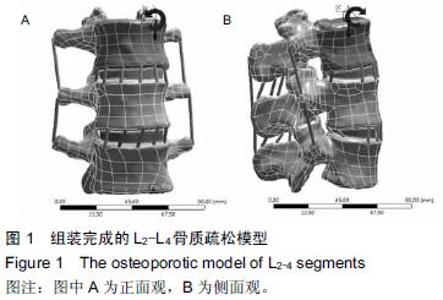
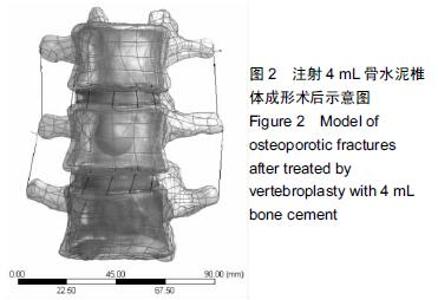
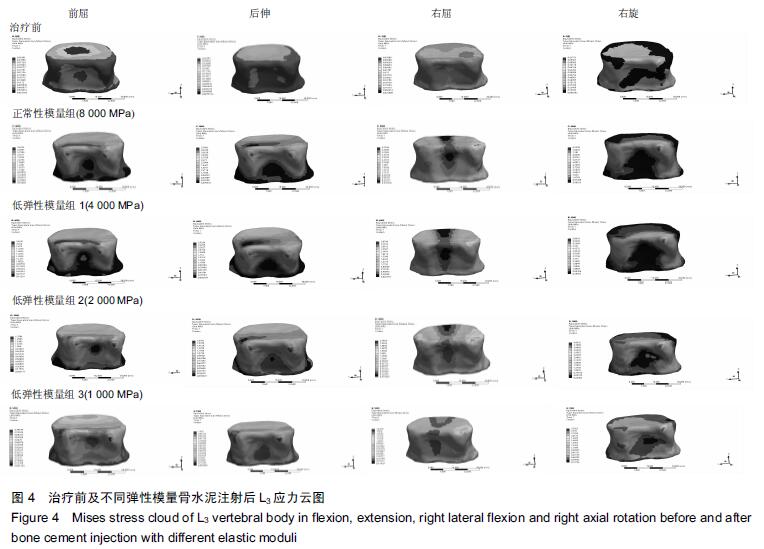
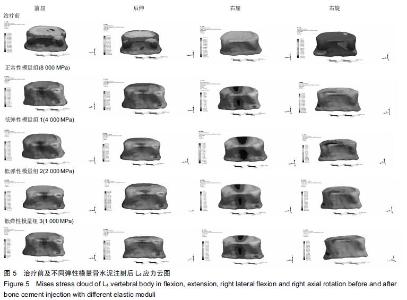
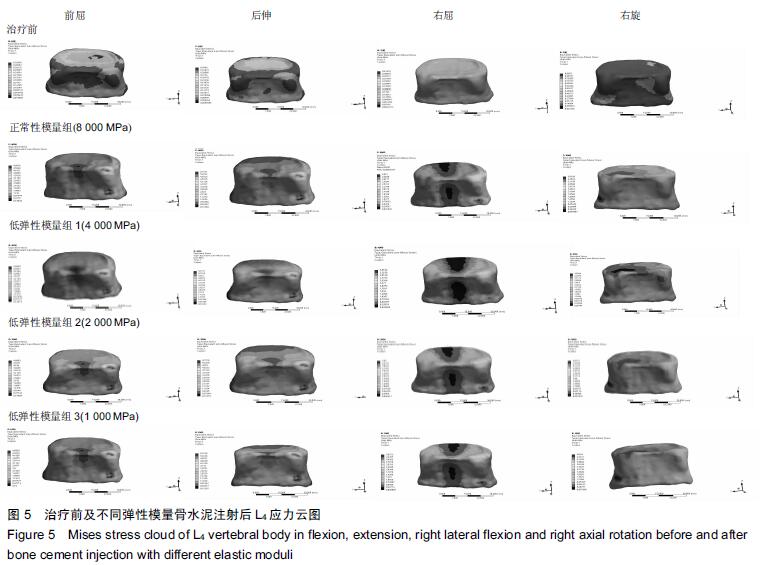
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (16): 2285-2293.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.16.001
Effect of bone cement with a low elastic modulus on the fractured and adjacent vertebrae in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite analysis
Bao Yong-zheng1, Zhu Zhou-xing2, Feng Yun-sheng3, Wu Qiang1, Hu Kong-he1, He Xiao-long1, Zhu Wen-gang1, Xi Xin-hua1, Zhong Xue-ren1, Zhou Long-ze1, Liao Jun-jian1, Dai Xiang-heng1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Yue Bei People’s Hospital, Shantou University Medical School, Shaoguan 512026, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Lechang City People’s Hospital, Shaoguan 512200, Guangdong Province, China; 3Nanxiong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shaoguan 512400, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-02-12Online:2016-04-15Published:2016-04-15 -
About author:Bao Yong-zheng, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Yue Bei People’s Hospital, Shantou University Medical School, Shaoguan 512026, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Shaoguan Medical and Health Research Project, No. Y13175
Cite this article
Bao Yong-zheng, Zhu Zhou-xing, Feng Yun-sheng, Wu Qiang, Hu Kong-he, He Xiao-long, Zhu Wen-gang, Xi Xin-hua, Zhong Xue-ren, Zhou Long-ze, Liao Jun-jian, Dai Xiang-heng . Effect of bone cement with a low elastic modulus on the fractured and adjacent vertebrae in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(16): 2285-2293.
share this article
|
[1] 邱兴,杨圣,芦健民,等.骨质疏松骨折椎体及相邻椎体骨水泥注入前后的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(17):3041-3048. [2] 严伟洪,仇胥斌,杨惠林,等. 胸腰段骨质疏松三维有限元模型的建立及临床应用[J]. 吉林医学,2011,2(32): 1053-1056. [3] 李秋军. 骨质疏松脊椎有限元模型的建立及临床应用[D].北京协和医学院,2009. [4] 张鹭,吴军,路锟,等. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折术后邻近椎体骨折的相关危险因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2015,35(16):4612-4614. [5] 张斌,尚咏. 经皮椎体后凸成形术后继发邻近椎体骨折的危险因素分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2014,17(3):249-252. [6] 李智斐,付拴虎,张家立,等. 椎体成形术后再骨折相关因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(9):790-794. [7] 易志坚,曹家树,王茂林,等. 经皮椎体成形术后椎体再发骨折的危险因素分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2013,6:474-476. [8] 罗斌,吴星火,邸方. 椎体后凸成形术后邻近椎体再发骨折发生率及相关危险因素的分析研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2013,15(1):23-27. [9] 刘建,俞雷钧,宋红浦,等. 经皮椎体成形术后非手术椎体骨折的危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2013,27(3):190-193. [10] 闫亮,昌震,贺宝荣,等. 椎体成形术后邻近椎体骨折的相关危险因素分析[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2013,42(6):676-678. [11] Yi X, Lu H, Tian F, et al. Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(1):21-30. [12] 徐德兴,陈昌礼,陈硕. 经皮椎体成形术后非手术椎体新发骨折的临床分析[J]. 华西医学, 2015,30(7):1217-1221. [13] Tanigawa N, Kariya S, Komemushi A, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: long-term evaluation of the technical and clinical outcomes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(6):1415-1418. [14] 黄天霁,寇玉辉,殷晓峰,等. 椎体强化术后再发椎体骨折的临床特点和危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 2(47):237-241. [15] Chen LH, Hsieh MK, Liao JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933. [16] 侯文根,孙晓辉,张超,等. 骨水泥体积分数对单节段骨质疏松性胸腰椎体压缩骨折行经皮椎体成形术患者邻近椎体骨折的影响[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2015,6(12):1119-1121. [17] Bleiler C, Wagner A, Stadelmann VA, et al. Multiphasic modelling of bone-cement injection into vertebral cancellous bone. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2015;31(1):e02696. [18] Matsuura Y, Giambini H, Ogawa Y, et al. Specimen-specific nonlinear finite element modeling to predict vertebrae fracture loads after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(22):E1291-1296. [19] Cho AR, Cho SB, Lee JH, et al. Effect of Augmentation Material Stiffness on Adjacent Vertebrae after Osteoporotic Vertebroplasty Using Finite Element Analysis with Different Loading Methods. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):E1101-1110. [20] Imai K. Computed tomography-based finite element analysis to assess fracture risk and osteoporosis treatment. World J Exp Med. 2015;5(3):182-187. [21] Giambini H, Qin X, Dragomir-Daescu D, et al. Specimen-specific vertebral fracture modeling: a feasibility study using the extended finite element method. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2015. [22] Imai K. Analysis of vertebral bone strength, fracture pattern, and fracture location: a validation study using a computed tomography-based nonlinear finite element analysis. Aging Dis. 2015;6(3):180-187. [23] Clouthier AL, Hosseini HS, Maquer G, et al. Finite element analysis predicts experimental failure patterns in vertebral bodies loaded via intervertebral discs up to large deformation. Med Eng Phys. 2015;37(6): 599-604. [24] Liebl H, Garcia EG, Holzner F, et al. In-vivo assessment of femoral bone strength using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) based on routine MDCT imaging: a preliminary study on patients with vertebral fractures. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0116907. [25] Liang D, Ye LQ, Jiang XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256. [26] Amjadi Kashani MR, Nikkhoo M, Khalaf K, et al. An in silico parametric model of vertebrae trabecular bone based on density and microstructural parameters to assess risk of fracture in osteoporosis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(12):1281-1295. [27] Okamoto Y, Murakami H, Demura S, et al. The effect of kyphotic deformity because of vertebral fracture: a finite element analysis of a 10° and 20° wedge-shaped vertebral fracture model. Spine J. 2015;15(4):713. [28] Wilcox R. The biomechanical effect of vertebroplasty on the adjacent vertebral body: a finite element study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2006;220(4):565-572. [29] Yan C, Dieter P, Mathieu C, et al. Cement distribution, volume, and compliance in vertebroplasty: some answers froman anatomy-based nonlinearfinite element study. Spine. 2008;33(16): 1722-1730. [30] Baroud G, Nemes J, Heini P, et al. I|oad shift of the intervertebral disc after vertebroplasty: a finite-element study. Eur Spine. 2003;12(4): 421-426. [31] Polikeit A, Nohe LP, Ferguson SJ. The efect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in all osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite element analysis. Spine. 2003;28(10): 991-996. [32] 贾小林,谭祖键,杨阜滨,等. 椎体后凸成形术与邻近椎体继发骨折的关系[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(2): 101-104. [33] 王涛,范恒俊,张福利,等. PKP后骨折椎体及邻近椎体应力变化有限元分析[J]. 山东医药,2014,54(22):8-10. [34] Persson C, Robert E, Carlsson E, et al. The effect of unsaturated fatty acid and triglyceride oil addition on the mechanical and antibacterial properties of acrylic bone cements. J Biomater Appl. 2015;30(3):279-289. [35] Boger A, Heini P, Windolf M, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine J. 2007;16: 2118-2125. [36] Boger A, Bisig A, Bohner M, et al. Variation of the mechanical properties of PMMA to suit osteoporotic cancellous bone. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008; 19(9):1125-1142. [37] Lam WM, Pan HB, Fong MK, et al. In vitro characterization of low modulus linoleic acid coated strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite containing PMMA bone cement. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;96(1):76-83. [38] López A, Hoess A, Thersleff T, et al. Low-modulus PMMA bone cement modified with castor oil. Biomed Mater Eng. 2011;21(5-6):323-332. [39] 包拥政,祝周兴,冯云升,等.骨水泥注射体积与骨质疏松压缩性骨折椎体及邻近椎体应力的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(52):8365-8372. [40] Yan L, Chang Z, Xu Z, et al. Biomechanical effects of bone cement volume on the endplates of augmented vertebral body: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(1):79-84. [41] Fei Q, Li QJ, Li D, et al. Biomechanical effect on adjacent vertebra after percutaneous kyphoplasty with cement leakage into disc: a finite element analysis of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;91(1):51-55. [42] Liebschner MA, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554. [43] Martin?i? D, Brojan M, Kosel F, et al. Minimum cement volume for vertebroplasty. Int Orthop. 2015;39(4): 727-733. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||