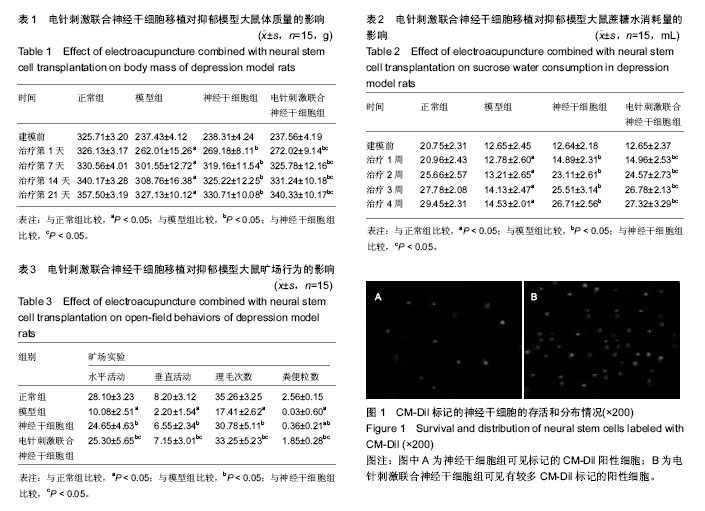
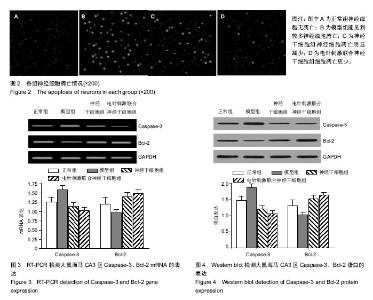
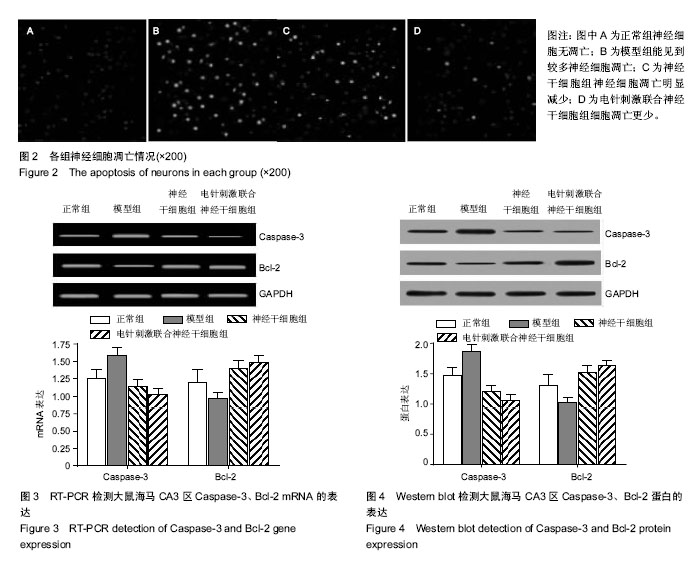
| [1] 黄洁云.抑郁症的发病机制与治疗进展[J].中国疗养医学,2013, 22(3):233-235.[2] 毛榕榕,田孟,徐林.抑郁的大脑:抑郁症的神经生物学研究和抗抑郁新药研发[J].自然杂志,2009,31(3):148-152.[3] Yu S, Holsboer F, Almeida OF. Neuronal actions of glucocorticoids: focus on depression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;108(3-5):300-309.[4] Duman RS, Kehne JH. Depression.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007;6(3):161-162.[5] 胡随瑜,王素娥,张春虎.抑郁症临床症状分层与中医辨证分型的关系[J].中西医结合学报,2011,9(9):933-936.[6] Han Y, Khodr CE, Sapru MK, et al. A microRNA embedded AAV α-synuclein gene silencing vector for dopaminergic neurons.Brain Res. 2011;1386:15-24.[7] Kupfer DJ, Frank E, Phillips ML. Major depressive disorder: new clinical, neurobiological, and treatment perspectives. Lancet. 2012;379(9820):1045-1055.[8] Alexopoulos GS, Murphy CF, Gunning-Dixon FM, et al. Serotonin transporter polymorphisms, microstructural white matter abnormalities and remission of geriatric depression. J Affect Disord. 2009;119(1-3):132-141.[9] 崔青,孙丽亚,肖红,等.抑郁症患者神经内分泌节律变化的对照研究[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2010,19(1):33-35.[10] 胡大吉,丁桂霞,李有田.细胞因子异常与抑郁症的发生[J].中华中医药学刊,2007,25(3):516-517.[11] 张园,刘学军.海马神经元凋亡与抑郁症[J].国际精神学杂志, 2014,41(3):153-155.[12] Drevets WC, Price JL, Furey ML. Brain structural and functional abnormalities in mood disorders: implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Brain Struct Funct. 2008; 213(1-2):93-118.[13] Dygalo NN, Kalinina TS, Bulygina VV, et al. Increased expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL in the brain is associated with resilience to stress-induced depression-like behavior. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(5):767-776.[14] Shishkina GT, Kalinina TS, Berezova IV, et al. Stress-induced activation of the brainstem Bcl-xL gene expression in rats treated with fluoxetine: correlations with serotonin metabolism and depressive-like behavior. Neuropharmacology. 2012; 62(1):177-183.[15] Kubera M, Obuchowicz E, Goehler L, et al. In animal models, psychosocial stress-induced (neuro)inflammation, apoptosis and reduced neurogenesis are associated to the onset of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011;35(3):744-759.[16] 户丽,梁佳,金树英,等.针刺治疗抑郁症作用机制近5年研究进展[J].针刺研究,2013,38(3):253-258.[17] 孙丽荚,武燕峰.中医药治疗抑郁症研究进展[J].中医药报,2011, 39(6):107-108.[18] 戴巍,李卫东,卢峻,等.电针对慢性应激抑郁大鼠海马神经元凋亡及JNK信号转导通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2010,35(5):330-334.[19] 梁佳,李卫东,吴元坪,等.电针对慢性应激抑郁模型大鼠海马神经元凋亡与再生的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(4): 947-950.[20] 卢金花,姜劲峰,王玲玲,等.电针治疗抑郁模型大鼠快速起效海马区BDNF-TrkB机制研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2011,27(5):51-54.[21] 孙健,刘健华,王谦,等.电针对抑郁症大鼠海马组织AC-cAMP- PKA信号通路的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(24): 3672-3674.[22] 刁波,刘琴,王丽萍,张宜.叶酸联合成体神经干细胞治疗创伤性脑损伤大鼠的实验[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(7):48-55.[23] 金树英,户丽,包伍叶,等.针刺对慢性应激抑郁大鼠血清和脑炎性细胞因子的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2014,30(5):57-60.[24] 乌吉斯古冷,佟海英,斯日古楞,等. 槟榔十三味丸(高尤-13)对慢性应激抑郁大鼠行为学及海马神经元凋亡的影响[J].中医学报, 2014,29(6):759-762.[25] 张露芬.实验针灸学[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2010.[26] 刘家言,万丹丹.人参皂苷对慢性应激抑郁模型小鼠的抗抑郁样作用[J].医药前言,2015,5(26):111-112.[27] 程瑞凤,华冰,景晶,等.甘草总黄酮抗大鼠应激抑郁行为作用及对海马脑区神经细胞凋亡调控相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2014,30(2):69-72.[28] 董爱国,赵丽丽,李海红.BDNF在抑郁症发病机制中的作用及其抗抑郁作用机制的研究进展[J].中国医疗前沿, 2011, 6(6):16-18.[29] 包伍叶,张敏,杨秀岩,等.电针对慢性应激抑郁模型大鼠海马神经干细胞巢蛋白的影响[J].中国基层医药.2014,21(4):481-483.[30] Kosten TA, Galloway MP, Duman RS, et al. Repeated unpredictable stress and antidepressants differentially regulate expression of the bcl-2 family of apoptotic genes in rat cortical, hippocampal, and limbic brain structures. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33(7):1545-1558.[31] Bachis A, Cruz MI, Nosheny RL, et al. Chronic unpredictable stress promotes neuronal apoptosis in the cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 2008;442(2):104-108.[32] van Breukelen F, Krumschnabel G, Podrabsky JE.Vertebrate cell death in energy-limited conditions and how to avoid it: what we might learn from mammalian hibernators and other stress-tolerant vertebrates. Apoptosis. 2010;15(3):386-399.[33] 赵珂,金季玲.滋水清肝饮对围绝经期抑郁症模型大鼠海马神经元细胞凋亡相关因子的影响[J].环球中医药,2010,3(5):336-338.[34] 黄泉智,许成勇,孙志高,等.舒郁宁心汤对抑郁大鼠海马Bcl-2和Bax表达的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012,18(3):236-238. |