Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (36): 5432-5439.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.36.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for post-transplant renal function: a Meta-analysis
Chen Cheng, Gu Yu-wei, Zhang Jun, Hu Lin-kun, Wei Xue-dong, Hou Jian-quan
- Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2016-06-17Online:2016-09-02Published:2016-09-02 -
Contact:Hou Jian-quan, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Chen Cheng, Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Cheng, Gu Yu-wei, Zhang Jun, Hu Lin-kun, Wei Xue-dong, Hou Jian-quan. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for post-transplant renal function: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(36): 5432-5439.
share this article
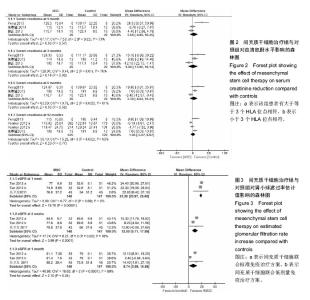
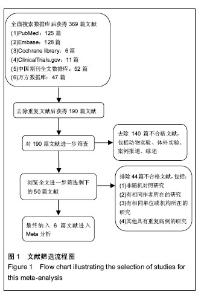
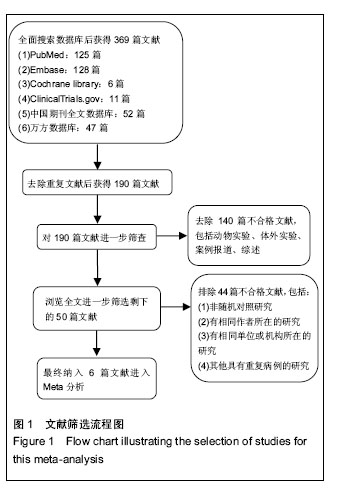
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 血清肌酐水平评价移植肾指标 见图2。 有3个研究报道了移植后1个月的血清肌酐水平[8-10],共58例,实验组和对照组均为29例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.02,I2=73%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=3.68,95%CI (-9.09,16.45),P=0.57]。 有3个研究报道了移植后3个月的血清肌酐水平[8-10],共58例,实验组和对照组均为29例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.01,I2=76%),故采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=1.09,95%CI(-13.96,16.14),P=0.89]。 有3个研究报道了移植后6个月的血清肌酐水平[8-10],共58例,实验组和对照组均为29例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.005,I2=81%),采用随机效应模型分析。Meta分析结果显示间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=3.39,95%CI (-8.64,15.41),P=0.58]。 有3个研究报道了移植后12个月的血清肌酐水 平[8-11],共954例,其中实验组625例,对照组329例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.002,I2=80%),故采用随机效应模型分析。Meta分析结果显示间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=1.05,95%CI(-5.97,8.07),P=0.77]。 2.3.2 肾小球滤过率估计值评价移植肾指标 见图3。 有2个研究报道了移植后1周的肾小球滤过率估计值水平[12-13],共295例,其中实验组148例,对照组147例。异质性检验显示各研究之间无异质性(P=0.68,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型分析,结果显示间充质干细胞治疗组的肾小球滤过率估计值比对照组平均高23.28 mL/min per 1.73 m2,其差异有显著性意义[WMD=23.28,95%CI(20.97,25.60),P < 0.000 01]。 有2个研究报道了移植后2周的肾小球滤过率估计值水平[12-13],共295例,其中实验组148例,对照组147例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.02,I2=76%),采用随机效应模型分析,Meta分析结果示间充质干细胞治疗组的肾小球滤过率估计值比对照组平均高12 mL/min per 1.73 m2,其差异有显著性意义[WMD=12.00,95%CI(6.11,17.89),P < 0.000 1]。 有2个研究报道了移植后4周的肾小球滤过率估计值水平[12-13],共295例。其中实验组148例,对照组147例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P < 0.000 1, I,故采用固定效应模型分析,结果示间充质干细胞治疗组的肾小球滤过率估计值比对照组平均高8.74 mL/min per 1.73 m2,其差异有显著性意义[WMD=8.74,95%CI(0.58, 16.89),P=0.04]。2=89%)"

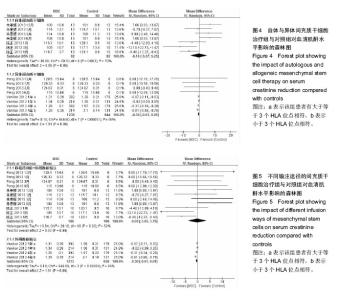
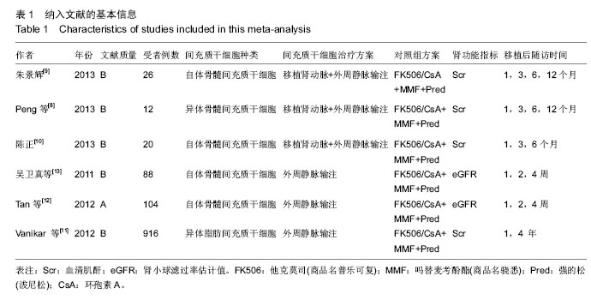
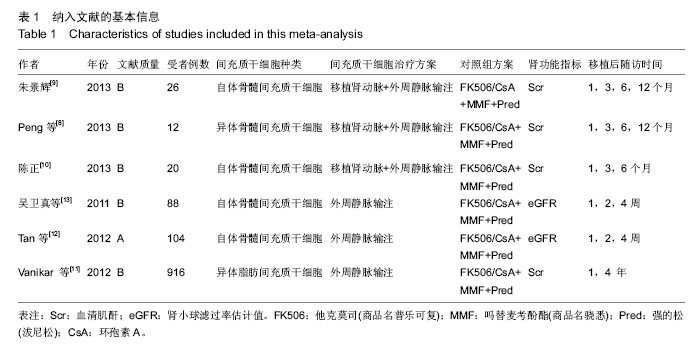
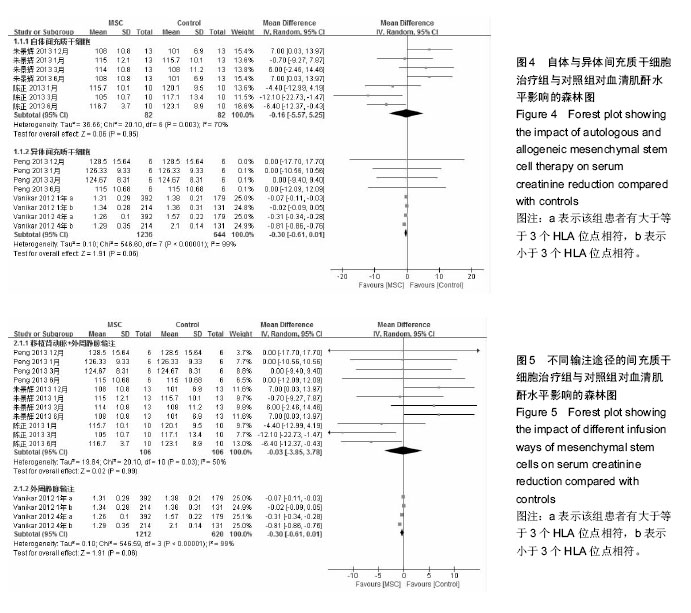
2.3.3 不同来源间充质干细胞对血清肌酐水平的影响 见图4。 有2个研究报道了移植后1,3,6,12个月的血清肌酐水平[9-10],共164例,实验组和对照组均为82例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.003,I2=70%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示自体间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义 [WMD=-0.16,95%CI(-5.57,5.25),P=0.95]。 有2个研究报道了移植后1,3,6,12个月和4年的血清肌酐水平[8,11],共1 880例,实验组1 236例,对照组644例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),故采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示异体间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=-0.30,95% (-0.61,0.01),P=0.06]。 2.3.4 不同输注途径的间充质干细胞对血清肌酐水平的影响 见图5。 有3个研究报道了移植后1,3,6,12个月的血清肌酐水平[8-10],共212例,实验组和对照组均为106例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P=0.03,I2=50%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示经移植肾动脉联合外周静脉输注间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=-0.03,95%CI (-3.85,3.78),P=0.99]。 有1个研究报道了移植后1年和4年的血清肌酐水平[11],共1 832例,实验组1 212例,对照组620例。异质性检验显示各研究之间有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),故采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示经外周静脉输注的间充质干细胞治疗组与对照组相比,其差异无显著性意义[WMD=-0.30,95%CI(-0.61,0.01),P=0.06]。"
| [1] Hardinger KL, Koch MJ, Brennan DC. Current and future immunosuppressive strategies in renal transplantation. Pharmacotherapy. 2004;24(9):1159- 1176. [2] Therasse A, Wallia A, Molitch ME. Management of post-transplant diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2013; 13(1): 121-129. [3] Guerra G, Ilahe A, Ciancio G. Diabetes and kidney transplantation: past, present, and future. Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12(5):597-603. [4] Ren G, Chen X, Dong F, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells and translational medicine: emerging issues. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(1): 51-58. [5] Algeri M, Conforti A, Pitisci A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells and chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):191-200. [6] Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience. J Intern Med. 2007;262(5):509-525. [7] Lalu MM, McIntyre L, Pugliese C, et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47559. [8] Peng Y, Ke M, Xu L, et al. Donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with low-dose tacrolimus prevent acute rejection after renal transplantation: a clinical pilot study. Transplantation. 2013;95(1):161-168. [9] 朱景辉.自体BM-MSC诱导亲属活体供肾移植免疫耐受的临床研究[D]. 广州:广州医学院, 2013. [10] 陈正. BM-MSC诱导移植免疫耐受和修复慢性移植肾损伤的初步研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013. [11] Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL. Stem cell transplantation in living donor renal transplantation for minimization of immunosuppression. Transplantation. 2012;94(8): 845-850. [12] Tan J, Wu W, Xu X, et al. Induction therapy with autologous mesenchymal stem cells in living-related kidney transplants: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;307(11):1169-1177. [13] 吴卫真,谭建明,孙星慧,等. 术前自体间充质干细胞输注用于肾移植诱导治疗的临床研究[J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 2011,32(11): 647-650. [14] Hariharan S, McBride MA, Cherikh WS, et al. Post-transplant renal function in the first year predicts long-term kidney transplant survival. Kidney Int. 2002; 62(1):311-318. [15] Bank JR, Rabelink TJ, de Fijter JW, et al. Safety and Efficacy Endpoints for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Renal Transplant Recipients. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:391797. [16] Ma YC, Zuo L, Chen JH, et al. Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17(10):2937-2944. [17] Chen C, Hou J. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy in kidney transplantation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7: 16. [18] Liu H, Xia X, Li B. Mesenchymal stem cell aging: Mechanisms and influences on skeletal and non-skeletal tissues. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015; 240(8):1099-1106. [19] Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC.Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells.J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:19. [20] Schrepfer S, Deuse T, Reichenspurner H, et al. Stem cell transplantation: the lung barrier. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(2):573-576. [21] Fischer UM, Harting MT, Jimenez F, et al. Pulmonary passage is a major obstacle for intravenous stem cell delivery: the pulmonary first-pass effect. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(5):683-692. [22] Leuning DG, Reinders ME, de Fijter JW, et al. Clinical translation of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in transplantation. Semin Nephrol. 2014;34(4):351-364. [23] Crop MJ, Korevaar SS, de Kuiper R, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells are susceptible to lysis by CD8(+) T cells and NK cells. Cell Transplant. 2011; 20(10):1547-1559. [24] Roemeling-van Rhijn M, Weimar W, Hoogduijn MJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: application for solid-organ transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2012; 17(1):55-62. [25] Zhang W, Qin C, Zhou ZM. Mesenchymal stem cells modulate immune responses combined with cyclosporine in a rat renal transplantation model. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(10):3404-3408. [26] Inoue S, Popp FC, Koehl GE, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat organ transplant model. Transplantation. 2006;81(11): 1589-1595. [27] 张磊,陈正,谢斯盛,等.自身间充质干细胞治疗慢性移植物肾病的安全性与可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(32):5140-5145. [28] El-Ansary M, Saadi G, Abd El-Hamid SM. Mesenchymal stem cells are a rescue approach for recovery of deteriorating kidney function. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012;17(7):650-657. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [5] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [6] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [8] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [9] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [10] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [11] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [12] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [13] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [14] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [15] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||