云,等.Transwell侵袭实验测定M受体对胆管癌细胞侵袭的影响[J].国际外科学杂志, 2011,38(5):298-301.[16] Inoue M, Shinohara ML. Intracellular osteopontin (iOPN) and immunity. Immunol Res 2011;49:160-172.[17] Xie H, Song J, Du R et al. Prognostic significance of osteopontin in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis 2007;39:67-172.[18] Sodek J, Zhu B, Huynh MH, et al. Novel functions of the matricellular proteins osteopontin and osteonectin/SPARC. Connect Tissue Res. 2002;43:308-419.[19] Rangaswami H, Bulbule A, Kundu C. Nuclear factor-inducing kinase plays a crucial role in osteopontin-induced MAPK/I kappa B alpha kinase-dependent nuclear factor kappa B-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-9 activation.J Biol Chem.2004;279(37):921-935.[20] Huang H, Zhang XF, Zhou HJ, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of osteopontin and caspase-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after curative resection. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1314-1319.[21] Phillips RJ, Helbig KJ, Van der Hoek KH, et al. Osteopontin increases hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in a CD44 dependant manner. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18: 3389- 3399. [22] Li TR, Zhao S, Song B, et al. Effects of transforming growth factor β-1 infected human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on high- and low-metastatic potential hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20(1):56. [23] Scaggiante B, Kazemi M, Pozzato G, et al. Novel hepatocellular carcinoma molecules with prognostic and therapeutic potentials. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(5): 1268-1288. [24] Lee D, Chung YH, Kim JA, et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 overexpression is closely related to invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2012;82:11-18. [25] Okumoto K, Hattori E, Tamura K, et al. Possible contribution of circulating transforming growth factor-beta1 to immunity and prognosis in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2004;24:21-28. [26] Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Dituri F, et al. Down-regulation of connective tissue growth factor by inhibition of transforming growth factor beta blocks the tumor-stroma cross-talk and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;51:523-534. [27] Giannelli G, Bergamini C, Fransvea E, et al. Laminin-5 with transforming growth factor-beta1 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1375-1383. [28] van Zijl F, Mair M, Csiszar A, et al. Hepatic tumor-stroma crosstalk guides epithelial to mesenchymal transition at the tumor edge. Oncogene. 2009;28:4022-4033. [29] Mima K, Hayashi H, Kuroki H, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression profiles as a prognostic factor for disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical significance of transforming growth factor-β signaling. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:149-154. |