Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (21): 3178-3184.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.21.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of zirconia bioceramics and its application in prosthodontics
Wang Qiang1, 2, Yin Jiao-jiao3, Yang Hua-zhe3
- 1School of Stomatology, 3School of Fundamental Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China; 2Institute of Oral Medicine of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2016-04-19Online:2016-05-20Published:2016-05-20 -
Contact:Wang Qiang, School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China; Institute of Oral Medicine of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Qiang, Ph.D., Associate investigator, School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China; Institute of Oral Medicine of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81500897; the China Scholarship Foundation, No. 201408210385; the Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education, No. L2013285; the Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Program, No. 2014305012; Shenyang Science and Technology Project, No. F11-262-9-16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Qiang, Yin Jiao-jiao, Yang Hua-zhe. Preparation of zirconia bioceramics and its application in prosthodontics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3178-3184.
share this article
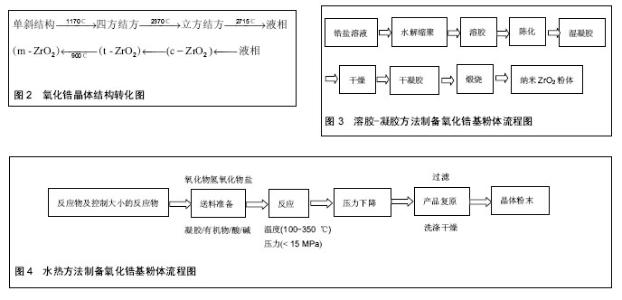
2.1 氧化锆的结构与性质 氧化锆具有良好的力学性能、热稳定性和化学稳定性。氧化锆具有高强度的力学性能,主要是因为其变相增韧现象,其晶体根据温度不同可在3种形态之间转换:单斜相(m相)、正方相 (t相)、立方相(c相)。单斜相主要存在于室温至1 170 ℃,而当温度介于1 170-2 370 ℃时主要为正方相,在 2 370 ℃以上则为立方相。所以在温度下降过程中就有从t相到m相的转变,这种转变大约会产生4.5%的体积增加。常压下氧化锆的晶体结构有3种:立方相结构(Cubic Zirconia,c-ZrO2),四方相结构(Tetrgonal Zirconia,t-ZrO2)和单斜相结构(Monoclinal,m-ZrO2)。这些结构可在不同温度范围内相互转换,并伴随着体积的变化,氧化锆的晶型转化,见图2。氧化锆的相变过程为马氏体相变,其所产生的体积变化会延缓,由于外部作用力所产生的裂纹扩展,使得ZrO2的增韧效果得以实现。为了保持在温度下降过程中氧化锆的稳定,人们加入了一些金属氧化物,如MgO、CaO,和Y2O3,以消除t相转换至m相时所产生的压力,从而防止裂缝的产生,同时增加其断裂韧性[21]。目前Y2O3稳定氧化锆(Y-TZP)具有最稳定的性能,被广泛应用于临床[22-23]。 目前,已获得临床应用的氧化锆全瓷冠修复体抗折强度大于900 MPa,抗断裂韧性大于5 MPa•m1/2,其韧性与铁及硬质合金相当,而断裂韧性和挠曲强度约是氧化铝陶瓷的2倍。氧化锆陶瓷这些优异的机械性能显著弥补了传统陶瓷材料在口腔临床应用中出现的韧性低、耐冲击性差及脆性大等问题,为其在口腔修复领域中的应用及推广创造了前提。 此外,由于口腔内部具有复杂的生物环境,作为口腔修复材料必须具有优良的化学稳定性。而氧化锆作为一种优良的生物惰性陶瓷,无论是作为口腔修复体还是植入体均表现出优异的化学稳定性能,完全满足作为口腔修复材料的标准。 2.2 氧化锆生物陶瓷的制备方法与工艺 目前,氧化锆基陶瓷的制备研究主要集中于以下方向[24-31]: ZrO2-AlO3(ZTA)增韧陶瓷体系,即将氧化锆微粒分散到其它母体陶瓷相(如氧化铝)体系;Y2O3-ZrO2 (Y-TZP)体系,即将第二相(如氧化钇)分散到氧化锆母体相体系;Mg-ZrO2(Mg-PSZ)体系,即以Mg为稳定剂的部分稳定氧化锆多晶陶瓷体系。这些研究为氧化锆基全瓷冠修复体在临床上的应用奠定了基础。 制备高性能的氧化锆基陶瓷的关键因素之一,是在制备工艺中将陶瓷制备与晶体生长控制技术(如纳米技术)相结合。氧化锆陶瓷的研制包括粉体合成、素坯成型、陶瓷烧结等几个方面。粉体合成方法主要有3类:气相法、固相法和液相法。气相法主要通过气体冷凝、真空蒸镀、加热蒸发等方法,使材料的蒸气聚集而获得粉体;固相法是通过机械粉碎或固相反应等获得粉体;而液相法则是按所制备的材料组成计量配制成溶液,使各元素呈离子或分子态,再选择一种合适的沉淀剂或用蒸发、升华、水解等操作,使金属离子均匀沉淀或结晶出来,最后将沉淀或结晶的脱水或者加热分解而得到所需材料粉体。考虑到制备粉体的成本和实验操作的难易程度,液相法是当前制备氧化锆陶瓷前驱粉体最为广泛和实用的方法。液相法包括沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法、水热法、微乳液法等,其中,沉淀法和微乳液法需要精确控制反应条件,增加了实验难度,而溶胶-凝胶方法和水热法是目前制备氧化锆粉体最为常用的方法。 溶液-凝胶法[32-38]:溶胶-凝胶方法是将锆盐溶解后,采用适当方法形成稳定凝胶,再经适当处理形成含大量水分的凝胶,最后干燥、脱水、煅烧制得纳米ZrO2粉体,其典型工艺流程见图3。该方法可以制得粒径较小、粒度分布窄、纯度高的粉体,且方法操作简单,设备价格低廉,有利于在提高原料纯度、减少有害杂质的同时降低制备的成本。但该方法在制备ZrO2粉体过程中会出现团聚现象,且晶粒尺寸无法精确控制,进而影响了陶瓷的机械性能及稳定性。这些因素限制了氧化锆增韧陶瓷在口腔医学领域的应用。 水热法[25-27]:又称热液法,在密闭容器中以水或有机溶剂为反应介质,通过高压热处理即可获得尺寸可控的微粒,其反应流程见图4。该方法不需高温煅烧,避免了湿化学法可能产生的硬团聚,产物纯度高、分散性好、晶粒尺寸精确可控,缺点是耗能高、生产周期长、设备复杂。此外,在氧化锆基复合陶瓷的制备中,由于水热析出顺序的不同易导致第二相的偏析(如Y3+在母体中分布不均匀),导致氧化锆四方相晶体结构稳定性变差。因此,无论对于溶胶-凝胶方法还是水热法,都需要对前驱体的形成及分散机制进行深入研究。如果结合两种方法的优点,通过对络合反应或水热反应平衡的控制有望获得高纯度、第二相分布均匀、晶粒尺寸精确可控的ZrO2基粉体,为下一步增韧陶瓷的制备奠定基础。 2.3 氧化锆生物陶瓷的临床应用与挑战 迄今为止,在成品氧化锆基全瓷冠修复体的制备上,美国的3M公司(3M ESPE),列支敦士登的义获嘉公司(Ivoclar Vivadent),德国的维他公司(VITA Zahnfabrik)和泽康公司(Cercon)等相继开发出In-Ceram、CAD/CAM等技术,得到的氧化锆冠体(粒径200-500 nm),满足临床应用指标(抗折强度大于900 MPa,抗断裂韧性大于5 MPa•m1/2)并已在临床中应用[28]。2009年,辽宁爱尔创生物材料有限公司生产的氧化锆在国内率先获批国家食品药品监督局医疗器械注册证,迈出了国产二氧化锆产品在口腔临床应用的第1步。经过近7年的发展,爱尔创氧化锆陶瓷逐渐得到了口腔行业的认可,国内市场尤其是民营口腔市场占有率逐年提升。随着全瓷修复体的临床普及,国产氧化锆面临着重大的机遇与挑战,品牌效应的提升及相关技能培训服务是进一步扩大市场占有率的关键步骤。 针对不同品牌的氧化锆陶瓷,长期临床观察发现,氧化锆基全瓷冠修复体也存在着不稳定(如饰瓷崩裂、基冠在潮湿环境下机械性能明显变差)等问题[28, 39-41]:目前临床上一般需要在利用CAD/CAM技术切削后的氧化锆基冠表面上覆盖饰瓷,以提高其抗折强度和颜色。这样,由于饰瓷涂层在基冠表面润湿性不理想且加热时具有不同的热膨胀系数,易产生瓷裂。而关于基冠的表面没有标准的处理方法,且其与饰瓷的界面结合并无深入的基础性研究,影响了氧化锆全瓷冠修复体的临床推广;工业化生产中满足临床指标的氧化锆全瓷冠粉体的烧结温度范围较宽(1 300-1 550 ℃),获得的晶粒尺寸差别较大。而烧结条件对晶粒尺寸、晶向和晶相稳定性的影响并无系统性深入研究,增加了临床结果的不确定性。同时,由于原料价格昂贵、成品制备加工工艺较复杂、纳米技术所引发的潜在特殊生物效应等问题,增加了制备高纯度(不含对人体有害成分)、高性能(机械性能、生物性能等)成品氧化锆瓷冠的难度和成本。因此,不仅需要从工艺上对氧化锆基粉体的制备进行优化,提高原料纯度、机械性能、生物性能和稳定性,而且需要从晶体学角度对晶体成核、生长、第二相及晶粒尺寸对于晶体结构稳定性,进而对基冠生物力学性能的影响及基冠与饰瓷的晶格匹配对其界面的影响等问题进行深入的理论分析,为工业生产和临床应用重新制订标准,提高材料的长期稳定性和安全性。另一方面,在修复体的加工过程中,应严格按照不同品牌的氧化锆修复体的加工工艺进行。例如品牌为爱尔创、3M、西诺德、义获嘉的瓷块,其加工工艺及临床应用特点是有差异的[42-48],如果不按照相应品牌的产品的加工工艺进行修复体的制备,难以获得性能优异的修复体。义获嘉品牌的氧化锆瓷块是一种非常理想的高强度修复体材料,易于加工,并可承受巨大的咬合力,同时还具有美观、稳定性好等特点,可用于前牙、后牙的修复,甚至长达14个单位的桥体制作[49]。3M品牌的Lava氧化锆和Lava Plus超透氧化锆的强度可达1 440 MPa,为了满足不同患者牙体颜色的区别,其使用专利染色技术,可提供8种颜色的基底冠,配合Lava CAD/CAM氧化锆系统可具有更精密的边缘适合性和自然通透效果[50]。因此,应该加强修复体制作人员的培训,使其对不同品牌的氧化锆产品的基本性能及加工工艺有所了解,制备出满足临床使用要求的性能优异的修复体产品。 氧化锆应用于临床的另一重要挑战是国产加工设备(CAD/CAM)的进一步普及,从而降低氧化锆修复体的价格。氧化锆修复体加工设备(CAD/CAM)基本被进口品牌垄断,根据不同配置,CAD/CAM加工设备的价格从几十万到上百万不等,这也是氧化锆修复体价格较高的主要原因。CAD/CAM设备的核心是扫描仪及配套软件,2015年9月,广东朗呈医疗器械科技有限公司研发、生产的口内扫描仪取得了中国医疗器械产品注册证,获得了上市通行证,迈出了国产口腔扫描仪临床应用的第1步。 "
| [1] 高长有,马列.医用高分子材料[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2006.[2] 周辉,梁瑜.多种生物材料细胞生物相容性及其安全性的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(38):7559-7562.[3] Derek WJ.Development of dental ceramics: An historical perspective.Dent Clini North Am. 1985; 29(4):621-644.[4] Rosenblum MA,Schulman A.A review of all-ceramic restorations.JADA. 1997;128:297-307.[5] Ghazal M, edderich J,Kern M.Wear of feldspathic ceramic, nano-filled composite resin and acrylic resin artificial teeth when opposed to different antagonists.Eur J Oral Sci.2008;116(6):585-592.[6] Roriz VM,Rosa AL,Peitl O,et al. Efficacy of a bioactive glass–ceramic (Biosilicate) in the maintenance of alveolar ridges and in osseointegration of titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;21(2):148-155.[7] 张光磊,张久兴,钟涛兴.牙科陶瓷的发展与全瓷修复技术的应用[J].北京生物医学工程, 2006,25(1): 109-111.[8] Marchi J,Delfino CS,Bressiani JC,et al.Cell Proliferation of Human Fibroblasts on Aluminaand Hydroxyapatite-Based Ceramics with DifferentSurface Treatments.Int J Appl Ceramic Technol. 2010;7(2): 139-147.[9] Eraslan O,Aykent F,Yücel MT,et al.The finite element analysis of effect of ferrulebeight on stress distribution at post-and-core-restored all-ceramic antertior crowns.Clin Oral Investing. 2009;13(2): 223-227.[10] Yamashita D,Machigashira M,Miyamoto M.Effect of surface roughness on initial responses of osteoblast-like cells on two types of zirconia.Dent Mater J.2009;28(4): 461-470.[11] 禹立强,李金源. 二氧化锆全瓷冠与传统冠修复体对牙周健康的影响[J].河北联合大学学报, 2012,14(4): 485-486.[12] 路振富,李健.口腔CAD/CAM设备及应用概述[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,6(6): 342-345.[13] Matthias K,Stefan MW.Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability.Dent Mater. 1998;14(1):64-71.[14] Kasuga H,Ohmori H,Watanabe Y,et al.Surface characteristics of efficient-ground alumina and zirconia ceramics for dental applications.Key Eng Mater. 2009; 404:69-75.[15] Shijo Y,Shinya A,Gomi H,et al.Studies on mechanical strength, thermal expansion of layering porcelains to alumina and zirconia ceramic core materials.Dent Mater J.2009;28(3):352-361.[16] Eric A,Anne P,Thomas H.Stiffness,elastic limit,and strength of newer types of endodontic posts.J Dent. 1999;27:275-278.[17] Sailer I,Gottner J,Kanel S,et al.Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Zirconia-Ceramic and Metal-Ceramic Posterior Fixed Dental Prostheses:A 3-year Follow-up.Int J Prosthodont. 2009;22(6): 553-560.[18] Turp V,Tuncelli B,Sen D,et al.Evaluation of hardness and fracture toughness, coupled with microstructural analysis, of zirconia ceramics stored in environments with different pH values.Dent Mater J. 2012;31(6): 891-902.[19] Kelly JR,Denry I.Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: an overview.Dent Mater. 2008;24(3): 289-298.[20] Wang H,Aboushelib MN,Feilzer AJ.Strength influencing variables on CAD/CAM zirconia frameworks. Dent Mater.2008;24(3):633-638.[21] Manicone PF,Rossi Iommetti P,Raffaelli L.An overview of zirconia ceramics: basic properties and clinical applications.J Dent.2007;35(11):819-826. [22] Swain MV.Limitation of maximum strength of zirconia-toughened ceramics by transformation toughening increment.J Am Ceram Soc. 1985;68(4): C97-C99.[23] Guazzato M,Albakry M,Quach L,et al.Influence of grinding, sandblasting,polishing and heat treatment on the flexural strength of a glass-infiltrated alumina reinforced dental ceramic.Biomaterials. 2004;25(11): 2153-2160.[24] Sarker D,Mohapatra D,Ray S,et al.Nanostructured Al2O3-ZrO2 composite synthesized by sol-gel technique: powder processing and microstructure.J Mart Sci.2007; 42:1847-1855.[25] Stefanic G,Music S,Ivanda M.Phase development of the ZrO2-ZnO system during the thermal treatments of amorphous precursors.JMol Str.2009;924-926:225.[26] Taavoni-Gilan A,Taheri-Nassaj E,Akhondi H.The effect of zirconia content on properties of Al2O3-ZrO2 (Y2O3) composite nanopowders synthesized by aqueous sol-gel method.J Non-Cryst Solids. 2009;355(4-5): 311-316.[27] Tholey MJ,Swain MV,Thiel N.SEM observations of porcelain Y-TZP interface.Dent Mater. 2009;25: 857-862.[28] Denry I,Kelly JR.State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent Mater. 2008;24:299-307.[29] 金恩龙.氧化锆陶瓷在口腔医学领域中的应用[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2007,34(1): 62-64.[30] Liang XJ,Qiu YX,Zhou SX.Preparation and properties of dental zirconia ceramics. J Univ Sci Technol. 2008; 15(6):764-768.[31] Kelly JR, Denry I. Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: An overview. Dent Mate, 2008;24:289-298.[32] Vladimir VS,Radovan PO.Electrical conductivity of sol-gel derived yttria-stabilized zirconia.Ceram Int. 2001;27(8):859-863.[33] Eriksson M,Klein LC,Liden E,et al. Preparation of nanoporous silica-zirconia layers by in situ sol-gel method.Materi Sci Technol.2006;22(5): 611-614.[34] Vladimir VS,Markus W,Horst H.Sintering Behavior of nanocrystalline zirconia prepared by chemical vapor synthesis.J Am Ceram Soc.2000;83(4):729-736.[35] Sia B,Duan L,Xie Y.ZrO2 nanopowders prepared by low-temperature vapor phase hydrolysis.J Am Ceram Soc.2000;83(5):1077-1080.[36] Zhipeng X,Jingtao M,Qing X.Effects of dispersants and soluble counter-ions on aqueous dispersibility of nano-sized zirconia powder.Ceram Int. 2004;30(2): 219-224.[37] Jing S,Lian G.Stabilizing Nano Zirconia Suspensions Using Polyacrylic Acid: Adsorption,Rheology and Interparticle Forces.Key Eng Mater. 2002;224-226: 663-666.[38] Li B,Wei X,Pan W.Synthesis of doped ceria–zirconia core–shell nanocomposites via sol–gel process.J Power Sources.2009;193(2):598-601.[39] Conrad HJ,Wook-jin S,Pesun IJ.Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: a system review.J Prosthet Dent.2007;98(5):389-404.[40] Swain MV.Unstable cracking (chipping) of veneering porcelain on all-ceramic dental crowns and fixed partial dentures.Acta Biomaterialia.2009;5:1668-1677.[41] Otrop A,Kihl ML,Carlsson GE.A 3-year retrospective and clinical follow-up study of Zirconia single crowns performed in a private practice.J Dent. 2009;37: 731-736.[42] 马红梅,李阳,陶世亮,等.CEREC AC椅旁即刻全瓷修复短期疗效评价[J].口腔医学,2014, 34(2):87-90.[43] 孙雪丹.IPS e.max CAD LT低度透明瓷块修复后牙缺损的临床效果观察[J].口腔医学,2013, 33(4):251-253.[44] 陈磊,孙强,廉云敏.Lava无饰瓷二氧化锆冠修复后牙的临床疗效初探[J].空军医学杂志,2014,30(2):108-110. [45] 强澈菱.Lava CAD/CAM二氧化锆全瓷冠前牙美容修复的临床评价[D].大连:大连医科大学,2010.[46] 关昌俊,陈小冬,赵佳明,等.Cercon系统氧化锆全瓷冠桥2238例的返工分析[J].口腔医学,2014,34(6):438-440.[47] 宋风生,邓丽.Cercon氧化锆修复体的临床应用研究[J].中国医药科学,2011,1(12):74-74.[48] R Xiao R,BF Chu,L Zhang,JK Cao. Aging perfonnances for resistinglow—temperature of three dental yttria-stabiIized zirconia ceramic core materials. Chin Med J.2012;125(11):1999-2003.[49] 李晶,李健.口腔CAD/CAM可切削氧化锆应用概述[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2015,8(3): 176-179.[50] Fischer J,Stawarczyk B,Tomic M,et al.Effect of Thermal Misfit between Different Veneering Ceramics and Zirconia Frameworks on in vitro Fracture Load of Single Crowns.Dent Mater J. 2007;26(6):766-772. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||