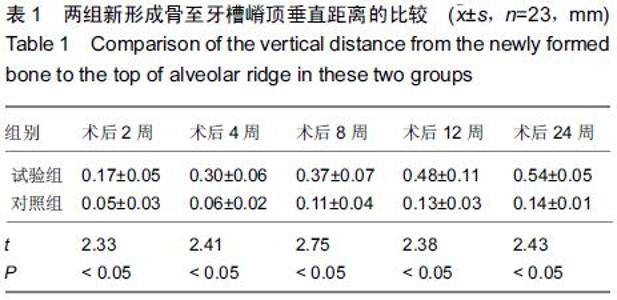
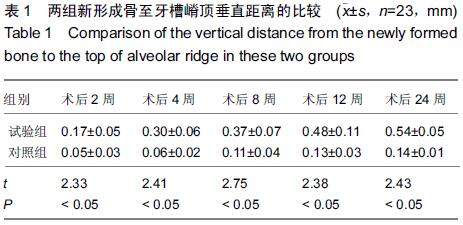
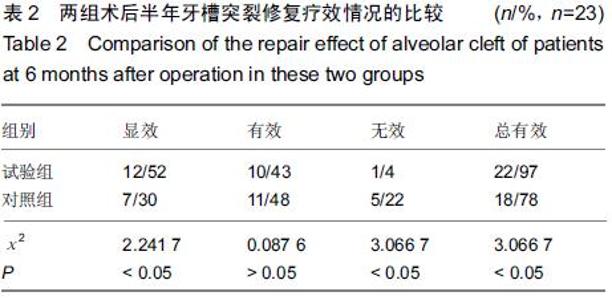
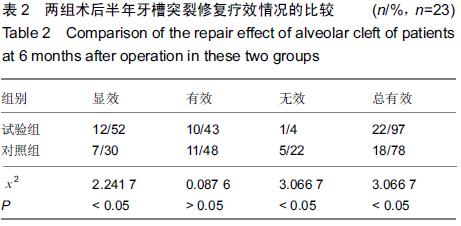
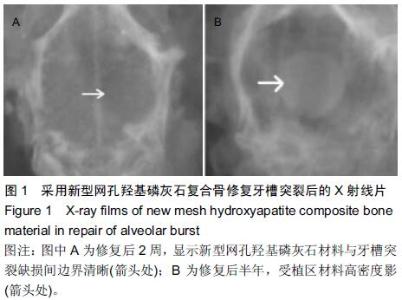
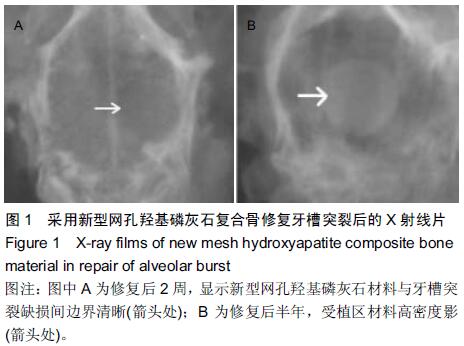
[2] Pan Z,Ding JD.Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Interface Focus. 2012;2(3):366-377.
[3] Masucci C,Franchi L,Defraia E,et al.Stability of rapid maxillary expansion and facemask therapy: a long-term controlled study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2011;140(4):493-500.
[4] 姜群,傅国,毕先燕,等.口腔修复膜与自体髂骨联合移植在牙槽嵴裂植骨中的临床观察[J].口腔医学研究,2010,26(1):108-110.
[5] 张志宏,刘志礼,高志增,等. 骨修复替代材料修复骨缺损的选择与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52):9836-9843.
[6] 鄂玲玲,王东胜,师占平,等.一种新型的兔牙槽骨缺损模型的建立[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2011,9(3):137-140.
[7] 陈德敏.丙烯酸酯类骨水泥材料的临床应用与研究进展[J].口腔材料器械,2010,19(2): 81-86.
[8] 任红革,李林,李振浩,等.续断对兔骨缺损修复中 BMP-2 基因表达的影响[J].延边大学医学学报,2012,35(3):163-166.
[9] 何祖求.自体骨联合人工骨在牙槽突裂修复中的应用[J].医学综述,2013,19(13): 2488-2490.
[10] 杨 超,石 冰 .牙槽突裂植骨术的技术改进与初步评价[J].中国实用口腔杂志,2012,5(6):327-332.
[11] 孙小春,陈慧丽,刘秋兴,等.自体髂骨游离移植在 26 例牙槽嵴裂修复术中的应用[J].江西医药,2011,46(6):493-495.
[12] 乔月娥,任秀云.应用AutoCAD确定牙槽骨水平界值范围研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2012,5(5):283-286.
[13] 周文清,吴燕平,柳锋,等.种植床自体骨复合人工骨在种植美学中的应用[J].口腔医学,2010,29(10):535-537.
[14] 余小明,张倩,田锟,等.骨诱导活性材料在修复牙槽突裂中的临床研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(4):391-394.
[15] 丁常春,陈传俊,陈晓阳,等.自体髂骨松质骨移植修复牙槽突裂的临床应用[J].中国医学创新,2011,8(6):74-75.
[16] Paradowska-Stolarz A,Dubowik M,Szel?g J,et al.Dental anomalies in the incisor-canine region in patients with cleft lip and palate literature review.Dev Period Med.2014;18(1): 66-69.
[17] Cho-Lee GY,García-Díez EM,Nunes RA,et al.Review of secondary alveolar cleft repair.Ann Maxillofac Surg.2013;3(1): 46-50.
[18] 张磊,韩 娟.双牙列义齿修复唇腭裂患者咬合关系紊乱的临床疗效观察[J].中国美容医学,2011,20(1):137-138.
[19] Park SH,Park DS,Shin JW,et al.Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering fabricated from two different materials by the rapid prototyping technique: PCL versus PLGA.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012;23(11):2671-2678.
[20] Park S,Kim JH,Kim IH,et al.Evaluation of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Plate and Screw System for Bone Fixation.J Craniofac Surg.2013;24(3):1021-1025.
[21] 王刚,张文云.人工骨修复牙槽骨缺损的研究进展[J].西南国防医学,2014,24(4):455-456.
[22] 刘鹏.纳米羟基磷灰石-胶原-重组人骨形成蛋白-2复合支架的制备及细胞相容性[D].山西医科大学,2012:1-35.
[23] Patrascu JM,Krüger JP,Böss HG,et al.Polyglycolic acid-hyaluronan scaffolds loaded with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells show chondrogenic differentiation in vitro and cartilage repair in the rabbit model.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2013;101(7):1310-1320.
[24] 罗涛,刘天涛,郭吕华,等.基因活化的仿生生物材料促进骨再生的实验研究[J].医学信息,2014,22(8):110-111.
[25] Miyamoto T.Regulators of osteoclast differentiation and cell-cell fusion. Keio J Med.2011;60(4):101-105.
[26] 陈铮晰,潘晓岗,陈振琦.上颌前牵引联合扩弓对唇腭裂植骨患者上颌骨影响的有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2012,21(3): 287-293.
[27] 陈剑飞,范忠.义齿修复在唇腭裂系列治疗中的应用[J].中国健康月刊,2011,30(9):48-49.
[28] 李志强,艾伟健,刘曙光.可吸收胶原生物膜用于齿槽裂植骨修复临床疗效研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(1):41-43.
[29] 秦科,吕婉瑜.牙颌面畸形正畸和手术联合治疗的正畸策略[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2011,4(5):268-272.
[30] Toscano D,Baciliero U,Gracco A,et al.Long-term stability of alveolar bone grafts in cleft palate patients.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2012;142(3):289-299.