Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (43): 6487-6493.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.43.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Titanium-based cermet as an artificial joint material: the surface hardness is increased by titanium carbide ceramics and complex pore structure
- Institute of Tribology and Reliability Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2016-07-24Online:2016-10-21Published:2016-10-21 -
Contact:Luo Yong, Doctor, Associate professor, Institute of Tribology and Reliability Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Yang Ting, Studying for master’s degree, Institute of Tribology and Reliability Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51575514; China Postdoctoral Foundation, No. 2015T80598
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Ting, Luo Yong, Cao Dong-dong, Ke Hai-bao.
share this article
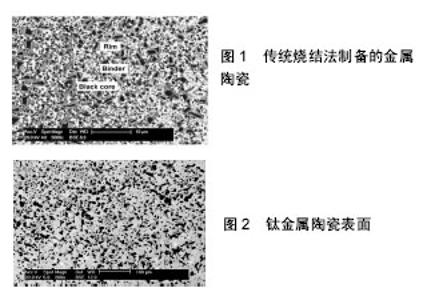
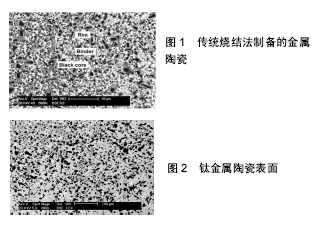
2.1 人工髋关节的发展 2.1.1 人工髋关节材料的进展 Gluck(1890年)对髋关节强直患者采用切断强直部,并用雕琢后的象牙股骨头与髋臼首次进行了全髋关节置换术,到1918年Delbet采用增强橡胶股骨头来治疗股骨颈骨折等,为早期髋关节置换做出努力,是人工髋关节的起源[1]。20世纪30年代,Wiles首次采用不锈钢材料制作股骨头和髋臼为病患者进行了关节置换手术,结果却不尽人意,最终是金属碎裂而导致置换失败[2],但从此金属材料也走上了医用生物材料的舞台。1938年,美国Smith Peterson发现了钴铬钼合金有着较强的生物惰性,在人体的生物相容性较好,于是将其开始用作关节置换假体,也就奠定了其在人工关节置换领域不可磨灭的作用[3]。1940年,Haboush在实验室开展钴铬钼合金球头和丙烯酸酯臼进行磨损试验。到了20世纪60年代,钛及及钛合金作为关节材料开始迅速普及[2]。1962年,John Charnley低摩擦关节问世,使人工全髋关节置换取得前所未有的成功[3]。随后,金属钴铬钼和陶瓷材料技术的发展使得人工关节出现了许多的配副,诸如金属对聚乙烯关节、金属对金属关节、陶瓷对陶瓷关节等,人工髋关节置换也在最近的40年里取得了巨大进步,人工关节的使用寿命和可靠性取得了显著进步。 2.1.2 人工髋关节的危机 虽然人工髋关节置换在最近的40年里取得了巨大的进步,但依旧不能用完美来形容,关节被召回事件频发,给人工髋关节带来了很大的危机。2002年,由于短期内陶瓷球头出现了大量的碎裂,Saint Gobain公司不得不宣布召回Zirconia球头(陶瓷对陶瓷)[4];2008年,由于临床应用后的失败率远远超出预期,Zimmer公司主动召回了旗下的Durom髋臼假体组件(金属对金属);2010年,由于失败率约为1/8,强生公司旗下的DePuy公司不得不主动召回其ASR XL髋关节假体(金属对金属),而召回公司说明召回的原因是患者出现了高翻修率[5];2012年,由于金属毒性和较高的翻修率,Stryker公司不得不召回其Rejuvenate髋关节假体(金属对金属);同年,也是由于关节翻修率高于英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所所设定的翻修率基准,施乐辉医用产品国际贸易(上海)有限公司对髋关节置换系统(商品名:Birmingham)进行了召回。 2.1.3 人工关节寿命的影响因素 随着人工关节的发展,人工关节置换已成为重建人体疾病或创伤关节功能的主要方法,一般设计的人工关节使用寿命较长,约为20年[6],但手术、人工关节设计以及人工关节材料都是影响人工关节寿命的主要因素。 手术:关节松动和关节假体磨损是术后关节寿命的最主要影响因素。研究发现,不管是最初阶段的金属对金属界面,发展阶段的金属对聚乙烯界面,还是后来的陶瓷对陶瓷界面,以及20世纪90年代才提出的陶瓷对聚乙烯界面,都有不可避免的磨损磨粒产生,其中高分子聚乙烯磨损颗粒还可以诱发体内的免疫反应,以致关节假体周围很容易发生骨溶解,最后将导致关节松动[7],也就使得摩擦磨损性能成为决定人工髋关节假体寿命的重要性能之一。 人工关节设计:靳忠民等[8]设计了双动人工关节,该设计方法可用于年轻患者因恶性骨肿瘤造成的股骨远端大段骨缺损的保肢手术治疗。张建等[9]探讨了利用双动人工关节置换技术治疗高龄转子间骨折,双动半髋关节置换技术在手术过程中有着很好的优点,时间短、出血少,而对于老年患者,因其手术耐受性较差,该手术更安全。另外,由于大、小转子骨折,假体放置时缺乏正常骨性标志,假体柄前倾角的确定及髋关节的软组织平衡困难,加之老年患者肌力差,故术后髋关节脱位率高。 人工关节材料:目前用于人工关节置换的材料主要有陶瓷材料、金属材料及高分子材料等[10]。采用不同的假体材料,置入人体后生物相容性不同,人工关节的使用寿命也就不同。传统的人工关节材料常采用钴铬钼与聚乙烯配副的方式,但常常会因为无法避免假体周围的骨溶解而造成关节松动,因此寿命不长。然而金属与金属的配副,虽然其拥有良好的耐磨损性能,但其磨损后所产生的磨损颗粒远远多于金属与其他材料配副时所产生的磨损颗粒,而由于磨损带来的金属粒子释放、过敏及更严重的问题引起了更广泛的关注,也受到了更多的质疑[3,11]。对于生物陶瓷材料,其力学性能较差,而且结合强度较其他材料也不足,一旦温度过高则会引起生物活性下降等[12]。不同假体材料置入后会与宿主产生不同的反应,影响与宿主的生物相容性,因此,改善材料的耐磨性及力学性能[13],增强假体与宿主的结合力,改善假体与宿主的生物相容性,以达到延长假体使用寿命的作用[11]。 2.2 人工髋关节面临的问题 2.2.1 金属对金属 人工髋关节配副中,最早被提出的配副界面即为金属对金属界面,由于不良的假体设计和粗糙的制作工艺,第一代金属对金属假体有着很高的失败率;第二代金属对金属假体为了改善关节制作工艺,减少关节假体的磨损,采用了锻造的碳增强钴铬钼合金;第三代金属—金属摩擦界面假体做了更好的改善,为了使金属的弹性模量更接近于人骨,金属内衬通常包被聚乙烯缓冲层[14]。虽然金属对金属假体在不断改善,但其产生的颗粒在体内可释放金属离子。有临床研究发现,患者手术后其血液及尿液中钴离子、铬离子及钼离子均有不同程度的增高。而这些金属离子一旦超过人体微量元素所需量,人体肾脏将是主要受累器官,除此之外,还会造成不同程度的过敏反应,以及其他器官也会受到不同程度的影响[15]。正是因为这些问题的产生,金属对金属关节出现了严重的危机,关节毒性问题导致金属对金属关节在世界范围内几乎已不再建议使用。 2.2.2 金属对聚乙烯 由于高分子材料有着良好的耐磨性、力学性能、耐蚀性及生物相容性,使其在人工髋关节假体材料方面得到了广泛的应用,并且被认为是最佳的人工全髋关节假体材料[16]。但在长期的临床研究中发现,金属对聚乙烯中出现的主要问题是由于摩擦产生的磨屑,尤其是超高分子聚乙烯磨屑,容易引起骨骼发炎和无菌松动,从而加剧了关节假体的磨损,以致人工全髋关节置换失效,关节假体的使用寿命也就显著降低了[17]。 针对这一情况,对超高分子量聚乙烯进行改性,得到高交联聚乙烯,希望可以增强超高分子量聚乙烯的耐磨损性。第一代照射后加热过熔点后,检测不出自由基,耐磨性能很好,但力学强度却下降了,出现了髋臼内衬碎裂的报道[18]。第二代通过不同的方法去除残留的自由基,既增加了聚乙烯的耐磨性能又不至于影响其强度,但是仍然有磨损颗粒存在,尺寸小于普通聚乙烯,没有彻底去除由于聚乙烯磨损颗粒造成的骨溶解和无菌松动。 对超高分子量聚乙烯改性的另一技术手段就是填料填充。作为医用填充材料,每一种材料都需要具有良好的生物相容性,所以常用的填料有玻璃、炭及碳化硅等纤维,石墨、生物陶瓷等无机粉状颗粒。石墨、碳纤维等软相材料的填充可提高超高分子量聚乙烯的自润滑性能,从而降低磨损;生物陶瓷、玻璃纤维等硬质材料的填充可直接提高材料的耐磨性;纤维材料的填充还可进一步提高材料的机械性能[19]。 虽然对超高分子量聚乙烯的改性改善了其耐磨损性,但长期的临床研究发现,由于超高分子量聚乙烯长期磨损严重,产生的磨屑也容易造成人工关节假体出现晚期松动现象等。 2.2.3 陶瓷对陶瓷 为解决上述金属与聚乙烯对副时产生的磨粒而引起的骨溶解和无菌松动问题,人们开始关注陶瓷材料[20]。从第一代陶瓷材料假体开始,陶瓷在人工髋关节方面的应用迄今已有40余年,而人们对其产品要求也越来越高,更高的纯度,更佳的密度,更小的晶体颗粒,质量控制也更加严格[21]。陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体的主要问题是易碎裂,但是随着人们对陶瓷材料的改进,陶瓷头的破碎率明显降低,反而正确的手术操作成为了决定人工假体的使用寿命,陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体对置入位置要求特别高,位置不佳极容易导致关节假体的撞击,从而加速假体的磨损,以致关节假体的置换失效[21]。 近年来,陶瓷对陶瓷人工关节假体出现了“咯吱”声异响的问题,这一问题受到了患者和研究者的广泛关注[22]。所谓关节异响是指一种具有特定频率的、可听得见的响声,而关节异响常常出现在硬对硬的接触摩擦配副面上,如金属对金属、陶瓷对陶瓷。关于关节异响问题,已影响到患者对手术的满意度,甚至严重影响患者术后的社交活动和生活质量。患者如果只是偶尔的异响并且没有出现髋关节的疼痛,则只需密切观察和随访,但是关节异响严重的患者,会使之不堪忍受异响的响度和频度,或者是导致髋关节疼痛,以致于需要经常对关节进行翻修,更有甚者,还需要重新置换人工髋关节,让患者再一次承受手术的痛苦[23]。 2.3 钛基金属陶瓷的提出 2.3.1 材料的选择 为了开发新型的人工关节材料,本团队在研制新型的人工关节材料基于2个方面的考虑:首先,对于金属关节材料来说,在元素的选择方面必须要考虑到其安全性及无毒性。在所有的金属材料中,生物相容性最好的5种元素分布是钛-Ti、锆-Zr、铌-Nb、钽-Ta和铂-Pt[24],同时,钛合金有着优异的生物相容性、杰出的耐腐蚀性、良好的力学性能、密度低、杨氏模量小等特点,如果在钛金属中添加以上几种生物相容性好的元素形成新型的钛合金,使得钛合金拥有更好的生物相容性[25],并且在人体内会更安全、更无毒;其次,从人工关节材料的性能方面,金属关节材料有着良好的力学性能以及可加工性,但其长期在体内的磨损腐蚀会导致关节假体的失效,而陶瓷材料具有坚硬、耐磨和化学稳定性,但其致命的弱点是脆性差、容易破裂、假体失败率高[26]。基于金属关节材料和陶瓷关节材料的优缺点,考虑到如果将金属和陶瓷材料的性能相结合,两者之间取长补短,形成心部强韧而表面坚硬耐磨的新型的金属陶瓷人工关节材料,有望进一步提高人工关节的稳定性和可靠性。 2.3.2 传统金属陶瓷的定义 金属陶瓷有效的结合了金属与陶瓷的性能,它拥有着良好的塑性、韧性、强度、硬度、耐磨性、耐腐蚀性及生物相容性等综合性能[27]。源于20世纪80年代金属陶瓷的发展,在英文中用Cermet表示,它是由单词ceramics中的cer和单词metal中的met结合起来构成的新单词[28]。 金属陶瓷的传统定义是由陶瓷和金属组成的非均质的复合材料[29]。传统的金属陶瓷是通过将陶瓷和金属研磨混合均匀,成型后在不活泼气氛中烧结,就可制得金属陶瓷。 由于金属陶瓷之间还存在着相界面,不能更加有效的将金属和陶瓷的性能结合起来,于是提出了功能梯度材料。功能梯度材料是指根据不同的使用要求,选择两种不同性能的材料在先进的材料复合技术下使得两种材料中间的组成结构、化学成分连续呈梯度变化,而且内部并不存在明显的界面,从而使材料的性质和功能沿厚度或长度方向也呈梯度变化的一种新型复合材料[30]。1987年,日本的新野正之、平井敏雄等材料学家们提出“功能梯度材料”这个术语[31]。功能梯度材料有如下优势:将功能梯度材料用作界面层来连接不相容的两种材料,可以显著提高黏结强度;将功能梯度材料用作涂层和界面层可以减小残余应力和热应力;将功能梯度材料用作涂层和界面层,可消除连接材料中界面交叉点及应力自由端点的应力奇异性;用功能梯度材料代替传统的均匀材料涂层,既可以增强连接强度也可以减小裂纹驱动力。正是由于功能梯度材料可以作为涂层广泛使用,因此金属陶瓷的概念又扩展到了功能梯度涂层,作为功能梯度涂层可以很好地提高材料表面的耐磨性。 2.3.3 钛基金属陶瓷概念的由来 新型的金属陶瓷主要是功能梯度涂层,即通过先进的表面处理技术形成金属和陶瓷的二维界面,根据所需配制不同体积分数的金属和陶瓷,从而制备出性能优异的功能梯度金属陶瓷[32]。 最早的梯度金属陶瓷是1995年日本科学家制备的,这一发明是在表面区域提高以Ti(C,N)为主要成分的面心立方相,这一相成分向材料内部逐渐减少,从而形成功能梯度材料[33]。而金属陶瓷在人工髋关节的成功应用是施乐辉公司(Smith & Nephew)开发的Oxinium产品,被称为“氧化锆金属”,被誉为“人工关节领域内近20多年中的重大突破”。 1985年,陶瓷球头被引入临床,但是由于球头不断出现碎裂,2002年Saint Gobain公司不得不宣布召回Zirconia球头(陶瓷对陶瓷),Zirconia在人工关节中的应用就此走入低谷。施乐辉公司(Smith & Nephew)却另辟蹊径,在锆铌合金(Zr-2.5Nb)表面进行氧化处理,制备了Oxinium(黑晶),表面形成5μm厚的陶瓷层,使其具有Zirconia高硬度、低摩擦、耐磨损和耐腐蚀的特点。Oxinium表面形成的二氧化锆陶瓷不是一种涂层[34],同时,Oxinium(黑晶)表面的陶瓷层是自氧化形成的,与下方的锆铌合金本体间具有化学连接,这一表层与本体几乎是不可分离的,即便用带钻石头的刻刀毁损这一表面,也不会造成连接界面分开。因此,Oxinium的提法是:氧化锆金属,不是功能梯度涂层。 基于性能功用相似性,制备方法相似性,Oxinium(黑晶)是通过自氧化形成的一种新型的心部具有金属强韧,表面具有陶瓷耐磨的“氧化锆金属”,钛基金属陶瓷也与Oxinium具有异曲同工之妙,在钛合金表面上通过碳扩散、反应制备出的一种新型的心部具有金属强韧,表面具有陶瓷耐磨的金属陶瓷。因此,综合金属陶瓷、功能梯度涂层和Oxinium(黑晶)在理论和实际两方面的情况,中国矿业大学葛世荣生物摩擦学团队于2008年正式提出了钛基金属陶瓷的概念[26]。 2.3.4 钛基金属陶瓷的定义 所谓钛基金属陶瓷就是一种从性能功能上来说,心部具有金属强韧,表面具有陶瓷坚硬耐磨;从成分结构上来说,是沿着某一方位(一维、二维或者三维)向另一方位连续地变化,使材料的性能和功能也呈现梯度变化;而从界面特征上来说,是在金属和陶瓷之间没有明显的界面特征,陶瓷与金属间应有牢固的结合,有别于通常的涂层的特殊材料。 钛基金属陶瓷的概念与传统的金属陶瓷、功能梯度涂层和Oxinium提出的过渡表面是相互联系、相互包容的,并不是一种对立关系,随着材料技术的发展和进步,将会进一步扩展材料的内涵,共同促进高性能的材料的发展。 2.4 钛基金属陶瓷的表征 X射线物相分析:中国矿业大学生物摩擦学团队在钛合金表面,采用分级渗碳技术制备出了钛基金属陶瓷,并对其进行了表面X射线衍射物相分析[35]。分析发现,实验生成的钛金属陶瓷与面心立方碳化钛的标准衍射图谱完全吻合,表明在钛合金表面均形成了单一的碳化钛陶瓷相。此外,没有观察到基体钛的衍射峰,表明表面的钛完全转化为碳化钛,在衍射图谱中也没有观察到TiO2和氮化钛的衍射峰,说明了该反应可有效降低氧气和氮气的浓度,该分级渗碳过程中极高的碳势使钛与氧的反应被有效地抑制,而碳粒子在高温下具有极强的活性和能量,在碳势的驱动下向钛合金基体扩散,随着扩散的进行,碳粒子与钛合金表面的钛发生反应,生成碳化钛陶瓷层。 X射线光电子能谱分析:中国矿业大学生物摩擦学团队前期的成果中对钛基金属陶瓷的表面成分进行了分析[35]。对其进行X射线光电子能谱分析发现,Ti2p峰对应有两个能级峰,分别是结合能为454.9 eV处的Ti2p3/2峰和461 eV处的Ti2p1/2峰,这两个峰正是碳化钛所对应的能级峰,充分表明了表面的钛是以碳化钛的形式存在的[36]。同时,钛金属陶瓷表面的钛不是以二氧化钛的形式存在[37]。在X射线光电子能谱浓度分析中注意到了大量的碳元素存在于表面,从C的X射线光电子光谱可以看出,C1s有2个很强的能级峰,一个是结合能为281.6 eV的C1s峰,对应于TiC中的C1s峰,另一个是结合能为284.7 eV处的C1s峰,对应于游离态的碳的C1s峰,表明钛金属陶瓷表面有游离态的碳单质存在[38]。 纳米压痕硬度:中国矿业大学生物摩擦学团队前期的研究中也对钛基金属陶瓷的微孔进行了纳米压痕表征,表征结果发现,未渗碳之前的钛合金纳米硬度仅5.161 5 GPa,而钛基金属陶瓷的纳米硬度可达到 15 GPa[39],钛金属陶瓷表面纳米硬度的提高表明生成了坚硬的碳化钛陶瓷,其坚硬的碳化钛陶瓷又形成复杂的微孔结构,而较厚的扩散层也对表面碳化钛提供了有效的支撑,因而使钛金属陶瓷显示出了较强的支撑能力和承受载荷的能力。 钛基金属陶瓷的表面形貌:图1为传统烧结法制备金属陶瓷的表面背散射图像[40],图2为钛金属陶瓷的表面背散射图像[41]。两者之间既有相似性,又彼此间存在区别。两者虽然都是多孔结构,但后者显然是更加均匀的微孔结构。据认为,这种独特的结构可在磨损试验过程中沉积润滑剂和碎屑,从而改善润滑,因此这将有助于减小磨损,这使得微多孔钛金属陶瓷在生物摩擦学的应用中被认为是潜在的超高耐磨损性材料。 "
| [1]马军峰,刘志斌,贾托,等.全陶瓷人工髋关节的研究进展[J].延安大学学报:医学科学版, 2012,(3):54-56. [2]朱金国,夏建龙.人工关节材料的研究进展与骨科临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(19): 3697-3700. [3]张晓南,徐瑞泽,吴刚,等.不同生物材料假体在人工关节置换中的应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(47): 8869-8874. [4]Rodeo SA,Maher SA,Hidaka C.What's new in orthopaedic research.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86(9):2085-2095. [5]李奇.努力提高金属对金属人工髋关节表面置换术的效果——严格掌握适应证和改善手术技术[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2010,4(5):570-572. [6]葛世荣,王庆良.人工关节改性材料的生物摩擦学研究[J].医用生物力学,2009,24(5):326-332. [7]刘军.人工髋关节假体磨损性能的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(35):6895-6898. [8]靳忠民,连芩,王臻,等.双动人工半膝关节假体的设计及应用[J].机械工程学报,2013, 39(2):66-74. [9]张健,安洪,周爱国,等.保留股骨距的骨水泥型双动半髋人工关节置换治疗高龄转子间骨折[J].激光杂志, 2006, 27(3):94-95. [10]Thillemann TM,Pedersen AB,Mehnert F,et al.The Risk of Revision After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Among Statin Users.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(5):1063- 1072. [11]肖小燕,刘建庭,肖瑾瑛.人工髋关节置换材料的摩擦和损耗影响因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(21):3911-3914. [12]李业海,徐俊杰.人工髋关节假体材料的生物相容性问题分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(39): 7767-7769. [13]Catelas I,Wimmer MA.New insights into wear and biological effects of metal-on-metal bearings.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2011;93(Supplement 2):76-83. [14]田鑫铎,尹文哲.人工髋关节金属对金属假体研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(12):1095-1097. [15]张方杰,雷光华.金属对金属全髋关节置换术后体内金属离子对机体的影响[J].现代生物学进展, 2011,1(13): 2558-2561. [16]Landgraeber S,Von Knoch M,Löer F,et al.ERCC1 expression in aseptic loosening after total hip replacement.J Biomed MaterRes Part A. 2010; 92(2):556-562. [17]吴竞萍,袁成清,严新平.人工髋关节超高分子量聚乙烯磨粒分析的现状及趋势[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2010, 27(1):236-240. [18]黄捷,杨丹,屈树新.超高分子量聚乙烯在人工髋关节中的摩擦磨损研究[J].材料导报, 2011,25(2):136-140. [19]王成焘.天然与人工关节中的摩擦学问题[J].生物医用力学,2009,24(5):317-325. [20]肖瑾瑛,肖小燕,唐方根,等.不同材料人工髋关节关节面磨损对无菌性松动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(35):6628-6631. [21]李强.陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节的磨擦界面特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(17):3184-3191. [22]范娜,陈光雄,钱林茂.陶瓷髋关节异响的研究进展和展望[J].摩擦学学报,2011,31(3):311-316. [23]刘敬锋, 冯建民. 陶瓷对陶瓷全髋关节置换后的异响问题[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(17):3148-3155. [24]Maya AEA,Grana DR,Hazarabedian A,et al.Zr–Ti–Nb porous alloys for biomedical application.Mater Sci Eng C.2012;32(2):321-329. [25]Souza SA,Manicardi RB,Ferrandini PL,et al.Effect of the addition of Ta on microstructure and properties of Ti–Nb alloys.J Alloy Compd.2010;504(2):330-340. [26]罗勇.钛金属陶瓷制备及其生物摩擦学性能研究[D].徐州:中国矿业大学,2008. [27]Al-Qutub AM,Allam IM,Samad MA.Wear and friction of Al–Al2O3 composites at various sliding speeds.J Mater Sci.2008;43(17):5797-5803. [28]徐强,张幸红,曲伟,等.金属陶瓷的研究进展[J].硬质合金, 2002,19(4):221-225. [29]宋杰光,王瑞花,王秀琴,等.烧结工艺对氧化铝-铝金属陶瓷材料性能的影响[J].材料热处理学报, 2015,36(2):17-20. [30]马涛,赵忠民,刘良祥,等.功能梯度材料的研究进展及应用前景[J].化工科技,2012, 20(1):71-75. [31]李智慧,何小凤,李运刚.功能梯度材料的研究现状[J].河北理工学院学报,2007,29(1):45-50. [32]Sobhy M.A comprehensive study on FGM nanoplates embedded in an elastic medium .Compos Struct. 2015; 134:966-980. [33]唐思文,刘德顺,李鹏南,等.TiCN基梯度功能金属陶瓷的制备及其切削性能[J].功能材料, 2014,45(13):13126-13130. [34]Morison ZA,Patil S,Khan HA,et al.A randomized controlled trial comparing Oxinium and cobalt-chrome on standard and cross-linked polyethylene.J Arthroplasty.2014; 29(9):164-168. [35]Luo Y,Ge S,Jin Z,et al.Formation of titanium carbide coating with micro-porous structure.Applied Physics A.2010;98(4):765-768. [36]Teghil R,D'Alessio L,De Bonis A,et al.Femtosecond pulsed laser ablation and deposition of titanium carbide.Thin Solid Films.2006;515(4):1411-1418. [37]King D,Liang X,Zhou Y,et al.Atomic layer deposition of TiO2 films on particles in a fluidized bed reactor.Powder Technol.2008;183(3):356-363. [38]Feng WR,Liu CZ,Chen GL,et al.Titanium carbonitride films on cemented carbide cutting tool prepared by pulsed high energy density plasma.Appl Surf Sci.2007; 253(11):4923-4927. [39]Luo Y,Chai W,Yang L,et al.The surface characterization of microporous titanium carbide coating on titanium alloys. P I Mech Eng-J Eng Tribol. 2014;228(5):521-528. [40]Zhao Y,Zheng Y,Zhou W,et al.Characterization of functionally gradient Ti (C, N)-based cermets fabricated by vacuum liquid phase sintering and nitriding treatment during cooling.Int J Refract Met H.2014;46:20-23. [41]Luo Y,Ge S,Liu H,et al.Microstructure analysis and wear behavior of titanium cermet femoral head with hard TiC layer.J Biomech.2009;42(16):2708-2711. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||