Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7006-7013.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tissue-engineered periosteum-coated biphasic calcium phosphate scaffold repairs bone defects in rabbits
- Department of Orthopaedics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2016-10-17Online:2016-11-18Published:2016-11-18 -
Contact:Xiang Zhou, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Xing Fei, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopaedics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31370984
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xing Fei, Peng Jing, Chen Long, Peng Kun, Li Lang, Xiang Zhou.
share this article
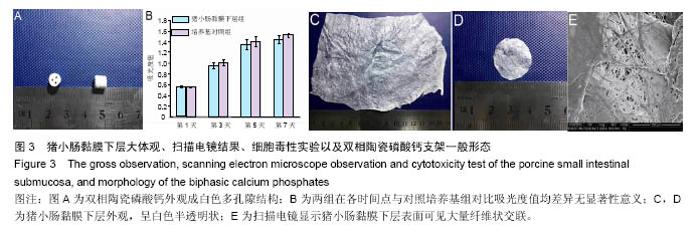
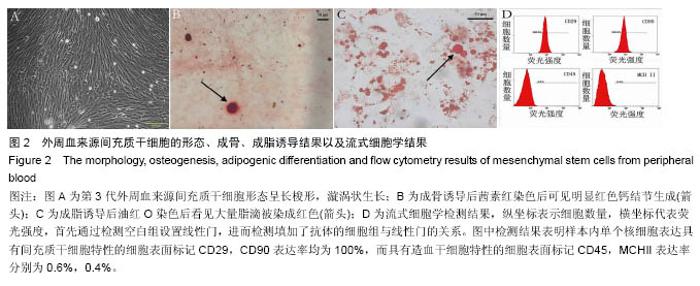
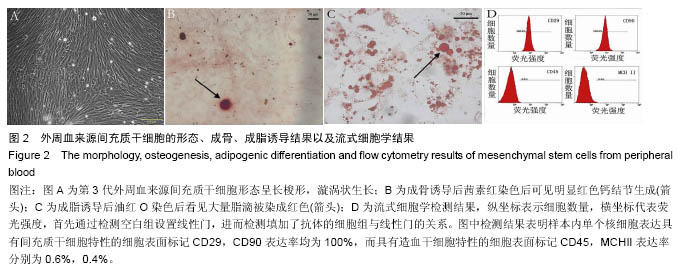
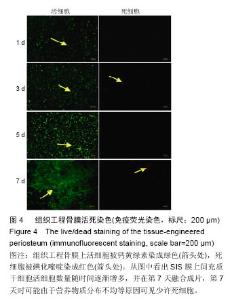
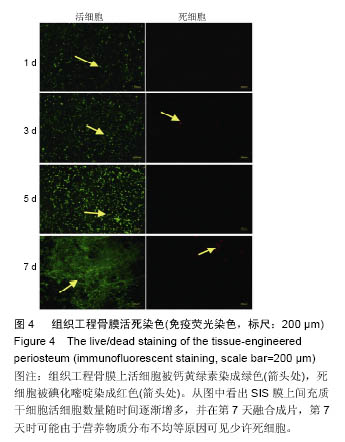
2.2 SIS膜材料细胞毒性实验检测结果 在猪小肠黏膜下层浸润液组和对照组中,间充质干细胞数量随时间均明显增加。第1,3,5,7天猪小肠黏膜下层浸润液组和相应培养基对照组间充质干细胞数量均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,图3A,B)。结果证实实验所用SIS膜的浸润液对间充质干细胞的增殖无明显影响。 2.3 构建的组织工程骨膜形态 制成的SIS膜呈白色半透明薄膜,弹性尚可,质韧(图3C,D)。扫描电镜结果中可见SIS膜内纵横交错的胶原纤维(图3E)。将间充质干细胞接种于SIS膜上构建组织工程骨膜并分别在第1,3,5,7天进行细胞活死染色(活细胞被钙黄绿素染成绿色,死细胞被碘化嘧啶染成红色)。结果发现,SIS膜上间充质干细胞活细胞数量随时间逐渐增多,并在第7天融合成片。此外,在第7天时可能由于营养物质分布不均等原因可见少许死细胞(图4)。"
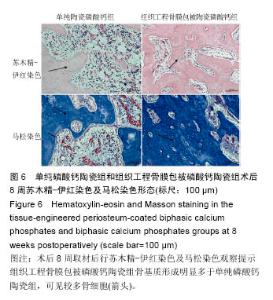
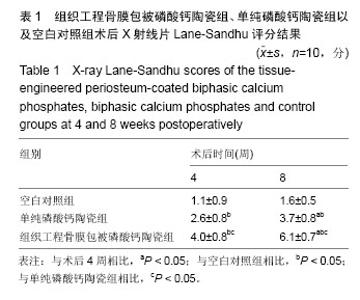
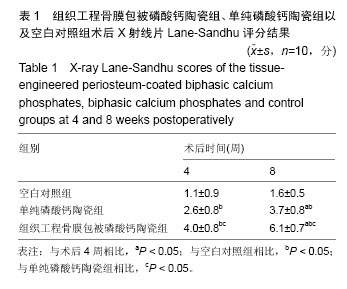
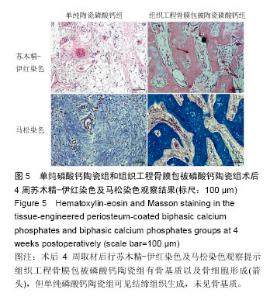
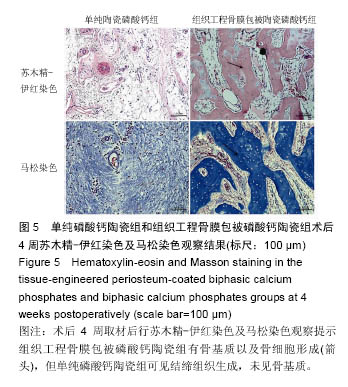
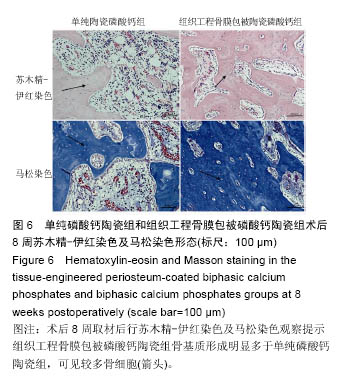
术后8周X射线片提示,组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组材料降解明显,材料与骨端组织融合,骨痂形成明显多于单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组,而空白对照组骨缺损处未见新骨形成。根据术后X射线进行Lane-Sandhu评分组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组为(6.1±0.7)分,单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组(3.7±0.8)分,空白对照组(1.1±0.9)分,各组差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05;表1)。组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组和单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组术后8周Lane-Sandhu评分均高于术后4周评分(P < 0.05)。术后8周苏木精-伊红染色及Masson染色提示骨缺损单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组和组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组材料均仍未降解完全,组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组材料降解明显优于单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组。同时,组织工程骨膜包被磷酸钙陶瓷组骨基质形成明显多于单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组,内有较多骨细胞,基质周围有更多成骨细胞分布(图6)。 2.5 不良反应分析 组织工程材料植入后,单纯磷酸钙陶瓷组出现1只兔子伤口感染迹象,经过肌注青霉素、伤口涂抹百多邦等治疗后恢复。其他各组实验动物术后恢复顺利未出现明显并发症。 "
| [1]Khan Y, Yaszemski MJ, Mikos AG, Laurencin CT. Tissue engineering of bone: material and matrix considerations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 1:36-42. [2]Laurie SW, Kaban LB, Mulliken JB, et al. Donor-site morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 1984;73:933-938. [3]韩冰,付小兵.间充质干细胞的研究进展与临床应用前景[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2006,20(12):1257-1261. [4]马锡慧,冯凯,石炳毅.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及其研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2011,15(32): 6064-6067. [5]Zvaifler NJ, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Adams G, et al. Mesenchymal precursor cells in the blood of normal individuals. Arthritis Res. 2000;2(6):477-488. [6]Deb A, Wang S, Skelding KA, et al. Bone marrow-derived cardiomyocytes are present in adult human heart: a study of gender-mismatched bone marrow transplantation patients. Circulation. 2003; 107(9):1247-1249. [7]Guilak F, Lott KE, Awad HA, et al. Clonal analysis of the differentiation potential of human adipose-derived adult stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(1):229-237. [8]Li S, Huang KJ, Wu JC, et al. Peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: candidate cells responsible for healing critical-sized calvarial bone defects. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(4):359-68. [9]杨志明.组织工程骨的研究成果及存在的问题[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(2):87-89. [10]贝抗胜,吴礼杨,孙庆文,等.人骨膜细胞生物学特性的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(12):1170-1174. [11]张大伟,田清业,刘光军,等.骨膜瓣复合异体骨移植修复大段骨缺损[J].组织工程与重建外科,2012,8(1):26-31. [12]Hall BK, Miyake T. All for one and one for all: condensations and the initiation of skeletal development. Bioessays. 2000;22:138-147. [13]Hodde J, Record R, Liang H, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in porcine-derived extracellular matrix. Endothelium. 2001;8:11-24. [14]Badylak S, Liang A, Record R, et al. Endothelial cell adherence to small intestinal submucosa: an acellular bioscaffold. Biomaterials. 1999;20:2257-2263. [15]Allman AJ, McPherson TB, Badylak SF, et al. Xenogeneic Extracellular Matrix Grafts Elicit A Th2-Restricted Immune Response1. Transplantation. 2001;71:1631-1640. [16]Giannoni P, Scaglione S, Daga A, et al. Short-time survival and engraftment of bone marrow stromal cells in an ectopic model of bone regeneration. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2009;16:489-499. [17]Nihouannen DL, Duval L, Lecomte A, et al. Interactions of total bone marrow cells with increasing quantities of macroporous calcium phosphate ceramic granules. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(10):1983-1990. [18]Schwartz C, Liss P, Jacquemaire B, et al. Biphasic synthetic bone substitute use in orthopaedic and trauma surgery: clinical, radiological and histological results. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1999;10:821-825. [19]Fu WL, Zhang JY, Fu X, et al. Comparative study of the biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood of rats. Tissue engineering Part A. 2012;18:1793-1803. [20]Abraham GA, Murray J, Billiar K, et al. Evaluation of the porcine intestinal collagen layer as a biomaterial. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51:442-452. [21]Zhao L, Zhao J, Yu J, et al. In vitro study of bioactivity of homemade tissue-engineered periosteum. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;58:1170-1176. [22]Lane JM, Sandhu HS. Current approaches to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987;18:213-225. [23]孙良,栾保华,李中华,等.兔外周血间充质干细胞的体外分离培养及诱导成骨[J].中国组织工程研究, 2009,13(27): 5291-5295. [24]Larsen SR, Chng K, Battah F, et al. Improved granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilization of hemopoietic progenitors using cytokine combinations in primates. Stem Cells. 2008;26:2974-2980. [25]Fu Q, Zhang Q, Jia LY, et al. Isolation and characterization of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016. [26]Dhar M, Neilsen N, Beatty K, et al. Equine peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, identification, trilineage differentiation and effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Equine Vet J. 2012;44: 600-605. [27]Lyahyai J, Mediano DR, Ranera B, et al. Isolation and characterization of ovine mesenchymal stem cells derived from peripheral blood. BMC Vet Res. 2012;8:1. [28]Ab Kadir R, Zainal Ariffin SH, Megat Abdul Wahab R, et al. Characterization of mononucleated human peripheral blood cells. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012. [29]Fu WL, Xiang Z, Huang FG, et al. Coculture of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells on strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds to generate vascularized engineered bone. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2014. [30]Dipersio JF, Stadtmauer EA, Nademanee A, et al. Plerixafor and G-CSF versus placebo and G-CSF to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells for autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood. 2009;113:5720-5726. [31]Clercq ED. The AMD3100 story: the path to the discovery of a stem cell mobilizer (Mozobil). Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:1655-1664. [32]Fu WL, Zhang JY, Fu X, et al. Comparative study of the biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood of rats. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2012;18:1793-1803. [33]Schönmeyr B, Clavin N, Avraham T, et al. Synthesis of a tissue-engineered periosteum with acellular dermal matrix and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2009;15:1833-1841. [34]Fan W, Crawford R, Xiao Y. Enhancing in vivo vascularized bone formation by cobalt chloride-treated bone marrow stromal cells in a tissue engineered periosteum model. Biomaterials. 2010;31:3580-3589. [35]Hattori K, Yoshikawa T, Takakura Y, et al. Bio-artificial periosteum for severe open fracture-an experimental study of osteogenic cell/collagen sponge composite as a bio-artificial periosteum. Biomed Mater Eng. 2005;15: 127-136. [36]Liang Y, Wen L, Shang F, et al. Endothelial progenitors enhanced the osteogenic capacities of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in a rat alveolar bone defect model. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;68:123-130. [37]张苍宇,王栓科,任广铁,等.组织工程骨膜同种异体体内成骨修复兔肩胛骨缺损的初步研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(3):384-388. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||