Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (36): 5364-5370.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.36.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Variation of blood biochemical indices in liver cirrhosis rats after adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
Han Hai-yan1, Song Wen-guang2
- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, 2Reproductive Medicine Center, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of CAPF, Tianjin 300162, China
-
Revised:2016-07-27Online:2016-09-02Published:2016-09-02 -
About author:Han Hai-yan, Laboratory technician, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of CAPF, Tianjin 300162, China Song Wen-guang, Technologist-in-charge, Reproductive Medicine Center, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of CAPF, Tianjin 300162, China Han Hai-yan and Song Wen-guang contributed equally to this work.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Hai-yan, Song Wen-guang. Variation of blood biochemical indices in liver cirrhosis rats after adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(36): 5364-5370.
share this article
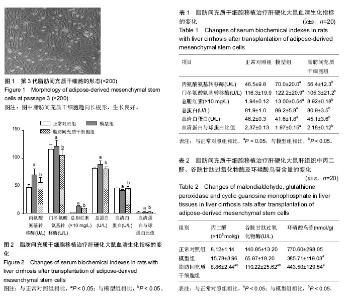
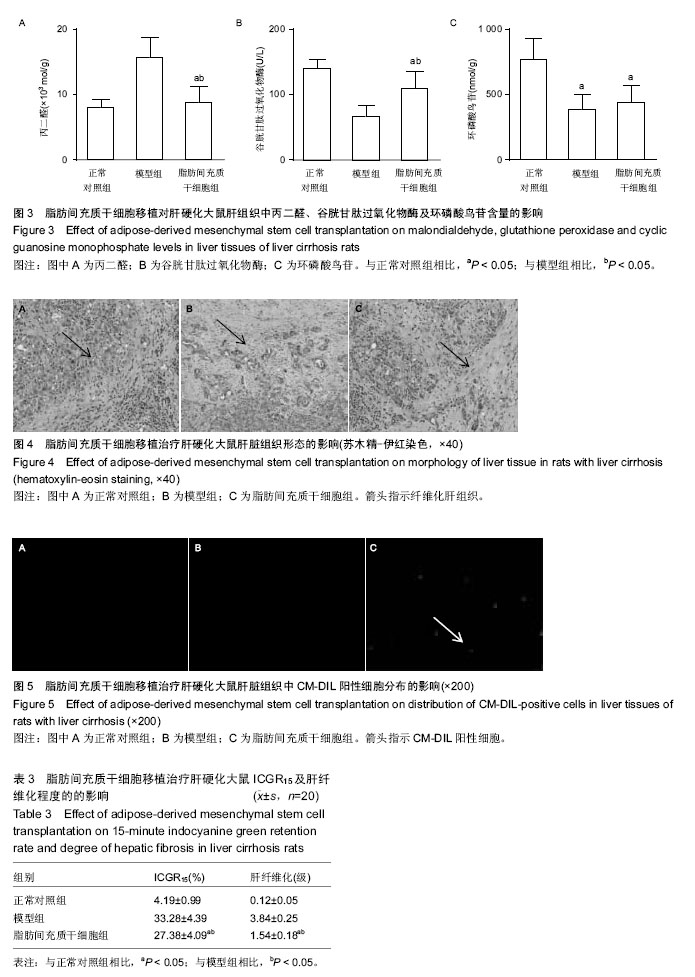
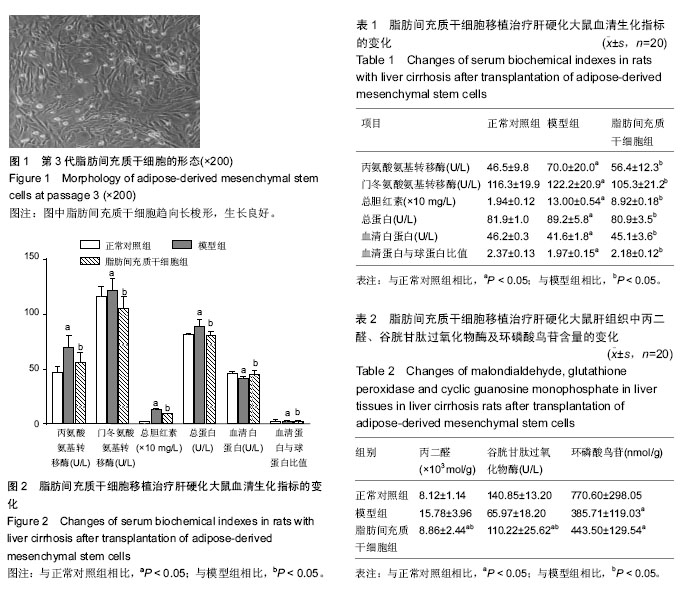
2.1 脂肪间充质干细胞的形态 脂肪间充质干细胞复苏后体外培养48 h,可见长梭形、纺锤状或不规则形态的脂肪间充质干细胞,传代培养后的脂肪间充质干细胞生长模式与原代培养的脂肪间充质干细胞相似,但细胞增殖速度要比原代显著加快。传代2 h后即可贴壁,3 d后成纤维样细胞明显增多,胞质丰富,胞核清晰。7 d后脂肪间充质干细胞单层融合可达90%,细胞呈平行排列生长或漩涡状克隆样生长。第3代脂肪间充质干细胞生长旺盛,形态渐趋一致、愈趋向长梭形,以一点为中心向两头呈放射状。细胞呈复层生长,胞膜完整、细胞状态良好,细胞间联系紧密(图1)。 2.2 实验动物数量分析 体内实验所用大鼠60只,全部进入结果分析。 2.3 血清生化检测结果 与对照组相比,模型组大鼠血清中丙氨酸氨基转移酶、门冬氨酸氨基转移酶、总胆红素、总蛋白含量均显著升高(P < 0.05),血清白蛋白、血清蛋白与球蛋白比值含量明显下降(P < 0.05),而与模型组相比,脂肪间充质干细胞组上述指标明显恢复(P < 0.05;表1,图2)。 2.4 肝组织丙二醛、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及环磷酸鸟苷水平 与对照组比较,模型组中丙二醛含量显著升高,而与模型组比较,脂肪间充质干细胞组大鼠肝组织中丙二醛含量均显著下降(P < 0.05),与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织中谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及环磷酸鸟苷含量明显下降,而与模型组比较,脂肪间充质干细胞组大鼠肝组织中谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及环磷酸鸟苷含量明显升高(P < 0.05;表2,图3)。 2.5 大鼠ICGR15及肝纤维化程度 与对照组比较,模型组ICGR15及肝纤维化程度明显上升,而与模型组比较,脂肪间充质干细胞组ICGR15及肝纤维化程度明显减轻(P < 0.05;表3)。 2.6 脂肪间充质干细胞移植效果 移植后4周,苏木精-伊红染色,正常对照组未见明显肝组织纤维化,肝纤维化程度为0级,模型组可见明显的肝组织纤维化组织,肝纤维化程度为4级,脂肪间充质干细胞组可见少量肝组织纤维化,肝纤维化程度为1级(图4)。脂肪间充质干细胞组可见CM-Dil标记的阳性脂肪间充质干细胞,阳性率可达90%,正常对照组及模型组未见CM-Dil标记阳性细胞(图5)。"
| [1] 于皆平,沈志祥,罗和生.实用消化病学[M].2版.北京:科学出版社,2007:743. [2] 陈园生,李黎,崔富强,等.中国丙型肝炎血清流行病学研究[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2011,32(9):888-891. [3] 吴家兵,龚磊,王爱红,等.2004-2011 年安徽省丙型病毒性肝炎流行特征分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2012, 16(11): 965-967. [4] Jin SG, Yan LN, Xiang B, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder after liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012;11(1):28-33. [5] Guimaro MS, Lacerda SS, Aguilar MR, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorders, mood disorders, and quality of life in transplant recipients with acute liver failure. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(1):187-188. [6] Neff GW, Duncan CW, Schiff ER. The current economic burden of cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 2011;7(10):661-671. [7] Lindenmair A, Hatlapatka T, Kollwig G, et al. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells from amnion and umbilical cord tissue and their potential for clinical applications. Cells. 2012;1(4):1061-1088. [8] 胡泽斌,王立生,崔春萍,等.干细胞临床应用安全性评估报告[J].中国医药生物技术,2013,8(5):349-361. [9] Amable PR, Teixeira MV, Carias RB, et al. Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jelly. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):53. [10] de Girolamo L, Lucarelli E, Alessandri G, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new ''cells as drugs'' paradigm. Efficacy and critical aspects in cell therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(13):2459-2473. [11] Puglisi MA, Tesori V, Lattanzi W, et al. Therapeutic implications of mesenchymal stem cells in liver injury. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:860578. [12] Almeida-Porada G, Zanjani ED, Porada CD. Bone marrow stem cells and liver regeneration. Exp Hematol. 2010;38(7):574-580. [13] Sirivatanauksorn Y, Dumronggittigule W, Limsrichamrern S, et al. Quality of life among liver transplantation patients. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(2):532-538. [14] Jung Y, Chung YI, Kim SH, et al. In situ chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells in a TGF-beta1 loaded fibrin-poly(lactide-caprolactone) nanoparticulate complex. Biomaterials. 2009;30(27):4657-4664. [15] Nincheri P, Luciani P, Squecco R, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards smooth muscle cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(10): 1741-1754. [16] 张云巍,徐丽娟,王淑芳,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞体外分离、培养的方法研究[J].肝脏.2014(10):752-755. [17] Ma S, Xie N, Li W, et al. Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):216-225. [18] Cuiffo BG, Karnoub AE. Mesenchymal stem cells in tumor development: emerging roles and concepts. Cell Adh Migr. 2012;6(3):220-230. [19] Takami T, Terai S, Sakaida I. Stem cell therapy in chronic liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012; 28(3):203-208. [20] Russo FP, Parola M. Stem cells in liver failure. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26(1):35-45. [21] Takami T, Terai S, Sakaida I. Advanced therapies using autologous bone marrow cells for chronic liver disease. Discov Med. 2012;14(74):7-12. [22] 闫俊卿,韩涛,朱争艳.脐血间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化的研究进展[J].武警医学院学报,2008,17(3):250-252. [23] 王方,张小岗,张静,等.自体骨髓干细胞治疗失代偿期肝硬化患者50例疗效观察[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2010,13(4): 272-274. [24] Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, et al. Stem cell therapy for liver disease: parameters governing the success of using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):2111-2121. [25] Pilgaard L, Lund P, Duroux M, et al. Transcriptional signature of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hASCs) preconditioned for chondrogenesis in hypoxic conditions. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(11):1937-1952. [26] Xie LW, Fang H, Chen AM, et al. Differentiation of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards a nucleus pulposus-like phenotype in vitro. Chin J Traumatol. 2009;12(2):98-103. [27] Li J, Gao JH, Lu F, et al. Experimental study of the effect of adipose tissue derived stem cells on the survival rate of free fat transplantation. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;25(2):129-133. [28] Li Q, Zhou X, Shi Y, et al. In vivo tracking and comparison of the therapeutic effects of MSCs and HSCs for liver injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62363. [29] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6): 845-854. [30] Hong J, Jin H, Han J, et al. Infusion of human umbilical cord?derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively relieves liver cirrhosis in DEN?induced rats. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(4):1103-1111. [31] Fiore EJ, Bayo JM, Garcia MG, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells engineered to produce IGF-I by recombinant adenovirus ameliorate liver fibrosis in mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(6):791-801. [32] Wang PP, Xie DY, Liang XJ, et al. HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43408. [33] Chen S, Xu L, Lin N, et al. Activation of Notch1 signaling by marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through cell-cell contact inhibits proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 2011;89(25-26):975-981. [34] Wells RG. Cellular sources of extracellular matrix in hepatic fibrosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2008;12(4):759-768, viii. [35] Suominen JS, Lampela H, Heikkilä P, et al. Myofibroblastic cell activation and neovascularization predict native liver survival and development of esophageal varices in biliary atresia. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(12):3312-3319. [36] 乔飞,张馨,盛云峰,等.脐带血干细胞治疗肝硬化失代偿期疗效观察[J].中国肝脏病杂志,2011,3(2):10-13. [37] di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 2008;57(2):223-231. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||