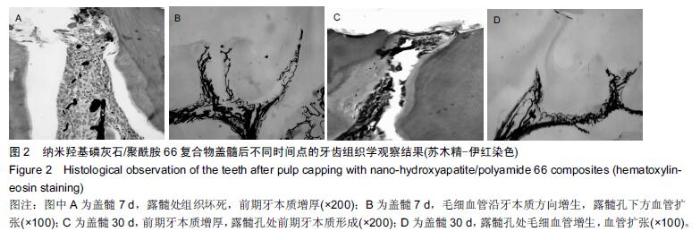
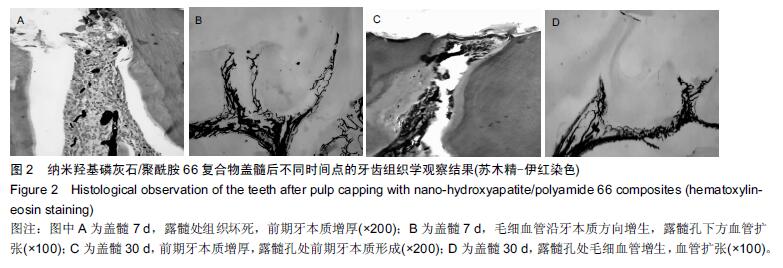
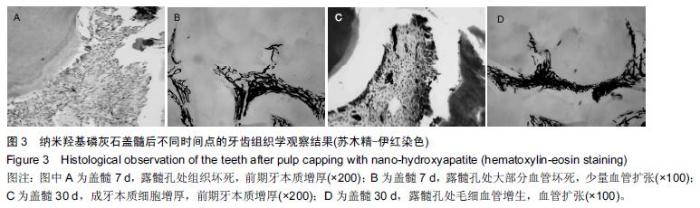
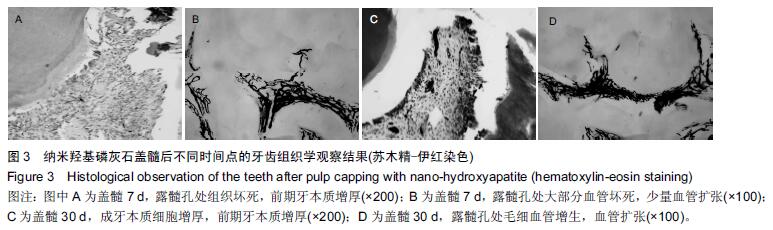
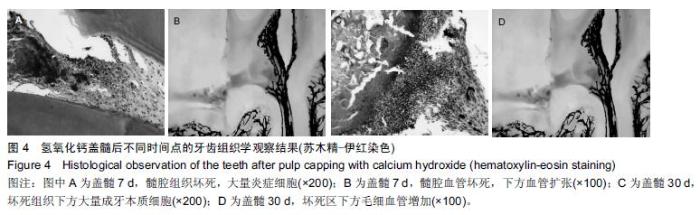
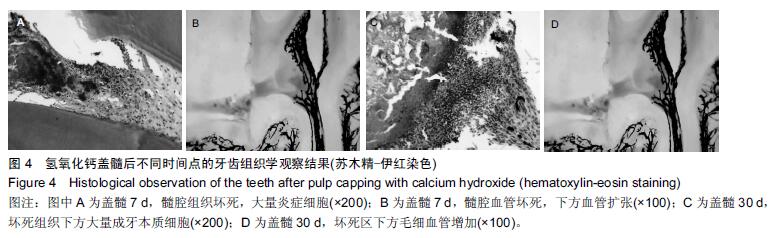
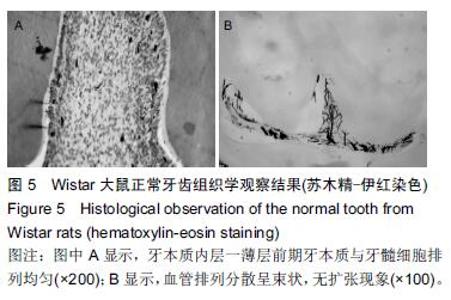
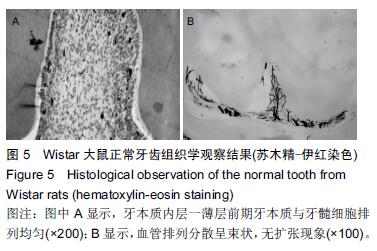
| [1] 杨琼.氢氧化钙制剂在牙体牙髓疾病治疗中的临床应用[J].中国药物经济学,2014,16(2):68. [2] 聂二民,姜瑞,张春元,等.比较5种不同盖髓剂长期护髓的差异[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(16): 2557-2561. [3] 李激.纳米材料与纳米技术在口腔内外科学中的应用概述[J].右江医学,2013,41(1):106-109. [4] Hill RG,Gillam DG,Chen X.The ability of a nano hydroxyapatite toothpaste and oral rinse containing fluoride to protect enamel during an acid challenge using 19 F solid state NMR spectroscopy.Mater Lett.2015;156:69-71. [5] Qu Y,Wang P,Man Y,et al.Preliminary biocompatible evaluation of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite porous membrane.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010;5:429-435. [6] 李晓红.多元羟基磷灰石纳米生物复合材料研究进展[J].内蒙古科技大学学报,2014,33(2):167-170. [7] 代震宇.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料的制备与应用研究[D].重庆医科大学,2011. [8] 李军,代震宇,赵增辉,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料的生物相容性研究[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2010, 35(12):1840-1843. [9] 严永刚,李玉宝,汪建新,等.聚酰胺66/羟磷灰石复合材料的制备和性能研究[J].塑料工业, 2000,28(3):38. [10] 王学江,汪建新,李玉宝,等.常压下纳米级羟基磷灰石针状晶体的合成[J].高技术通讯, 2000,11(6):92. [11] 叶玲,苏勤,周东学,等.新型纳米粉和材料根管封闭效果的实验研究[J].华西医科大学学报,2002,33(4):559. [12] 邱伟,杨爱蓉.氢氧化钙与羟基磷灰石直接盖髓术后牙本质桥早期形成的临床效果观察[A].上海交通大学口腔医学院、上海市口腔医学会.2007年第七次全国牙体牙髓病学学术会议论文集[C].上海交通大学口腔医学院、上海市口腔医学会,2007:2. [13] 王健平,王本材,贾鑫.纳米羟基磷灰石和氢氧化钙对成牙本质细胞活性影响的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(3):417-420. [14] 李瑞锡.血管墨汁灌注透明法在微血管研究中的应用及体会[J].云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1991,11(2): 81-84. [15] Cox CF,Subay RK,Suzuki S,et al.Biocompatibility of variousdental materials: pulp healing with a surface seal.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1996;16(3): 240. [16] Faraco IM Jr, Holland R. Response of the pulp of dog s tocapping with mineral trioxide aggregate or a calcium hydroxidecement.Dent Traumatol.2001;17(4):163. [17] 穆云静.可固化氢氧化钙根管封闭剂生物相容性及根尖封闭性的研究[D].第四军医大学,2012. [18] 张欣,孙红.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合物修复骨缺损的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(34): 6403-6406. [19] 李瑞琦,张国平,任立中,等.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合生物材料的特征及应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(19):3747-3750. [20] 李志宏,武继民,李瑞欣,等.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合材料的研究进展[J].医疗卫生装备,2007,2(4):30-32. [21] 邢晓艳,张青松.纳米羟基磷灰石在口腔医学中的应用[J].继续医学教育,2013,27(10):54-55. [22] 任夏敏,范德增.纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及在口腔领域中的应用[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(3):178-180. [23] 陈富波,徐晓.羟基磷灰石盖髓研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2009,18(2):97-100. [24] 邱伟,时咏梅,徐进云.纳米羟基磷灰石直接盖髓诱导牙本质桥早期形成的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(21):3869-3872. [25] 冯娇,刘海蓉,李永生,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺6医用复合材料的制备及性能表征[J].复合材料学报, 2015,32(6): 1602-1610. [26] 代震宇.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料的制备与应用研究[D].重庆医科大学,2011. [27] 李军,代震宇,赵增辉,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料的生物相容性研究[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2010, 35(12):1840-1843. [28] 温从游,孟纯阳,蒋电明.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料的研究及应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(3): 464-469. [29] 桑裴铭,张明.医用纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物材料研究现状及进展[J].医学综述, 2012,18(13): 2072- 2074. [30] 苏勤,叶玲,周学东,等.聚酰胺/纳米羟磷灰石复合生物材料盖髓封闭性能的体外实验研究[J].华西医大学报, 2002, 33(4):561-562. [31] 苏勤,叶玲,周学东,等.纳米羟磷灰石/聚酰胺66作为盖髓材料的体外抗菌作用[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2007,25(1): 26-28. [32] 吴兰,李玉宝,杨维虎,等. n-HA晶体及n-HA/PA66复合材料与人皮质骨的定性和定量对比研究[J].功能材料, 2005, 36(6):892-895. [33] 苏勤,叶玲,周学东.纳米羟磷灰石/聚酰胺66盖髓的动物实验研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2005,36(1):43-45. [34] 刘帆,宋楠.纳米羟磷灰石/聚酰胺66糊剂根充术后疼痛的临床观察[J].中国误诊学杂志,2012,12(4):867-868. |