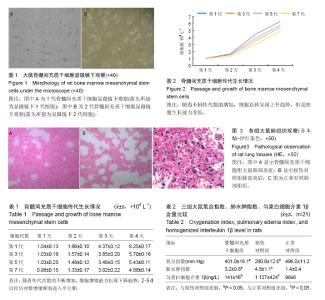
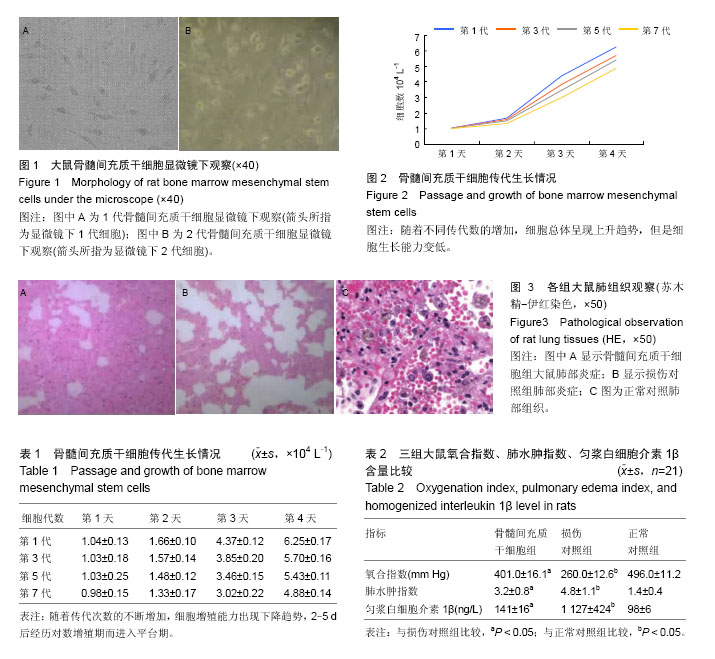
| [1] Pereira T, Armada-da Silva PA, Amorim I, et al. Effects of human-mesenchymal stem cells is olatedfromwharton's jelly of the umbilical cord and conditioned media on skeletal muscle regenerationusing a myectomymodel. Stem Cells Int.2014;2014: 376918.
[2] 强勇,梁贵友.间充质干细胞移植治疗急性呼吸窘迫综合征的研究进展[J/CD].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2014,4(3):211-216.
[3] 甄国华,刘红梅,张珍祥,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对木瓜蛋白酶和[-(60)Co]射所致大鼠肺气肿的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2008,24(8):1529-1533.
[4] Fang X,Neyrinck AP,Matthay MA,et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells restore epithelial protein permeability in cultured human alveolar type II cells by secretion of angiopoietin-1. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(34):26211-26222.
[5] 陈建,许林.胸外科手术致急性呼吸窘迫综合征的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2009,22(02):205-208.
[6] 黄坤,吴晓梅,王欣燕,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向肺泡细胞转化的实验研究[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2011,10(06): 572-576.
[7] Bassi EJ,Aita CA,Camara NO. Immune regulatory properties of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells:Where do we stand. World J Stem Cells.2011; 3(1):1-8.
[8] Lee RH,Pulin AA,Seo MJ,et al. Intravenous hMSC improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009; 5(1):54-63.
[9] Bove PF,Grubb BR,Okada SF,et al. Human alveolar typeⅡ cells secrete and absorb liquid in response to local nucleotide signaling.J Biol Chem.2010;285(45) : 34939-34949.
[10] 周晓光,刘秀香,刘任红,等.高氧暴露早产大鼠肺泡上皮细胞损伤与细胞外基质变化的动态研究[J].中国新生儿科杂志,2008,23(4):215-218.
[11] 李百玲,柴家科,段红杰,等.肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞在急性呼吸窘迫综合征/急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2014,9(3):323-325.
[12] Goto H,Ledford JG,Mukherjee S,et al.The Role of Surfactant Protein A in Bleomycin-induced Acute Lung Injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2010;181(12) : 1336-1344.
[13] Bove PF,Grubb BR,Okada SF,et al.Human alveolar typeⅡ cells secrete and absorb liquid in response to local nucleotide signaling.J Biol Chem.2010;285(45) : 34939-34949.
[14] 中华医学会重症病学分会.急性呼吸窘迫综合征/急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊断与治疗指南(2006)[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2007,16(4):343-349.
[15] 顾晓凌,宋勇.线粒体DNA在急性呼吸窘迫综合征发生、发展中的作用[J].中华肺部疾病杂志:电子版,2012,5(4): 348-350.
[16] 马李杰,李王平,金发光.急性呼吸窘迫综合征/急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].中华肺部疾病杂志:电子版,2013,6(1):65-68.
[17] 刘涛,任成山.炎症介质在急性呼吸窘迫综合征/急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制中的作用[J].中华肺部疾病杂志:电子版,2013,6(3):265-269.
[18] Spragg RG,Bernard GR,Checkley W,et al. Beyond mortality: future clinical research in acute lung injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2010; 181(10): 1121-1127.
[19] Meyer NJ,Li M,Feng R,et al.ANGPT2 genetic variant is associated with trauma-associated acute lung injury and altered plasma angiopoietin-2 isoform ratio. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2011;183(10):1344-1353.
[20] Brown LM,Calfee CS,Matthay MA,et al. A simple classification model for hospital mortality in patients with acute lung injury managed with lung protective ventilation. Crit Care Med.2011;39(12):2645-2651.
[21] Kangelaris KN,Sapru A,Calfee CS,et al.The association between a Darc gene polymorphism and clinical outcomes in African American patients with acute lung injury. Chest.2012;141(5):1160-1169.
[22] 施卉,任成山.急性呼吸窘迫综合征/急性呼吸窘迫综合征基础及临床研究进展[J].中华肺部疾病杂志:电子版, 2013, 6(4):350-355.
[23] 李天林,文文,赖国祥,等.血管紧张素转化酶2在海水淹溺诱导大鼠急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的作用[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2012,11(6):537-540.
[24] 张新红,段蕴铀,芮萌,等.不同剂量地塞米松对海水淹溺型急性呼吸窘迫综合征的治疗作用观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2009,34(7):815-818.
[25] Hayashi Y, Tsuji S, Tsujii M,et al.Topical implantation of mesenchymal stem cells has beneficial effects on healing of experimental colitis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;326(2):523-531.
[26] Sueblinvong V,Weiss DJ. Cell therapy approaches for lung diseases:current status. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9(3): 268-273.
[27] Todeschi MR,E Backly R,Capelli C,et al. Transplantedumbilical- cordmesenchymal stem cellsmodify the in vivo microenvironmenten- hancingangiogenesis and leading to boneregeneration. Stem Cells Dev.2015;24(13): 1570-1581.
[28] Wang L,Seshareddy K,Weiss ML,et al.Effect of initial seeding-density on human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromalcells for fibro cartilage tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(5):1009-1017.
[29] 华静,冯华松,王庆,等.海水淹溺致大鼠急性呼吸窘迫综合征模型的建立.现代生物医学进展,2013,13(27):5242- 5246.
[30] 张红霞,王蒙蒙,李惠萍,等.白藜芦醇对博来霉素诱导小鼠肺损伤的保护作用.第二军医大学学报,2013,34(12): 1287-1290.
[31] 张祺嘉钰,王国全,余林中,等.两种内毒素经支气管给药致急性呼吸窘迫综合征模型再评价研究[J].中药药理与临床,2012,28(5):226-229.
[32] 张兵华,费晋秀,赵亚玲,等.兔海水淹溺性肺水肿与钠钾-ATP酶的关系及不同剂量地塞米松对其影响[J].陕西医学杂志,2011,40(1):11-14.
[33] Ohno N,Kajiume T,Sear Y,et al.Short-term culture of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34 cells enhances engraftment into NOD/SCID mice through increased CXCR4 expression. Stem Cells Dev.2009;18(8): 1221-1226.
[34] 顾兴,金发光,刘同刚.三七总皂苷对海水淹溺兔肺泡巨噬细胞TNF-αmRNA表达的影响.中国中医急症,2011, 20(10):1608-1610.
[35] 曹万英,金发光,罗颖,等.乌司他丁治疗大鼠海水淹溺型急性呼吸窘迫综合征的实验观察[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2011,10(2):139-143.
[36] 郭帅,曾志勇,杨胜生,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对海水淹溺致急性呼吸窘迫综合征治疗作用的研究进展[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2015,22(4):375-379.
[37] Peek GJ,Mugford M,Tiruvoipati R,et al.Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 374(9698):1351-1363. |