Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (45): 6795-6800.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.45.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interventional effect of umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation in rats with gestational hypertension
Cui Xue-mei, Jing Xiao-xiao
- Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Zhengzhou Central Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450007, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-09-29Online:2016-11-04Published:2016-11-04 -
Contact:Jing Xiao-xiao, Master, Physician, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Zhengzhou Central Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450007, Henan Province, China -
About author:Cui Xue-mei, Associate chief physician, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Zhengzhou Central Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450007, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cui Xue-mei, Jing Xiao-xiao. Interventional effect of umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation in rats with gestational hypertension[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(45): 6795-6800.
share this article

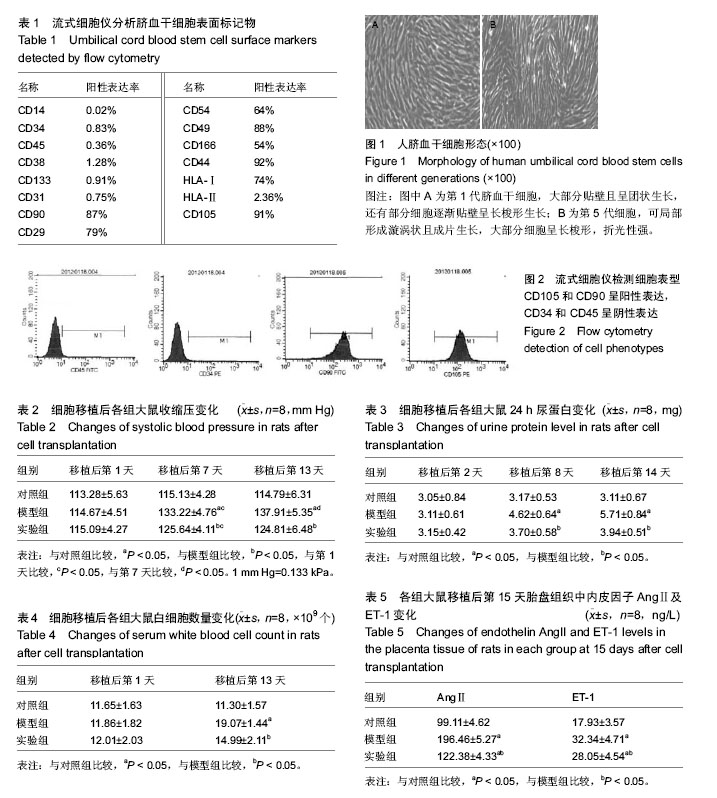
2.1 实验动物数量分析 健康SPF级10周龄SD雄性大鼠15只,SD雌性大鼠30只,妊娠大鼠共28只,随机取24只妊娠期大鼠随机分为3组:对照组、模型组和实验组,均进入结果分析。 2.2 脐血干细胞形态学观察及鉴定结果 培养第1天,显微镜下可见细胞迅速贴壁,细胞形态为梭形或卵圆形;培养第2天,脐血干细胞均匀分布,体积较大,形态为长梭形或多角状(图1A)。传代后细胞生长迅速,数量明显增多,生长较均匀一致,培养3 d细胞融合成片状,排列紧密、整齐有序,长满培养瓶底部。传5代仍可保持基本生物学特性不变(图1B)。流式细胞仪检测脐血干细胞表面标记物CD105、CD90、CD44、CD29、CD49、HLA-Ⅰ呈阳性表达,CD14、CD34、CD45、CD38、CD133、CD31和HLA-Ⅱ呈阴性表达,见表1,图2。 2.3 脐血干细胞移植后各组大鼠收缩压测定结果 从表2数据分析可知:细胞移植后第1天,3组大鼠收缩压比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。细胞移植后第7天,3组大鼠收缩压比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),与对照组比较,模型组大鼠收缩压明显升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),并且随着内毒素作用时间的延长,模型组大鼠收缩压不断升高,与模型组比较,实验组大鼠收缩压明显有所降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),且血压较稳定。细胞移植后第13天,模型组大鼠收缩压已经达到(137.91±5.35) mm Hg(1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa),与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 脐血干细胞移植后各组大鼠24 h尿蛋白测定结果 从表3数据分析可知:细胞移植第2天,3组大鼠24 h尿蛋白比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。细胞移植第8天,与对照组相比,模型组大鼠24 h尿蛋白明显增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),并且随着内毒素作用时间的延长,24 h尿蛋白不断升高,说明内毒素可造成正常妊娠大鼠尿蛋白升高;到第14天,与模型组相比,实验组大鼠24 h尿蛋白有所降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.5 脐血干细胞移植后各组大鼠白细胞计数结果 从表4数据分析可知:细胞移植第1天,3组大鼠白细胞数量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。细胞移植第13天,与对照组相比,模型组大鼠白细胞数量明显升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,实验组大鼠白细胞数量有明显降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.6 各组胎盘组织内皮损伤相关因子AngⅡ及ET-1表达 由表5数据分析可知:模型组及实验组大鼠静脉注射内毒素后,内皮损伤因子AngⅡ及ET-1与对照组比较均有明显升高,这可能是大鼠注射内毒素后通过诱发炎症反应,损伤了内皮细胞功能,导致内皮损伤因子AngⅡ和ET-1分泌的增加,进而导致血管收缩,大鼠收缩压增高。与模型组相比,实验组大鼠内皮损伤因子AngⅡ和ET-1表达降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] 林其德.妊娠高血压综合征病因学研究进展与展望[J].中华妇产科杂志2003,38(8):471-473. [2] Sacks GP, Studena K, Sargent K, et al. Normal pregnancy and preeclampsia both produce inflammatory changes in peripheral blood leukocytes akin to those of sepsis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 179(1):80-86. [3] Freeman DJ, McManus F, Brown EA, et al. Short- and long-term changes in plasma inflammatory markers associated with preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2004; 44(5):708-714. [4] Takacs P, Green KL, Nikaeo A, et al. Increased vascular endothelial cell production of interleukin-6 in severe preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 188(3):740-744. [5] Kauma S, Takacs P, Scordalakes C, et al. Increased endothelial monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin-8 in preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 100(4):706-714. [6] Azizieh F, Raghupathy R, Makhseed M. Maternal cytokine production patterns in women with pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2005;54(1): 30-37. [7] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [8] Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al. A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004;200(2):123-135. [9] Zvaifler NJ, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Adams G, et al. Mesenchymal precursor cells in the blood of normal individuals. Arthritis Res. 2000;2(6):477-488. [10] Jiang Y, Vaessen B, Lenvik T, et al. Multipotent progenitor cells can be isolated from postnatal murine bone marrow, muscle, and brain.Exp Hematol. 2002; 30(8):896-904. [11] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25): 13625- 13630. [12] Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110. [13] Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004;364(9429):149-155. [14] Pountos I, Giannoudis PV. Biology of mesenchymal stem cells. Injury. 2005;36 Suppl 3:S8-S12. [15] Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Peister A, et al. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem. 2004;329(1):77-84. [16] Hayashi O, Katsube Y, Hirose M, et al. Comparison of osteogenic ability of rat mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, periosteum, and adipose tissue. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;82(3):238-247. [17] Planat-Benard V, Silvestre JS, Cousin B, et al. Plasticity of human adipose lineage cells toward endothelial cells: physiological and therapeutic perspectives. Circulation. 2004;109(5):656-663. [18] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [19] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1):11-20. [20] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822. [21] Faas MM, Schuiling GA, Baller JF, et al. A new animal model for human preeclampsia: ultra-low-dose endotoxin infusion in pregnant rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171(1):158-164. [22] Vizi ES, Szelényi J, Selmeczy ZS, et al. Enhanced tumor necrosis factor-alpha-specific and decreased interleukin-10-specific immune responses to LPS during the third trimester of pregnancy in mice. J Endocrinol. 2001;171(2):355-361. [23] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [24] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843. [25] Meisel R, Kuypers L, Dirksen U, et al. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine provides early protective antibody responses in children after related and unrelated allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2007;109(6):2322-2326. [26] Zheng ZH, Li XY, Ding J, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell and mesenchymal stem cell-differentiated chondrocyte suppress the responses of type II collagen-reactive T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(1):22-30. [27] Viney JL, MacDonald TT, Kilshaw PJ. T-cell receptor expression in intestinal intra-epithelial lymphocyte subpopulations of normal and athymic mice. Immunology. 1989;66(4):583-587. [28] Augello A, Tasso R, Negrini SM, et al. Cell therapy using allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents tissue damage in collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1175-1186. [29] Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, et al.Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1439-1441. [30] Ringdén O, Uzunel M, Rasmusson I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 2006;81(10):1390-1397. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||