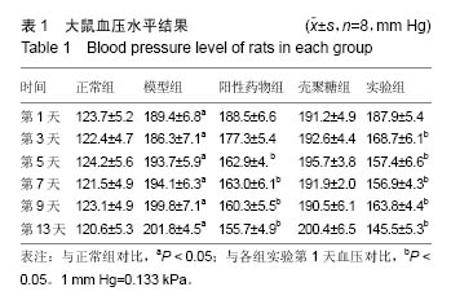
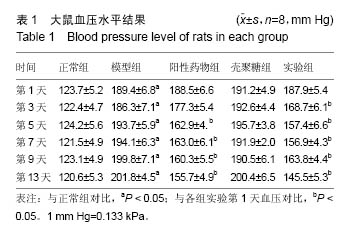
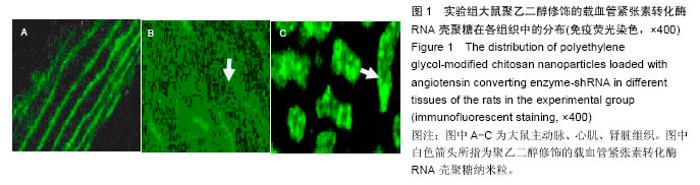
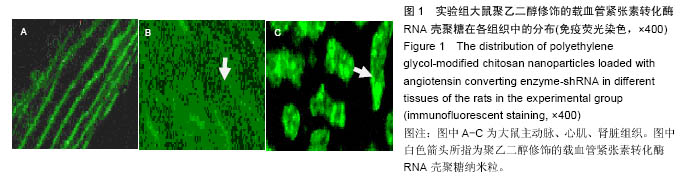
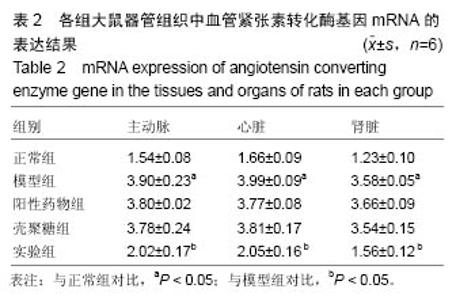
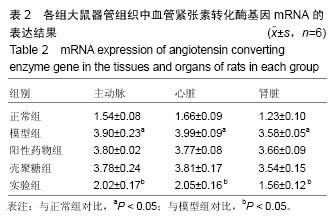
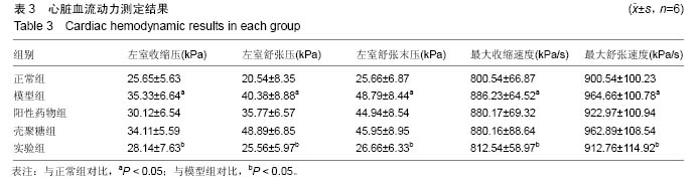
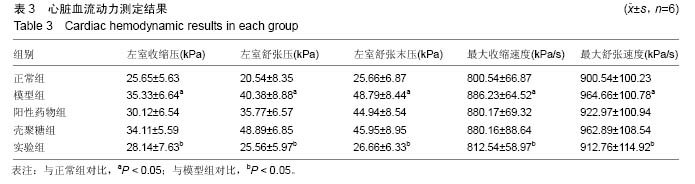
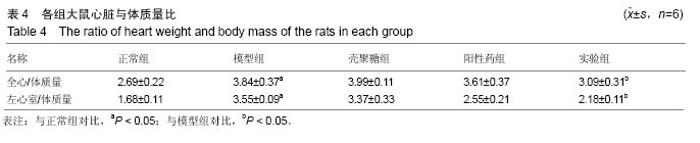
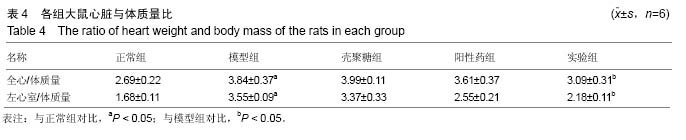
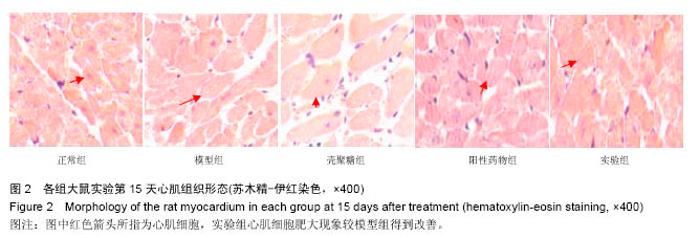
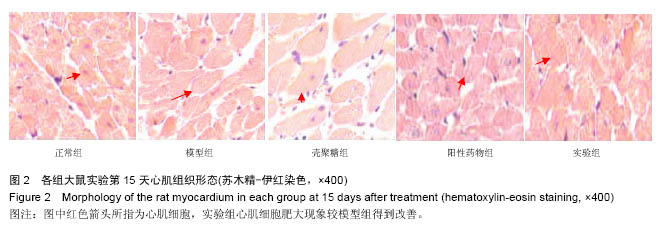
| [1]潘俊龙.高血压常见药物与治疗方法的研究进展[J].中国当代药学,2014,21(5):185-186.
[2]陈会英,张树彪,彭孝军,等.壳聚糖在离子液体中均相接枝聚乙烯亚胺及其基因转运[J].高分子学报, 2014,08(11): 1089-1095.
[3]张未,潘仕荣,张璇,等.聚乙二醇-壳聚糖共聚物作为基因传递载体的体外研究[J].药学学报,2008,8(2):848-854.
[4]张迪.RGD短肽修饰壳聚糖作为钛表面hBMP-2 cDNA基因载体表达效率的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2014.
[5]罗金,杨菁,程琰,等.以壳聚糖纳米微球为载体的Crisp1-DNA避孕疫苗的制备及体外表达[J].生殖医学杂志,2016,10(1):947-952.
[6]张杨,王庆卫,李梦,等.药物输送中壳聚糖纳米粒的应用[J].现代养生,2016,18(1):36.
[7]纪萍,詹园,苏铭吉,等.基于壳聚糖的衍生物在药物中的应用进展[J].胶体与聚合物,2016,3(1):133-136.
[8]顾忠雪.壳聚糖在药物制剂中的应用分析[J].化工管理, 2016,23(10):150.
[9]朱海振,俞婕,江飞龙,等.纳米壳聚糖递送分子信标成像肺癌细胞的研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2016,8(1):629-635.
[10]Hou C, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. Preparation, characterization and transfection efficiency of cationic PEGylated PLA nanoparticles as genedelivery systems. J Biotechnol. 2007;130(2):107-113.
[11]王西,吴修利,赵珺.壳聚糖微球制备方法及其在医药应用的研究进展[J].长春大学学报,2015,5(10):64-68.
[12]姚金凤,郭晨阳,杨红,等.壳聚糖纳米粒在药物输送中的应用研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2013,1(1):90-94.
[13]张玮,张学农.壳聚糖纳米粒制备技术研究进展[J].抗感染药学,2008,2(4):65-69.
[14]周闻舞,顾海铮.壳聚糖微/纳米粒在定向给药系统中的应用研究[J].药物评价研究,2010,4(8):290-295.
[15]Qiu Y, Shil PK, Zhu P, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) activator diminazene aceturate ameliorates endotoxin-induced uveitis in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(6):3809-3818.
[16]张未,潘仕荣,张璇,等.聚乙二醇-壳聚糖共聚物作为基因传递载体的体外研究[J].药学学报,2008,8(2):848-854.
[17]于莲,崔丹,应晓英,等.表面修饰脂质纳米粒给药系统的研究进展[J].中国现代应用药学,2011,6(29):329-332.
[18]唐大川.壳聚糖对视网膜神经细胞生长的促进作用及其作为基因载体的初步研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
[19]Zhao X, Yu SB, Wu FL, et al. Transfection of primary chondrocytes using chitosan-pEGFP nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2006;112(2):223-228.
[20]尹登科,杨晔,胡容峰,等.载碱性成纤维细胞生长因子质粒纳米粒的制备及体外转染活性研究[J].中国医院药学杂志,2011,17(1):1417-1421.
[21]高奋.载ACEshRNA-PEG壳聚糖纳米粒的制备以及对自发性高血压大鼠的治疗作用[D].太原:山西医科大学, 2009.
[22]赵惠萍.不同PH值的PEG化壳聚糖质粒纳米粒的制备及其对大鼠主动脉内皮细胞转染的研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2009.
[23]李敬.基于壳聚糖的纳米载体系统的构建及其肿瘤靶向性研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2012.
[24]冯超.基于壳聚糖的纳米凝胶口服药物输送载体的构建及其透粘膜机理的研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2014.
[25]郝英魁,杨学东.载药壳聚糖纳米粒的研究进展[J].中国药学杂志,2005,40(17):1292-1295.
[26]李典,徐若诗,徐小平.壳聚糖微/纳米粒子的制备及其在黏膜给药中的应用[J].华西药学杂志,2014,2(12):219-221.
[27]胡俊,刘玉玲.载药纳米粒的研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2004,5(7):54-58.
[28]储敏.聚乙二醇1000维生素E琥珀酸酯(TPGS)修饰壳聚糖纳米粒作为抗肿瘤药物传递载体的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
[29]吴立明,习温瑜,管正红.壳聚糖纳米粒制备的研究进展[J].齐鲁药事,2008,27(11):682-685.
[30]吴叶,刘袖洞,王云红,等.海藻酸钠纳米粒制备的研究进展[J].材料导报,2016,5(7):7-11.
[31]Nah JW, Choi YJ, Cho CS, et al. Galactosylated chitosan/DNA nanoparticles prepared using water-soluble chitosan as a gene carrier. Biomaterials. 2004;25(17):3783-3792.
[32]Wang YS, Li YX, Song N, et al. In vitro stability of targeting antitumor drug methotrexate-succinyl-chitosan conjugate. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2003;24(11):2103-2106.
[33]曹斌.叶酸改性半乳糖化壳聚糖药物载体材料制备及性能研究[D].武汉:武汉理工大学,2011.
[34]张金莲.血管紧张素II-1型受体的shRNA对自发性高血压大鼠血压作用的实验研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2006. |