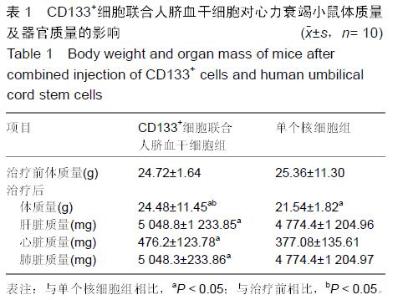
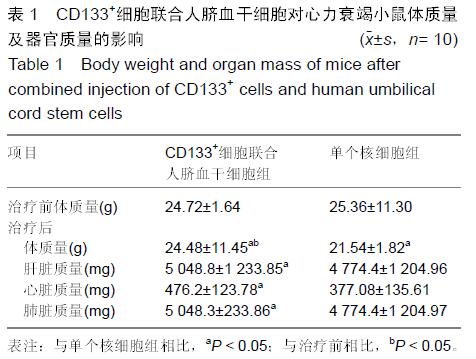
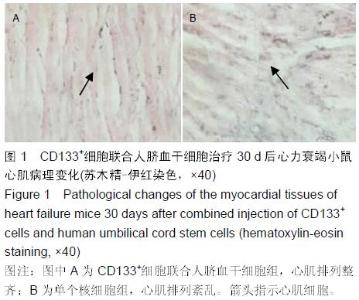
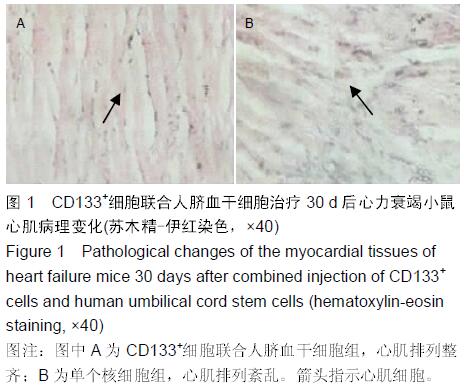
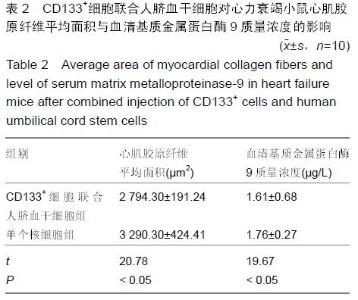
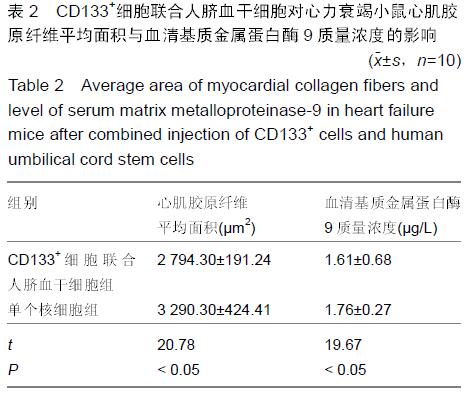
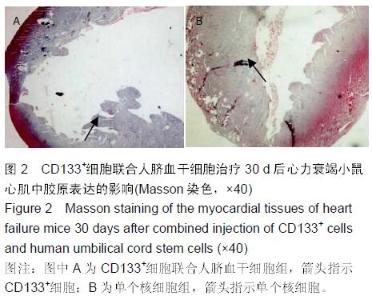
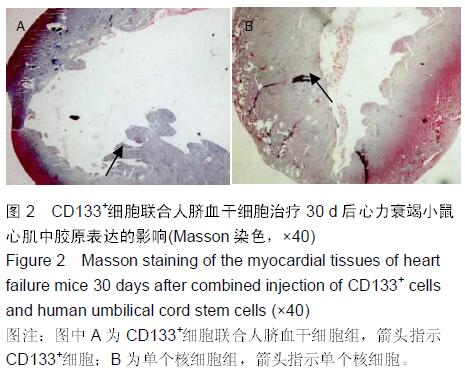
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (14): 2066-2072.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.14.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
CD133+ cells in combination with human umbilical cord stem cells in mouse heart failure
Hou Mei1, Zhang Hong-xing2, Ye Qing3, Zhang Yong4
- 1Department of Cadre Treatment, 2Department of Medical Oncology, 3Department of Cardiology, 4Department of Tumor Radiotherapy, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2016-02-16Online:2016-04-01Published:2016-04-01 -
Contact:Zhang Hong-xing, Associate chief physician, Department of Medical Oncology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Hou Mei, Attending physician, Department of Cadre Treatment, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81560462
Cite this article
Hou Mei, Zhang Hong-xing, Ye Qing, Zhang Yong. CD133+ cells in combination with human umbilical cord stem cells in mouse heart failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(14): 2066-2072.
share this article
| [1] Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(1): e6-e245. [2] Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, et al. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123(8):933-944. [3] Domanski MJ, Krause-Steinrauf H, Massie BM, et al. A comparative analysis of the results from 4 trials of beta-blocker therapy for heart failure: BEST, CIBIS-II, MERIT-HF, and COPERNICUS. J Card Fail. 2003;9(5): 354-363. [4] Janssens S, Dubois C, Bogaert J, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived stem-cell transfer in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006; 367(9505): 113-121. [5] 中华医学会心血管病学分会.中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2014[J].中华心血管病杂志,2014,42(2):98-122. [6] Wollert KC, Drexler H. Cell therapy for the treatment of coronary heart disease: a critical appraisal. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010;7(4):204-215. [7] Traverse JH, Henry TD, Pepine CJ, et al. Effect of the use and timing of bone marrow mononuclear cell delivery on left ventricular function after acute myocardial infarction: the TIME randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2380-2389. [8] Perin EC, Willerson JT, Pepine CJ, et al. Effect of transendocardial delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells on functional capacity, left ventricular function, and perfusion in chronic heart failure: the FOCUS-CCTRN trial. JAMA. 2012;307(16):1717-1726. [9] 顾云,辛毅,吴永涛,等.参附注射液抑制大鼠缺血再灌注损伤期间心肌细胞凋亡的作用机制[J].新乡医学院学报, 2012, 29(2):85-88. [10] 李丹,李蓓,石亚楠,等.心力衰竭与活性氧关系研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2013,27(1):8-10. [11] Traverse JH, Henry TD, Ellis SG, et al. Effect of intracoronary delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells 2 to 3 weeks following acute myocardial infarction on left ventricular function: the LateTIME randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;306(19): 2110-2119. [12] Huang XP, Sun Z, Miyagi Y, et al. Differentiation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells induces immunogenicity and limits their long-term benefits for myocardial repair. Circulation. 2010;122(23):2419-2429. [13] Hare JM, Fishman JE, Gerstenblith G, et al. Comparison of allogeneic vs autologous bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: the POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2369-2379. [14] 邱小华,戴育成,胡葵葵.脐带间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(6):88-91. [15] Ye L, Zhang S, Greder L, et al. Effective cardiac myocyte differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells requires VEGF. PLoS One. 2013;8(1): e53764. [16] Chachques JC. Cellular cardiac regenerative therapy in which patients? Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009; 7(8):911-919. [17] Cortes-Morichetti M, Frati G, Schussler O, et al. Association between a cell-seeded collagen matrix and cellular cardiomyoplasty for myocardial support and regeneration. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(11):2681-2687. [18] Perin EC, Willerson JT. CD34+ autologous human stem cells in treating refractory angina. Circ Res. 2011; 109(4):351-352. [19] Losordo DW, Henry TD, Davidson C, et al. Intramyocardial, autologous CD34+ cell therapy for refractory angina. Circ Res. 2011;109(4):428-436. [20] Irollo E, Pirozzi G. CD133: to be or not to be, is this the real question? Am J Transl Res. 2013;5(6):563-581. [21] Mizrak D, Brittan M, Alison M. CD133: molecule of the moment. J Pathol. 2008;214(1):3-9. [22] Donovan LK, Pilkington GJ. CD133: holy of grail of neuro-oncology or promiscuous red-herring? Cell Prolif. 2012;45(6):527-537. [23] Fargeas CA, Florek M, Huttner WB, et al. Characterization of prominin-2, a new member of the prominin family of pentaspan membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(10):8586-8596. [24] Barcelos LS, Duplaa C, Kränkel N, et al. Human CD133+ progenitor cells promote the healing of diabetic ischemic ulcers by paracrine stimulation of angiogenesis and activation of Wnt signaling. Circ Res. 2009;104(9):1095-1102. [25] Pozzobon M, Bollini S, Iop L, et al. Human bone marrow-derived CD133(+) cells delivered to a collagen patch on cryoinjured rat heart promote angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(10): 1247-1260. [26] 赵瑞刚,蔡俊彦,王军力.N端脑钠肽在心力衰竭诊治中的应用进展[J].河北医药,2013,35(2):268-270. [27] 滕伟,薛永亮,何兆辉,等.磷酸肌酸钠对冠心病并慢性心力衰竭患者B型利钠肽及心功能的影响[J].中国医药导报, 2012,9(18):59-60. [28] Fosbøl EL, Seibaek M, Brendorp B, et al. Long-term prognostic importance of resting heart rate in patients with left ventricular dysfunction in connection with either heart failure or myocardial infarction: the DIAMOND study. Int J Cardiol. 2010;140(3):279-286. [29] Schroten NF, Ruifrok WP, Kleijn L, et al. Short-term vitamin D3 supplementation lowers plasma renin activity in patients with stable chronic heart failure: an open-label, blinded end point, randomized prospective trial (VitD-CHF trial). Am Heart J. 2013;166(2): 357-364. e2. [30] Gheorghiade M, Böhm M, Greene SJ, et al. Effect of aliskiren on postdischarge mortality and heart failure readmissions among patients hospitalized for heart failure: the ASTRONAUT randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;309(11):1125-1135. [31] 王辉,张知翠,罗晓菊,等.人脐血干细胞移植建立人鼠嵌合体动物模型实验研究[J].实用医院临床杂志,2008,5(4): 40-43. [32] Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, et al. Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation. 2002;106(15):1913-1918. [33] 李丽,王明元,程根林,等.流式细胞术在成分血残留白细胞检测中的应用[J].临床输血与检验,2004,6(3):177-179. [34] Romanic AM, Harrison SM, Bao W, et al. Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeted deletion of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;54(3):549-558. [35] Li YY, McTiernan CF, Feldman AM. Interplay of matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases and their regulators in cardiac matrix remodeling. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;46(2):214- 224. [36] 徐赤裔,周建庆,方建江,等.干细胞移植治疗实验犬心肌梗死后心力衰竭的作用[J].浙江医学,2007,29(9):931-934. [37] Qiao H, Zhang H, Zheng Y, et al. Embryonic stem cell grafting in normal and infarcted myocardium: serial assessment with MR imaging and PET dual detection. Radiology. 2009;250(3):821-829. [38] 郝牧,漆佩静,李刚,等.人脐带间充质干细胞对脐血CD34~+细胞在NOD/SCID小鼠体内造血重建的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2010,32(1):71. [39] 毛平,彭盘俐,许力.人脐血单个核细胞体外扩增后植入NOD/SCID小鼠重建多系造血[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2006,27(4):231-234. [40] 谭玲,陈勇华,张春明,等.人脐血CD133细胞的分离及其体外扩增的研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2007,7(6): 853-856. [41] 车京津,张承宗,陈元禄,等.缬沙坦、苯那普利及合用时对心肌梗死后心室重构影响的比较[J].中国心血管杂志, 2002,7(6):381-384. [42] 张军霞,李瑞,赵鹏,等.CD133免疫磁珠分选脐血内皮祖细胞的培养及鉴定[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2008, 15(2):159-162. [43] Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, et al. CD133(+) and CD133(-) glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles. Cancer Res. 2007;67(9):4010-4015. [44] 吴计生,段淑云,郝建平.免疫组化抗原修复的应用进展[J].实用医技杂志,2006,13(20):3592-3593. [45] 康文慧,马元,罗明.两种剂量异丙肾上腺素制备心衰大鼠模型心功能的比较[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2009,30(4): 50-53. [46] 冯清华,张晶.心理干预联合药物治疗老年慢性心力衰竭患者疗效观察[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2011,3(4): 295-296. [47] 中国康复医学会心血管病专业委员会,中国老年学学会心血管病专业委员会.慢性稳定性心力衰竭运动康复中国专家共识[J].中华心血管病杂志,2014,42(9):714-720. [48] Freyssin C, Verkindt C, Prieur F, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation in chronic heart failure: effect of an 8-week, high-intensity interval training versus continuous training. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(8):1359-1364. [49] 沈玉芹,蒋金法,王乐民,等.有氧运动康复对慢性心力衰竭患者运动心排血量及相关参数的影响[J].中华心血管病杂志,2011,39(8):700-705. [50] 陈巍,林平,李玲.中文版心力衰竭患者自我护理行为量表的信效度检测[J].中华护理杂志,2013,48(7):629-631. [51] 党海舟,李明凯,徐明,等.主动脉弓缩窄术和腹腔注射IPH致小鼠慢性心衰两种模型的比较和评价[J].心脏杂志, 2012,24(2):168-172. [52] 孙晓靖.他汀类药物对异丙肾心衰大鼠心肌细胞凋亡影响的研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2009. [53] Koutna I, Peterkova M, Simara P, et al. Proliferation and differentiation potential of CD133+ and CD34+ populations from the bone marrow and mobilized peripheral blood. Ann Hematol. 2011;90(2):127-137. [54] 谢亚序,康大伟,李秀华.慢性心力衰竭心肌纤维化大鼠模型的建立[J].承德医学院学报,2011,28(1):10-12. [55] To LB, Haylock DN, Dowse T, et al. A comparative study of the phenotype and proliferative capacity of peripheral blood (PB) CD34+ cells mobilized by four different protocols and those of steady-phase PB and bone marrow CD34+ cells. Blood. 1994;84(9):2930-2939. [56] Freund D, Oswald J, Feldmann S, et al. Comparative analysis of proliferative potential and clonogenicity of MACS-immunomagnetic isolated CD34+ and CD133+ blood stem cells derived from a single donor. Cell Prolif. 2006;39(4):325-332. [57] Charrier S, Boiret N, Fouassier M, et al. Normal human bone marrow CD34(+)CD133(+) cells contain primitive cells able to produce different categories of colony-forming unit megakaryocytes in vitro. Exp Hematol. 2002;30(9):1051-1060. [58] Menasche P. Cardiac cell therapy: lessons from clinical trials. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(2):258-265. [59] Minami I, Yamada K, Otsuji TG, et al. A small molecule that promotes cardiac differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells under defined, cytokine- and xeno-free conditions. Cell Rep. 2012;2(5):1448-1460. [60] Fonoudi H, Ansari H, Abbasalizadeh S, et al. A Universal and Robust Integrated Platform for the Scalable Production of Human Cardiomyocytes From Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015; 4(12):1482-1494. [61] Willems E, Spiering S, Davidovics H, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt pathway potently promote cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cell-derived mesoderm. Circ Res. 2011;109(4): 360-364. [62] Lian X, Hsiao C, Wilson G, et al. Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(27):E1848-1857. [63] Lian X, Zhang J, Azarin SM, et al. Directed cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling under fully defined conditions. Nat Protoc. 2013;8(1): 162-175. [64] Frank S, Zhang M, Schöler HR, et al. Small molecule-assisted, line-independent maintenance of human pluripotent stem cells in defined conditions. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41958.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||