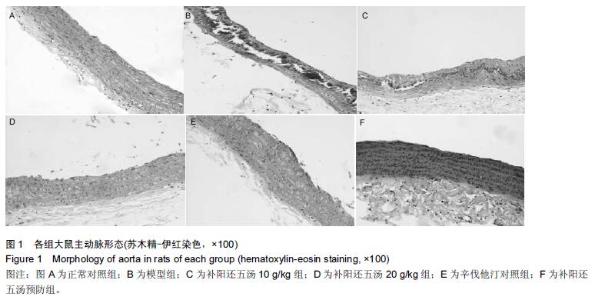
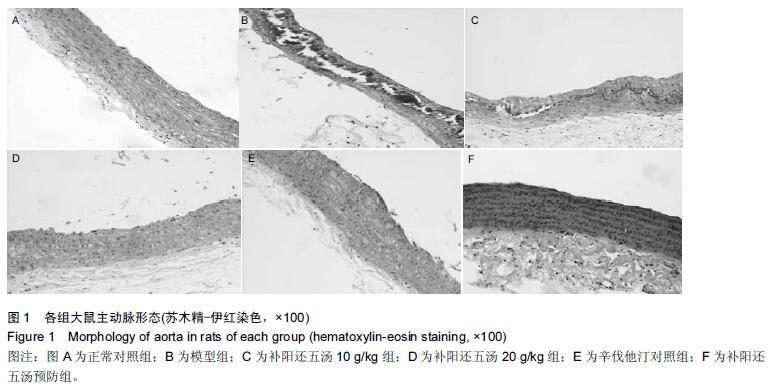
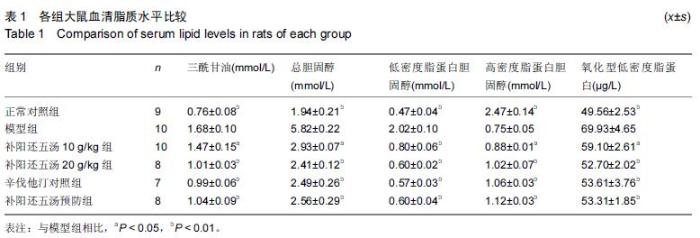
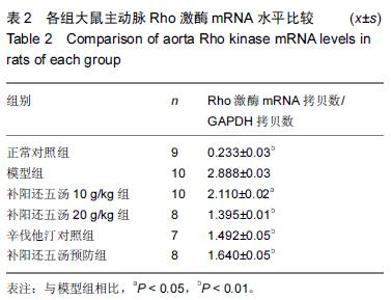
| [1] 王鹏,修春红,王岚峰.颈动脉粥样硬化与心脑血管疾病的关系[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2014,22(11): 1175-1178. [2] 王椿野,赵振武,李新龙,等.基于现代文献的动脉粥样硬化中医病机研究[J].环球中医药, 2013,6(2): 92-95. [3] 骆丽娟.益气补肾活血方治疗颈动脉粥样硬化的临床观察[J].辽宁中医杂志,2011,38(2):311-312. [4] Vucevic D,Radak D,Milovanovic I,et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms of angiogenesis in atherogenesis. Med Pregl. 2013;66(7-8):297-306. [5] 吴先杰,王永霞.动脉粥样硬化发生机制研究现状及思路[J]. 中国实用诊断与治疗杂志,2012,26(7):629-631. [6] 蔡光先,赵玉庸.中西医结合内科学[M].2版.北京:中国中医药出版社.2010:192-198. [7] 林艾雯,陈竹君.动脉粥样硬化与内皮细胞损伤机制的研究进展[J]. 岭南心血管病杂志,2015,21(4):580-582. [8] 席静,张玉东.Rho/Rho激酶与动脉粥样硬化的研究进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2010,12(10):955-956. [9] Anwar KN,Fazal F,Malik AB,et al. RhoA/Rho-associated kinasepathway selectively regulates thrombin-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells via activation of I kappa B kinase beta and phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J Immunol. 2004;173(11):6965-6972. [10] Nakakuki T,Ito M,Iwasaki H,et al. Rho/Rho-kinase pathway contributes to C-reactive protein-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vase Biol. 2005; 25:2088-2093. [11] Li S,Gao YT, Lei Y, et al. Roles of myosin light chain kinase and Rho-kinase in migration of rabbit intracranial vascular smooth muscle cells.Chin Stroke. 2008;3:566-571. [12] Sahai E,Marshall CJ. ROCK and Dia have opposing effects on adherens junctions downstream of Rho. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:408-415. [13] 陈亚丽,苏瑞瑛.Rho激酶在动脉粥样硬化和血管疾病中的重要作用[J]. 河北医药, 2012, 34(2):256-258. [14] 刘敏,张玉东.抑制Rho/Rho激酶信号对动脉粥样硬化大鼠心血管系统的保护作用[J].山东医药, 2013, 53(24): 41-43. [15] 张子新,慕翠翠,吉虓, 等. 通心络对糖尿病动脉粥样硬化大鼠Rho/Rho激酶底物影响的研究[J].现代医学,2014, (8): 843-846. [16] 刘志勇,游宇,易文凤,等.补阳还五汤通过调节HUVEC细胞Rho/Rho激酶信号通路作用于动脉粥样硬化的研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2015,26(5):595-600. [17] Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2007; 100(2):174-190. [18] Nohria A, Grunert ME, Rikitake Y. Rho激酶的抑制可改善冠状动脉疾病患者的内皮功能[J]. 世界核心医学期刊文摘:心脏病学分册,2007,3(6):23-24. [19] 王吉萍,郭晓华,王陵军,等. Rho/ROCK信号通路参与晚期糖基化终产物诱导的人皮肤微血管内皮细胞骨架结构改变[J].生理学报,2009,61(2):132-138. [20] 李伟,周乐.脂多糖诱导血管内皮细胞骨架重构中RhoA/ ROCK通路的作用及中药干预[J].世界中西医结合杂志, 2014,9(12):1359-1363. [21] 张红珍.动脉粥样硬化的中西医防治[M]. 山西:山西科技出版社,2014:102-103. [22] 马志红.Rho激酶信号通路对大鼠动脉粥样硬化形成的影响及法舒地尔的心血管保护作用[D].河北医科大学, 2011. [23] 潘俊杰.组织因子途径抑制物2对动脉粥样硬化不稳定斑块的保护作用及机制探讨[D]. 复旦大学,2011. [24] 况军,王巍.荷叶碱对小鼠动脉粥样硬化血管炎症及基质金属蛋白酶的影响[J].临床心血管病杂志,2015, 31(1): 97-100. [25] 李华伟.基质金属蛋白酶-2和超敏C反应蛋白水平与冠状动脉病变程度的相关性[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2015, 19(1):17-19. [26] 许成岗,武红斌.多生化指标联合检测预测动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定性的可行性研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2015,13(15):1768-1770. [27] 李军,王朝阳.补阳还五汤对急性脑缺血大鼠血管新生影响的实验研究[J].中国中医急症,2011,20(2):273-274. [28] 翟丽莉,吕建华.补阳还五汤的药理研究与临床新用[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2009,7(2):9-10. [29] 贺琴,张霞,赵琴,等.补阳还五汤防治心血管病研究进展[J].西南国防医药,2013,23(5): 570-571. [30] 戴晨光,李学奇.维生素D与心血管疾病关系的研究进展[J].微循环学杂志, 2015,25(1):62-63. [31] 王凤,章怡祎,刘萍.动脉粥样硬化动物模型的研究进展[J].东南大学学报,2014,55(2):235-238. [32] 龚博君,李自成. 主动脉中膜钙化型动脉粥样硬化模型的建立[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(20): 5687-5689. [33] 周红,吴晓燕,袁艺标,等.三种剂量维生素D3结合高脂饲料建立大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型的比较[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2012,20(11):995-998. [34] 张安邦,黄昕,李令根,等.复合方法制备SD大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2015,21(3): 282-285. [35] 周永刚,蓝小红,李祥,等.动脉粥样硬化大鼠实验模型的建立与评价[J].解放军药学学报.2011,27(5):399-403. [36] 蒋文潇,王保和. 王保和教授益气活血法治疗胸痹经验介绍[J]. 光明中医,2015,30(1): 18-19. [37] 刘桂林. 张继东运用益气活血法治疗胸痹心痛经验[J]. 河南中医,2015,35(4): 701-702. [38] 周芹. 益气活血法治疗老年冠心病心绞痛40例[J].河南中医,2015,35(9):2079-2081. [39] 周晓玲.冠心病心绞痛予益气活血法治疗的观察探讨[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(15):277-278. [40] 庄贺,侯王君,赵艳青,等.邵念方教授益气活血法治疗冠心病医案2则[J].中医药导报,2014,20(7):150-150. |