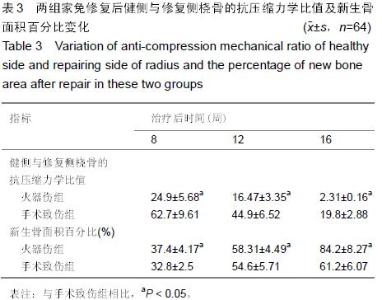
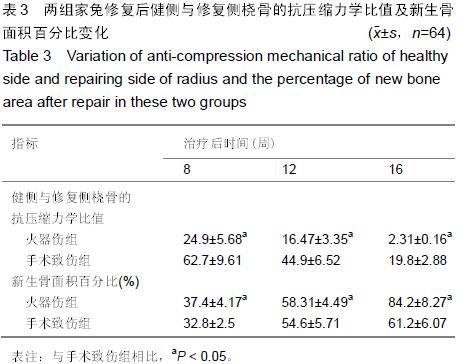
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (47): 7561-7566.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.47.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human vascular endothelial growth factor 121 gene-modified materials repair firearm-induced radial defects
Wang Jian-zhong1, Li Bing-cang2, Ren Bao1, Gao Fei1, Li Cong-jie1, Liu Wei1, Wang Xiao-dong1, Lei Ming1, Gao Wen-shan1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 2the Sixth Laboratory, Institute of Field Surgery, Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University of PLA, National Key Laboratory of Wound, Burn Injury and Complex Wounds, Chongqing 400042, China
-
Received:2015-10-21Online:2015-11-19Published:2015-11-19 -
Contact:Li Bing-cang, the Sixth Laboratory, Institute of Field Surgery, Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University of PLA, National Key Laboratory of Wound, Burn Injury and Complex Wounds, Chongqing 400042, China -
About author:Wang Jian-zhong, M.D., Associate chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Mandatory Subjects of Army Medical Science and Technology Research during the Tenth Five-Year Period, No. 01L060; Science and Technology Research Development Program of Hebei Province of China, No. 072761417
Cite this article
Wang Jian-zhong, Li Bing-cang, Ren Bao, Gao Fei, Li Cong-jie, Liu Wei, Wang Xiao-dong, Lei Ming, Gao Wen-shan. Human vascular endothelial growth factor 121 gene-modified materials repair firearm-induced radial defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(47): 7561-7566.
share this article
| [1] 刘岩,马信龙.人工骨修复材料及金属钛材料在骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(12):2229-2232. [2] 马育林,戴如春,盛志峰,等.骨细胞密度对骨生物力学性能的影响[J].中华老年医学杂志,2009,28(6):500-504.
[3] 辛雷,苏佳灿.人工骨修复材料的现状与展望[J].创伤外科杂志, 2011, 13(3):272-284.
[4] 宋雪莲,于静涛,刘扬,等.壳聚糖在骨组织工程中应用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,6(5):306-310.
[5] 孟志斌,李德豪,周健强,等.可吸收珊瑚羟基磷灰石与天然珊瑚修复骨缺损的组织学及影像学分析[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2007,4(5):10-15.
[6] 侯喜君,王春华,李霖,等.β-磷酸三钙煅烧骨修复兔股骨远端骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(3):400-406.
[7] 杨华清,张明宇,党晓谦,等.复合同种异体成骨细胞的β-磷酸三钙人工骨修复桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(34): 6061-6066.
[8] 张文志,王潇,段丽群,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合人工椎体在颈椎病前路椎体次全切除术中的临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(9):783-785.
[9] Swetha M, Sahithi K, Moorthi A, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of nano-hydroxyapatite-zinc for bone tissue engineering applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;12(1):167-172.
[10] Shen L, Yang H, Ying J, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced hydroxyapatite/ polylactide biocomposites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009; 20(11): 2259-2265.
[11] 姚旺祥,马安,朱六龙,等.浓缩自体骨髓复合纤维蛋白胶修复兔桡骨陈旧性骨缺损[J].中国医学科学院学报,2011,33(4): 387-392.
[12] 肖裕华,李绍琴,潘文峰,等.纤维蛋白胶复合骨形态发生蛋白与VEGF修复兔桡骨缺损的实验研究[J].实用临床医学,2013,14(6): 17-19.
[13] Pei M, He F, Boyce BM, et al. Repair of full-thickness femoral condyle cartilage defects using allogeneic synovial cell-engineered tissue constructs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(6):714-722.
[14] 佟刚,雷静,钟翠红,等.不同PH与蛋白含量的胶原海绵植入缺损骨组织部位的疗效及安全性考察[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012, 29(6):1125-1130.
[15] 杨春蓉,王迎军,陈晓峰.纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原/磷酸丝氨酸仿生复合骨组织工程支架材料的制备及表征[J].中国科学杂志,2013, 58(3):267-271.
[16] 李娟,郑闱颖,卢岩,等.骨形成蛋白-2基因修饰的β磷酸三钙/胶原复合材料修复颅骨缺损[J].材料科学与工程学报,2013,31(2): 248-252.
[17] Ramay HR, Zhang M. Biphasic calcium phosphate nanocomposite porous scaffolds for load-bearing bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2004;25(21):5171-5180.
[18] Maquet V, Boccaccini AR, Pravata L, et al.Porous poly (a-hydroxyacid)/ Bioglasss composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. I: preparation and in vitro characterization. Biomaterials. 2004;25(18):4185-4194.
[19] Niemeyer P, Szalay K, Luginbuhl R, et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a non-autogenous setting for bone regeneration in a rabbit critical-size defect model. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(3):900-908.
[20] Liu Y, Pei G, Jiang S. New porous beta-tricalcium phosphate as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;12(23):4563-4567.
[21] 彭吾训,王蕾,邓进,等.一种组织工程骨修复兔股骨头坏死模型的效果评价[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(7):661-664.
[22] 赵玫,吴海珍,王鑫,等.牙源性双相陶瓷的研制及其骨缺损修复实验[J].安徽医科大学学报,2013,48(6):617-620.
[23] 姚彪,钱卫庆,尹宏,等.新型α-半水硫酸钙/双相生物陶瓷人工骨修复兔桡骨骨缺损的X射线评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(47): 7550-7555.
[24] inheiro AL, Santos NR, Oliveira PC, et al. The efficacy of the use of IR laser phototherapy associated to biphasic ceramic graft and guided bone regeneration on surgical fractures treated with wire osteosynthesis: a comparative laser fluorescence and Raman spectral study on rabbits. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28(3):815-822.
[25] Wu CC, Yang KC, Yang SH, et al. In vitro studies of composite bone filler based on poly(propylene fumarate) and biphasic α-tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite ceramic powder. Artif Organs. 2012;36(4):418-428.
[26] Froum SJ, Wallace SS, Cho SC, et al. Histomorphometric comparison of a biphasic bone ceramic to anorganic bovine bone for sinus augmentation: 6- to 8-month postsurgical assessment of vital bone formation: a pilot study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008;28(3):273-281.
[27] Pinheiro AL, Aciole GT, Ramos TA, et al. The efficacy of the use of IR laser phototherapy associated to biphasic ceramic graft and guided bone regeneration on surgical fractures treated with miniplates: a histological and histomorphometric study on rabbits. Lasers Med Sci. 2014; 29(1):279-288.
[28] 刘瑞丽,吴学建,王利民,等.多孔双相陶瓷复合重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子缓释微球的异位成骨活性[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(7):1045-1047.
[29] 周献伟,孙勇.纳米磷酸钙陶瓷人工骨治疗跟骨骨缺损的X射线评价[J].中国医师杂志,2011,13(5):676-677.
[30] 王蕾,彭吾训,张爱华,等.双相陶瓷生物骨-骨形态发生蛋白-碱性成纤维细胞生长因子复合物修复股骨头坏死模型的实验研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2013,19(5):426-431.
[31] 王丽丽.复合性生物活性陶瓷在颌骨囊肿骨缺损修复中的应用[J].黑龙江医药,2012,25(1):128.
[32] 郑磊,王前,魏宽海,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对成骨细胞粘附特性影响的实验研究. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2000,14(5):305-307.
[33] 陈亚军,叶古祥,孙国娣.MTT法体外测定胃癌化疗药物敏感性[J].中国普通外科杂志,2003,12(1):47-49.
[34] Hu BL, Joshua MN, Dong CY, et al. Development of a novel recombinant adenovirus containing gfp–zeocin fusion expression cassette for conditional replication in p53-deficient human tumor cells. J Viroll Meth. 2004;117(2):129-136.
[35] Allipour Birgani S, Mailänder M, et al. Efficient therapy of ischaemic lesions with VEGF121-fibrin in an animal model of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015.
[36] Ciomber A, Smagur A, Mitrus I, et al. Antitumor effects of recombinant antivascular protein ABRaA-VEGF121 combined with IL-12 gene therapy. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2014;62(2):161-168.
[37] Zhang Y, Hong H, Niu G, et al. Positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression with (61)Cu-labeled lysine-tagged VEGF121. Mol Pharm. 2012;9(12):3586-3594.
[38] Rosengart TK, Bishawi MM, Halbreiner MS, et al. Long-term follow-up assessment of a phase 1 trial of angiogenic gene therapy using direct intramyocardial administration of an adenoviral vector expressing the VEGF121 cDNA for the treatment of diffuse coronary artery disease. Hum Gene Ther. 2013;24(2):203-208.
[39] Mohamedali KA, Niu G, Luster TA, et al. Pharmacodynamics, tissue distribution, toxicity studies and antitumor efficacy of the vascular targeting fusion toxin VEGF121/rGel. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(11):1534-1540.
[40] Smirnikhina SA, Lavrov AV, Bochkov NP. Dynamics of elimination of plasmids and expression of VEGF121 gene transfected into human mesenchymal stem cells by different methods. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;151(1):121-125.
[41] Cho EJ, Yang J, Mohamedali KA, et al. Sensitive angiogenesis imaging of orthotopic bladder tumors in mice using a selective magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent containing VEGF121/rGel. Invest Radiol. 2011;46(7):441-449.
[42] Mohamedali KA, Li ZG, Starbuck MW, et al. Inhibition of prostate cancer osteoblastic progression with VEGF121/rGel, a single agent targeting osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and tumor neovasculature. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2328-2338.
[43] Woods AK, Hoffmann DS, Weydert CJ, et al. Adenoviral delivery of VEGF121 early in pregnancy prevents spontaneous development of preeclampsia in BPH/5 mice. Hypertension. 2011;57(1):94-102.
[44] Xu D, Fuster MM, Lawrence R, et al. Heparan sulfate regulates VEGF165- and VEGF121-mediated vascular hyperpermeability. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(1):737-745.
[45] Cai C, Böttcher MC, Werner JA, et al. Differential expression of VEGF121, VEGF165 and VEGF189 in angiomas and squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(3):805-810.
[46] Smagur A, Boyko MM, Biront NV, et al. Chimeric protein ABRaA-VEGF121 is cytotoxic towards VEGFR-2-expressing PAE cells and inhibits B16-F10 melanoma growth. Acta Biochim Pol. 2009;56(1):115-1124.
[47] Kawai H, Minamiya Y, Ito M, et al. VEGF121 promotes lymphangiogenesis in the sentinel lymph nodes of non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. Lung Cancer. 2008;59(1):41-47.
[48] Clere N, Bermont L, Fauconnet S, et al. The human papillomavirus type 18 E6 oncoprotein induces Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 121 (VEGF121) transcription from the promoter through a p53-independent mechanism. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(15):3239-3250.
[49] Pan Q, Chathery Y, Wu Y, et al. Neuropilin-1 binds to VEGF121 and regulates endothelial cell migration and sprouting. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(33):24049-24056.
[50] Liu LS, Wei DH, Tang CK, et al. A HUVEC line with a stable expression of the VEGF121 gene to achieve complete endothelialization of blood conduits. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2007;35(3):319-331.
[51] von Wronski MA, Tweedle MF, et al. Binding of the C-terminal amino acids of VEGF121 directly with neuropilin-1 should be considered. FASEB J. 2007;21(7):1292-1293.
[52] Hsu AR, Cai W, Veeravagu A, et al. Multimodality molecular imaging of glioblastoma growth inhibition with vasculature-targeting fusion toxin VEGF121/rGel. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(3):445-454.
[53] Catena R, Muniz-Medina V, Moralejo B, et al. Increased expression of VEGF121/VEGF165-189 ratio results in a significant enhancement of human prostate tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(10):2096-2109.
[54] Kim S, Mohamedali KA, Cheung LH, et al. Overexpression of biologically active VEGF121 fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 2007;128(3):638-647.
[55] 张元平,崔继秀,裴国献,等.植入神经的自体骨髓基质细胞-β磷酸三钙复合体修复兔长骨骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2006,10(13):62-66.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||