Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (28): 4189-4195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.28.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of bone marrow stromal stem cells against acute lung injury after hip fracture in aged rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Zhang Gui-tong1, 2, Feng Jie-yang2, Liu Jia2, Zhang Yan-jin2, Xiang Zi-min2, Meng Fan-xing2,Sun Tian-sheng1, 2
- 1Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
2Beijing Army General Hospital, Beijing 100700, China
-
Revised:2016-05-19Online:2016-07-01Published:2016-07-01 -
Contact:Sun Tian-sheng, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Beijing Army General Hospital, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Zhang Gui-tong, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project, No. 2010DFA31250
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Gui-tong, Feng Jie-yang, Liu Jia, Zhang Yan-jin, Xiang Zi-min, Meng Fan-xing,Sun Tian-sheng. Protective effect of bone marrow stromal stem cells against acute lung injury after hip fracture in aged rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(28): 4189-4195.
share this article
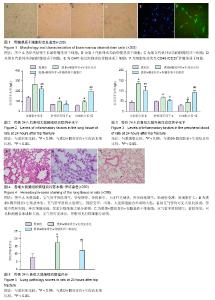
2.1 骨髓基质干细胞形态及鉴定结果 ①形态观察发现,贴壁细胞呈单个分散或成簇生长,细胞形态均匀,多呈长梭形、纺锤形(图1A,B,C,D);②细胞免疫荧光检测紫外线激发后DAPI标记的骨髓基质干细胞的细胞核显示蓝色,红光激发后CD29单克隆抗体显示绿色荧光,CD45单克隆抗体不显影(图1E,F);③流式细胞仪检测到CD29阳性细胞占全部细胞94%以上,CD45阳性细胞为5%。 2.2 实验动物数量分析 参加实验动物数量30只,全部进入结果分析。 2.3 肺组织及血浆中炎症因子水平 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠闭合性髋部骨折后,肺组织出现炎细胞浸润、黏液分泌、气管腔狭窄或闭塞,肺组织白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素10水平增高。 静脉注射骨髓基质干细胞后,肺组织病理改变较生理盐水组减轻,促炎因子白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平低于生理盐水组,抗炎因子白细胞介素10水平高于生理盐水组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 血浆中促炎因子白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平低于生理盐水组,抗炎因子白细胞介素10水平高于生理盐水组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.4 肺部组织病理学改变 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠髋部骨折后,在原有病变的基础上,出现大量中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞浸润与聚集,管腔分泌物明显增多。经尾静脉注射骨髓基质干细胞,肺部炎症细胞浸润少,分泌物减少(图4)。 给予骨髓基质干细胞干预后上述表现明显减轻,两组之间的肺组织损伤评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图5。"

| [1] Schrøder HM, Andreassen MD, Villadsen I, et al. Increasing age-specific incidence of hip fractures in a Danish municipality. Dan Med Bull. 1995;42(1): 109-111. [2] Dash SK, Panigrahi R, Palo N, et al. Fragility Hip Fractures in Elderly Patients in Bhubaneswar, India (2012-2014): A Prospective Multicenter Study of 1031 Elderly Patients. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015; 6(1):11-15. [3] Karampampa K, Ahlbom A, Michaëlsson K, et al. Declining incidence trends for hip fractures have not been accompanied by improvements in lifetime risk or post-fracture survival--A nationwide study of the Swedish population 60 years and older. Bone. 2015;78:55-61. [4] Forsén L, Sogaard AJ, Meyer HE, et al. Survival after hip fracture: short- and long-term excess mortality according to age and gender. Osteoporos Int. 1999; 10(1):73-78. [5] Deakin DE, Boulton C, Moran CG. Mortality and causes of death among patients with isolated limb and pelvic fractures. Injury. 2007;38(3):312-317. [6] Paksima N, Koval KJ, Aharanoff G, et al. Predictors of mortality after hip fracture: a 10-year prospective study. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66(2):111-117. [7] Crisostomo PR, Markel TA, Wang Y, et al. Surgically relevant aspects of stem cell paracrine effects. Surgery. 2008;143(5):577-581. [8] Tominaga T, Takeshita H, Takagi K, et al. E-PASS score as a useful predictor of postoperative complications and mortality after colorectal surgery in elderly patients. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016;31(2): 217-225. [9] de Luise C, Brimacombe M, Pedersen L, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and mortality following hip fracture: a population-based cohort study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2008;23(2):115-122. [10] Roche JJ, Wenn RT, Sahota O, et al. Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2005; 331(7529):1374. [11] Wang CB, Lin CF, Liang WM, et al. Excess mortality after hip fracture among the elderly in Taiwan: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Bone. 2013;56(1):147-153. [12] Alzahrani K, Gandhi R, Davis A, et al. In-hospital mortality following hip fracture care in southern Ontario. Can J Surg. 2010 Oct;53(5):294-298. [13] Gan L, Chen X, Sun T, et al. Significance of Serum mtDNA Concentration in Lung Injury Induced by Hip Fracture. Shock. 2015;44(1):52-57. [14] Sun T, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. Plasma concentrations of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and outcome prediction in elderly hip fracture patients. Injury. 2011; 42(7):707-713. [15] Kim Y, Jo SH, Kim WH, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of intravenously injected adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in dogs with acute spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6: 229. [16] 邬晓勇,刘玉杰,石斌,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进交叉韧带重建后腱骨愈合的研究[J].军医进修学院学报, 2010,31(10):954-956. [17] Weiss ML, Anderson C, Medicetty S, et al.Immune properties of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly- derived cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26(11):2865-2874. [18] Falavigna A, da Costa JC. Mesenchymal autologous stem cells. World Neurosurg. 2015;83(2):236-250. [19] 王鑫,苟文隆,徐小龙,等.骨髓间充质干细胞归巢促小鼠骨折愈合的实验研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2015,36(3): 218-223. [20] 李志锐,王玉,陈继凤,等.激素性股骨头坏死模型骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特性评估[J]. 军医进修学院学报, 2012, 33(5): 525-527,552. [21] Richardson SM, Kalamegam G, Pushparaj PN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine: Focus on articular cartilage and intervertebral disc regeneration. Methods. 2016;99:69-80. [22] 雷琰,刘长卿.骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清液治疗支气管哮喘及对肺部炎症的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(36): 5764-5768. [23] Lu D, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Intraarterial administration of marrow stromal cells in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2001;18(8):813-819. [24] Guartite A, Hbid K, Alharar R, et al. Stab wound of the spinal cord complicated by meningitis and subarachnoid fistula. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2001;20(1):47-49. [25] Mobasheri A, Kalamegam G, Musumeci G, et al. Chondrocyte and mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies for cartilage repair in osteoarthritis and related orthopaedic conditions.Maturitas. 2014;78(3): 188-198. [26] 何晓青,林育辉,黄淑玲,等.内源骨髓间充质干细胞在心肌梗死后的迁移、归巢与分化 [J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(19):2981-2985. [27] Sekiya I, Larson BL, Smith JR, et al. Expansion of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma: conditions that maximize the yields of early progenitors and evaluate their quality. Stem Cells. 2002;20(6): 530-541. [28] Hiltunen A, Vuorio E, Aro HT. A standardized experimental fracture in the mouse tibia. J Orthop Res. 1993;11(2):305-312. [29] 石涛,张立海,陈华,等.髋部骨折的性别及年龄分布分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2013, 34(1):58-59. [30] 郝玮.综合治疗老年髋部骨折的疗效分析[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2013. [31] Hao Z, Tiansheng S, Zhi L,et al. Hip fracture aggravates systemic inflammation and lung injury in aged chronic cigarette smoke exposed rats.J Orthop Res. 2014;32(1):24-30. [32] 王晓伟,孙天胜,秦聪聪.多发伤患者炎性因子变化及其临床意义[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(5):406-408. [33] Coldren CD, Nick JA, Poch KR, et al. Functional and genomic changes induced by alveolar transmigration in human neutrophils. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;291(6):L1267-1276. [34] Choban PS, Mcknight T, Flancbaum L, et al. Characterization of a murine model of acute lung injury (ALI): a prominent role for interleukin-1. J Invest Surg. 1996;9(2):95-109. [35] 卢诚.TNF-a、IL-1β在Perthes病髋关节滑膜组织中的表达及意义[D]. 南昌:南昌大学,2014. [36] Wang C, Ge J, Ni S. Effect of interleukin-6 polymorphism on fracture risk. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):9599-9602. [37] Sun T, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. Patterns of cytokine release and evolution of remote organs from proximal femur fracture in COPD rats. Injury. 2011;42(8): 825-832. [38] Zhang H, Sun T, Liu Z, et al. Systemic inflammatory responses and lung injury following hip fracture surgery increases susceptibility to infection in aged rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:536435. [39] Baëhl S, Garneau H, Le Page A, et al. Altered neutrophil functions in elderly patients during a 6-month follow-up period after a hip fracture. Exp Gerontol. 2015;65:58-68. [40] Sun Y, Yao Z, Lin P, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammatory factor-induced dysfunction of INS-1 cells on chip. Cell Biol Int. 2014; 38(5):647-654. [41] Zuo D, Tang Q, Fan H, et al. Modulation of nuclear factor-κB-mediated pro-inflammatory response is associated with exogenous administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of experimental colitis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4): 2741-2748. [42] Wang YW, Xu DP, Liu Y, et al. The Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α at Different Concentrations on Osteogenetic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26(7):2081-2085. [43] 刘婉薇,陈韵,郑跃,等. 炎症预激活骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基修复小肠黏膜急性辐射损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(10): 1544-1550. [44] 刘慧娟,戴王娟,康树敏,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺氧缺血性脑损伤大鼠脑内肿瘤坏死因子-α及白细胞介素-1 β水平的影响[J].中华围产医学杂志,2016,19(4): 301-307. [45] 刘虹,丁颖威,侯跃辉,等.携带SOD基因的骨髓间充质干细胞对小鼠百草枯肺损伤的保护作用[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2016,34(1):1-7. [46] 刘凯,李宗杰,吴海卫,等.重组人促红细胞生成素联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠体外循环肾炎症反应的影响[J].医学研究生学报,2016,29(4):364-368. [47] 刘仕欣, 颛孙永勋,谭磊,等.骨髓间充质干细胞逆转支气管哮喘小鼠气道重塑及其机制的初步研究[J].国际呼吸杂志,2016,36(2):81-85. [48] 陈杨葭,张艳金,刘佳,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对髋部骨折诱导的老年大鼠急性肺损伤的保护机制[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(6):672-676. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [9] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [13] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [14] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [15] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||