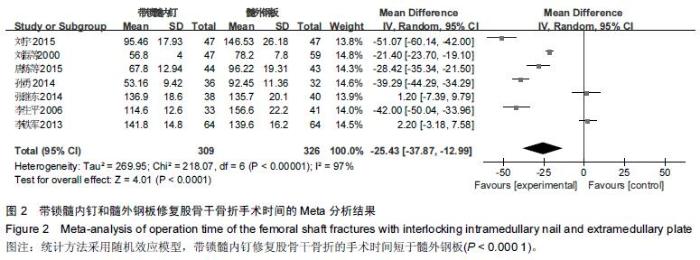
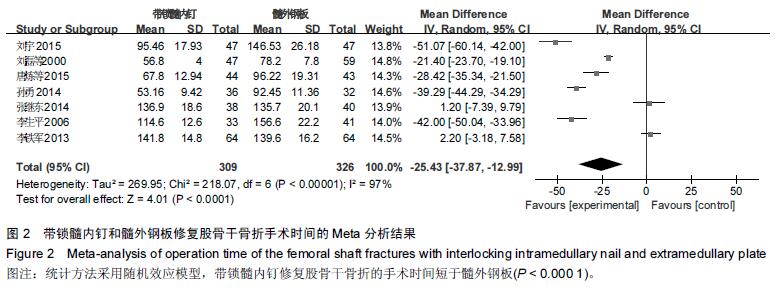
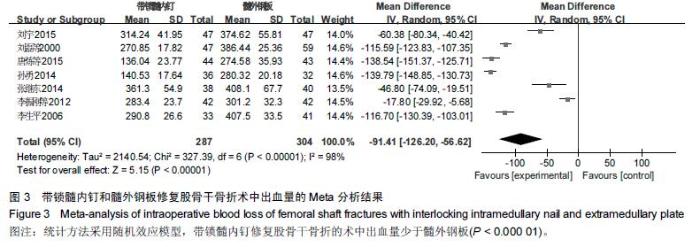
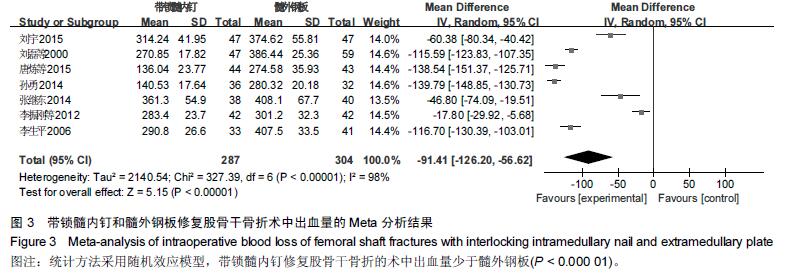
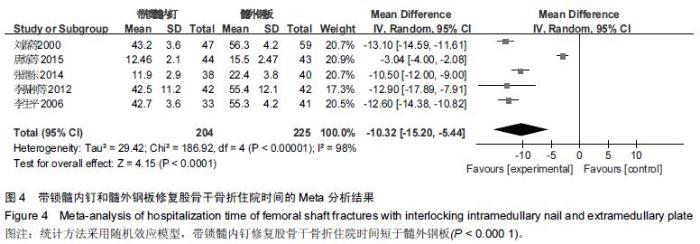
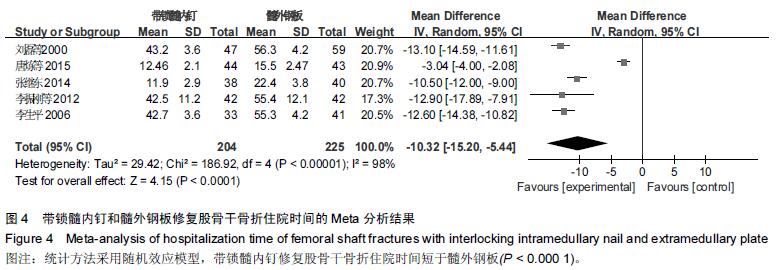
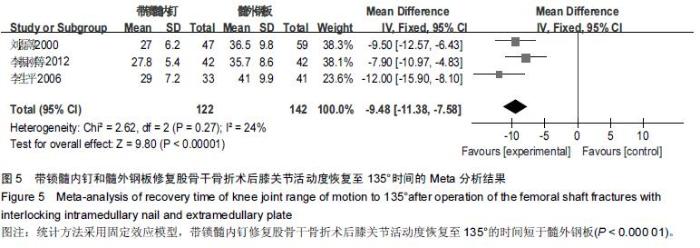
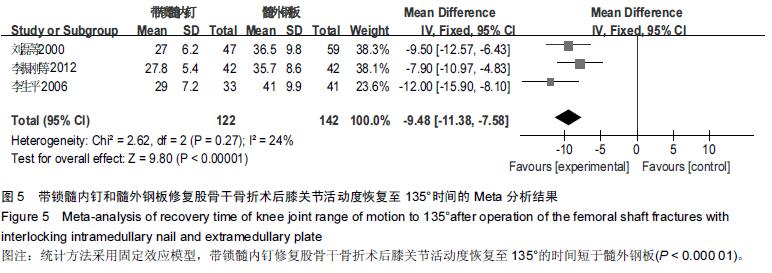
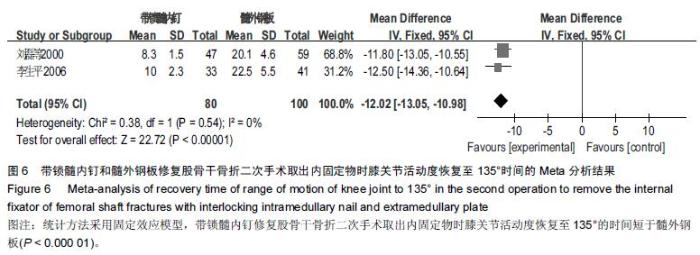
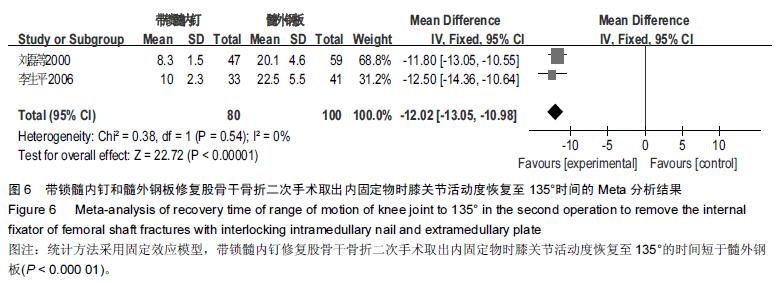
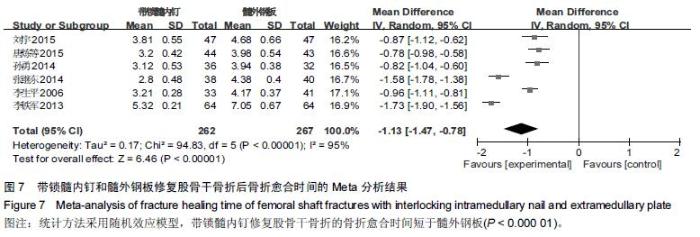
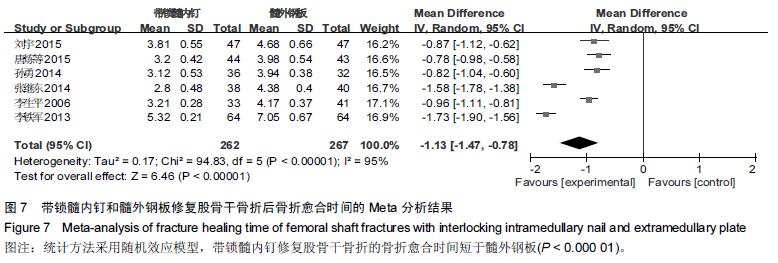
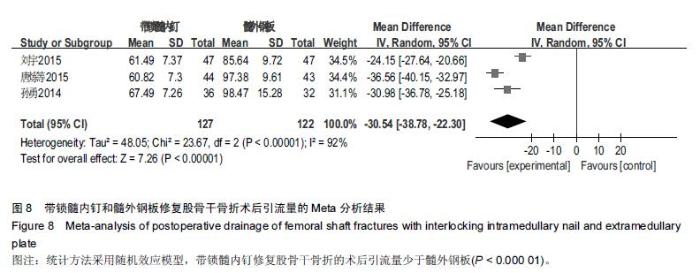
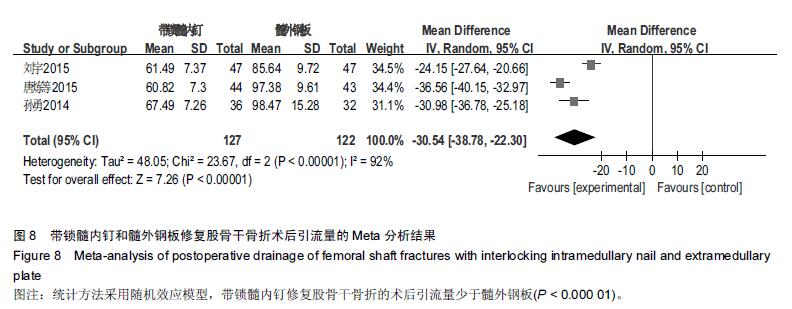
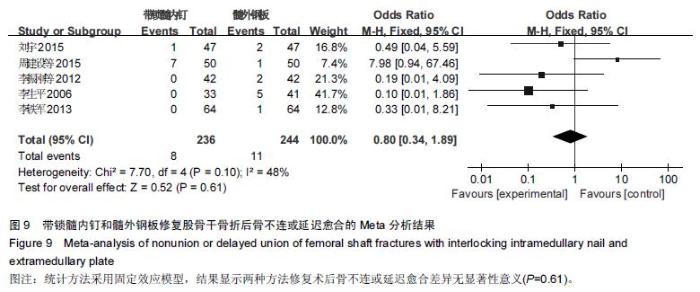
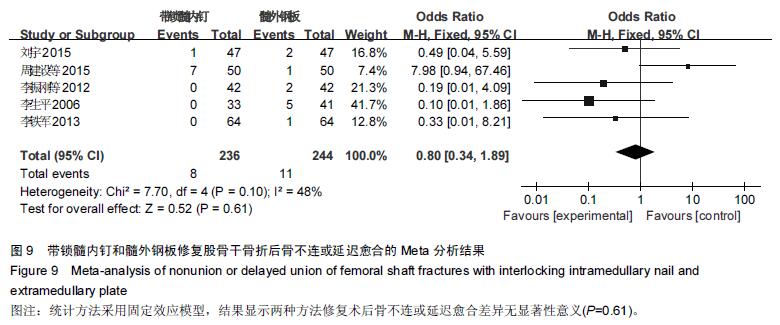
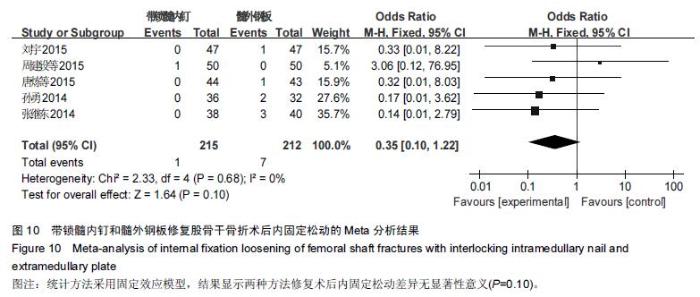
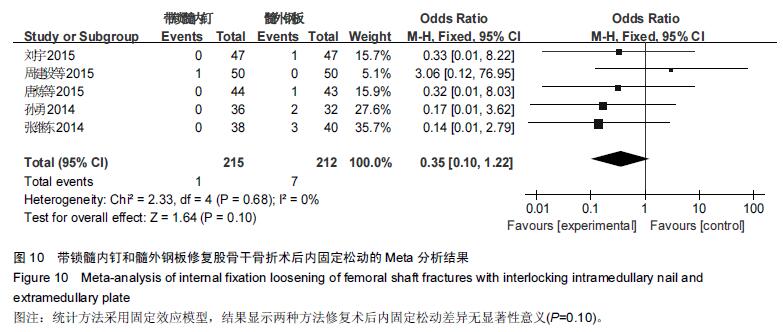
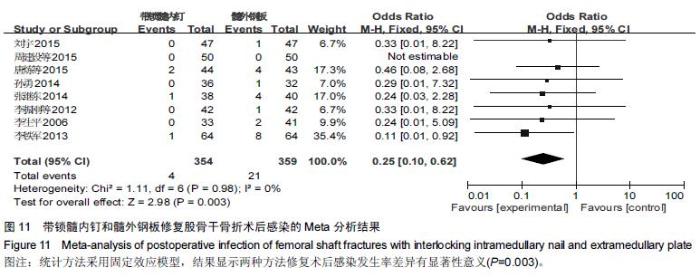
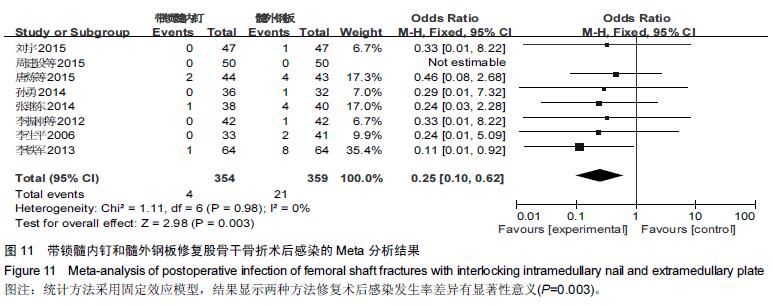
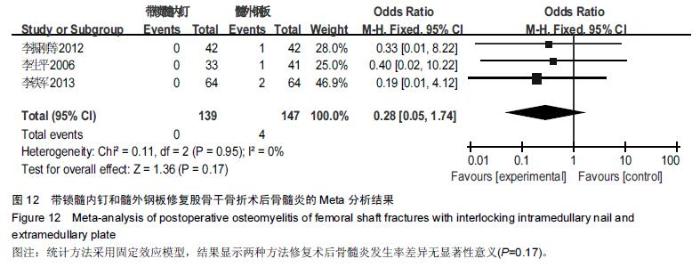
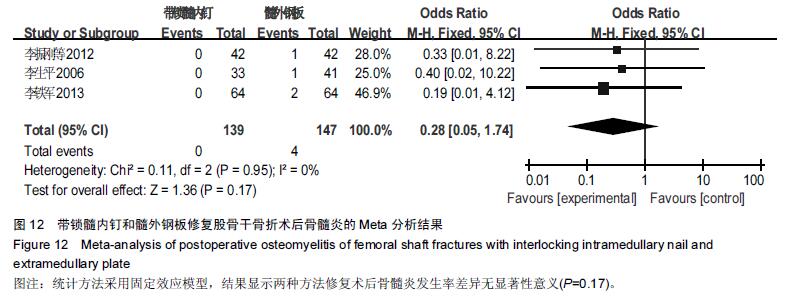
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2575-2584.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.020
Meta-analysis of femoral shaft fractures treated with interlocking intramedullary nail and extramedullary plate
Abulimiti•Amuti, Zhang Xie-zhuo, Xu Chao, Ding Hui-yong
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2016-02-13Online:2016-04-22Published:2016-04-22 -
About author:Abulimiti?Amuti, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
Cite this article
Abulimiti•Amuti, Zhang Xie-zhuo, Xu Chao, Ding Hui-yong. Meta-analysis of femoral shaft fractures treated with interlocking intramedullary nail and extramedullary plate[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(17): 2575-2584.
share this article
|
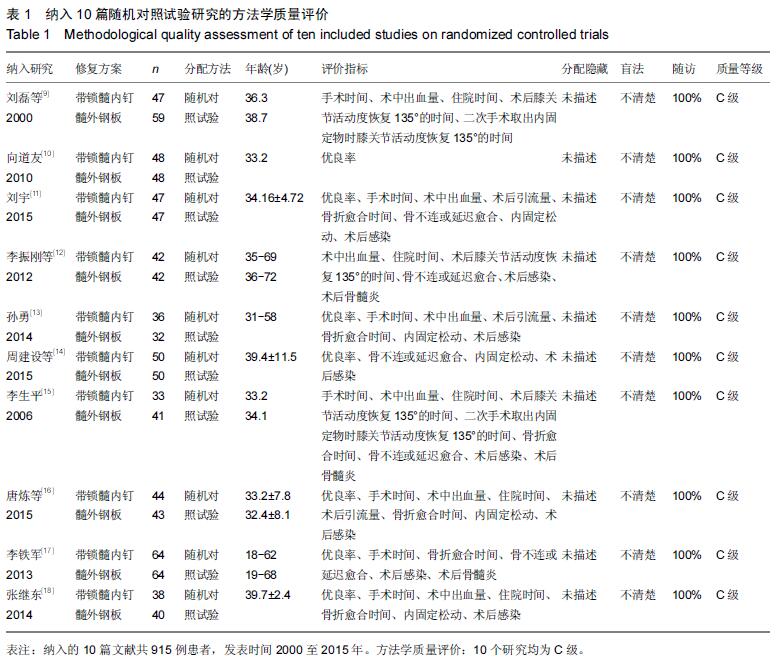
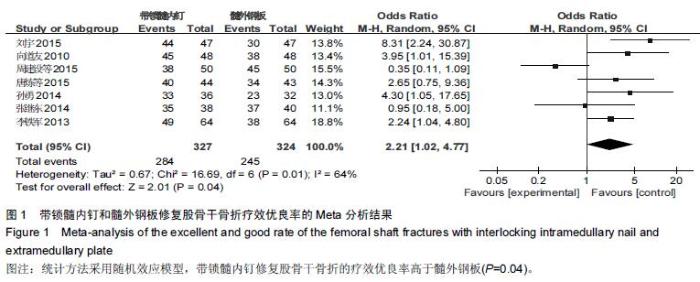
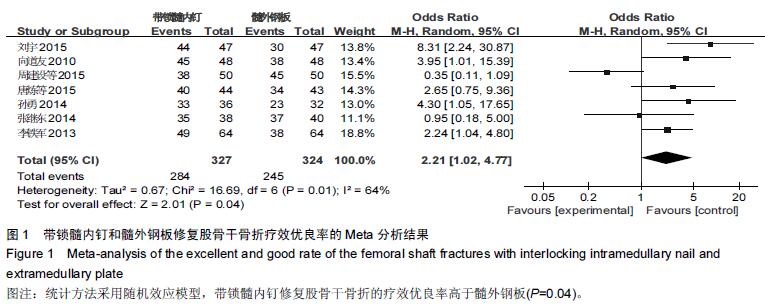
[1] 智春升,李忠强,刘灿祥,等.四肢骨折治疗方法研究[J].中外医疗,2012,31(16):21-22 [2] 常焕武.导航带锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干骨折22例临床分析[J].基层医学论坛,2012,16(32):4239-4240. [3] 危伟良.股骨干骨折不愈合的原因及相关因素分析[J].局部手术学杂志,2012,21(4):439-440 [4] 陆裕朴.实用骨科学[M].1版.北京:人民军医出版社, 1998: 660. [5] 孙绪谦,张大江,董志强.交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折应注意的问题[J].基层医学论坛,2012,16(2):189-190. [6] 沙爱林.股骨干骨折闭合复位与切开复位的治疗效果比较[J].中国医药指南,2010,8(32):108-109. [7] Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JP, et al. Cochrane Reviews’ Handbook4.2.1//the Cochrane Library. UK: John Wiley &Sons, Ltd, 2004. [8] Smith AM,Mardones RM,Sperling JW, et al. Early complications of operatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2007;16:14-24. [9] 刘磊,马文松.钢板与带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折疗效比较[J].广东医学,2000,21(7):585-586. [10] 向道友.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折的临床疗效评价48例[J].四川医学,2010,31(9):1325-1326. [11] 刘宇.带锁髓内钉内固定治疗成人股骨干骨折临床疗效观察[J].河南医学研究,2015,24(3):93-94 [12] 李振刚,周媛.带锁髓内钉与加压钢板治疗股骨干骨折疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(5):535-539. [13] 孙勇.带锁髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗股骨干骨折疗效观察[J].河南外科学杂志,2014,20(4):100-101. [14] 周建设,薛俊联.锁定钢板固定于交锁髓内钉内固定方法治疗股骨干粉碎性骨折的疗效比较[J].医学信息, 2015, 28(20):126-127. [15] 李生平.带锁髓内钉与加压钢板治疗股骨干骨折74例临床疗效分析[J].广西医学,2006,28(1):64-66. [16] 唐炼,陈洁盈.交锁髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗股骨干骨折的临床疗效对照研究[J].国外医药(抗生素分册), 2015, 36(1):42-44. [17] 李铁军.髓内钉与锁定加压钢板治疗股骨干骨折疗效的临床对照分析[J].中国保健营养(中旬刊),2013,8(8):607-608. [18] 张继东.交锁髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗股骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中外医疗,2014, (36):38-39. [19] Kavnezis LA, Mlew AW. “Biological” internal fixation of long bone fractures: a biomechanical study of a “noncontact” plate system. Injury. 1998;29(9):689. [20] 王斌,闫文平.交锁髓内钉治疗下肢骨干骨折体会[J].基层医学论坛,2012,16(16):1385-1386. [21] 姚战锋.股骨远端骨折应用逆行交锁髓内钉的临床治疗观察[J].基层医学论坛,2012,16(25):3389-3390. [22] 王亦璁.近年骨折治疗观点反思[J].中华创伤杂志, 1998, 14(1):1-3. [23] Megas P, Syggelox SA, Kontakis G, et al. Intramedullary nailing for the treat ment of aseptic femoral shaft non-unions after plating failure: effectiveness and timing. Injury. 2009;40(7):732-737. [24] Tejwani NC. Intramedullary nail fracture compression techniques: when and how to do it? J Orthp Trauma. 2009;23:18-21. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||