Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (45): 7374-7380.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.45.028
Extracorporeal shock wave and myocardial angiogenesis: effects on endogenous stem cells, cytokines and local microenvironment
Ma Yi-ming, Li Li, Cai Hong-yan, Guo Tao
- Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-28Online:2015-11-05Published:2015-11-05 -
Contact:Cai Hong-yan, Master’s supervisor, Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Ma Yi-ming, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81260027; the Scientific Plan Project of Yunnan Province, No. 2014FZ023; the Scientific Plan Project of Yunnan Provincial Health Department, No. 2012WS0005
Cite this article
Ma Yi-ming, Li Li, Cai Hong-yan, Guo Tao. Extracorporeal shock wave and myocardial angiogenesis: effects on endogenous stem cells, cytokines and local microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(45): 7374-7380.
share this article
| [1] Fukumoto Y, Ito A, Uwatoku T, et al. Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy ameliorates myocardial ischemia in patients with severe coronary artery disease. Coron Artery Dis. 2006;17(1):63-70. [2] Wang Y, Guo T, Cai HY, et al. Cardiac shock wave therapy reduces angina and improves myocardial function in patients with refractory coronary artery disease. Clin Cardiol. 2010;33 (11):693-699.
[3] Yang P, Guo T, Wang W, et al. Randomized and double-blind controlled clinical trial of extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy for coronary heart disease. Heart Vessels. 2013;28(3): 284-291.
[4] Lorier G, Touriño C, Kalil RA. Coronary angiogenesis as an endogenous response to myocardial ischemia in adults. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2011;97(6):e140-148.
[5] Nishida T, Shimokawa H, Oi K, et al. Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy markedly ameliorates ischemia-induced myocardial dysfunction in pigs in vivo. Circulation. 2004;110 (19):3055-3061.
[6] Uwatoku T, Ito K, Abe K, et al. Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy improves left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction in pigs. Coron Artery Dis. 2007;18(5): 397-404.
[7] Ito Y, Ito K, Shiroto T, et al. Cardiac shock wave therapy ameliorates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in pigs in vivo. Coron Artery Dis. 2010;21(5):304-311.
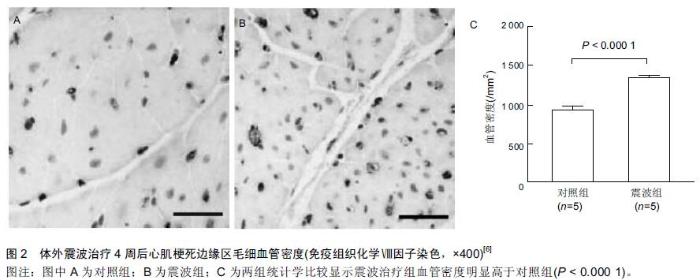
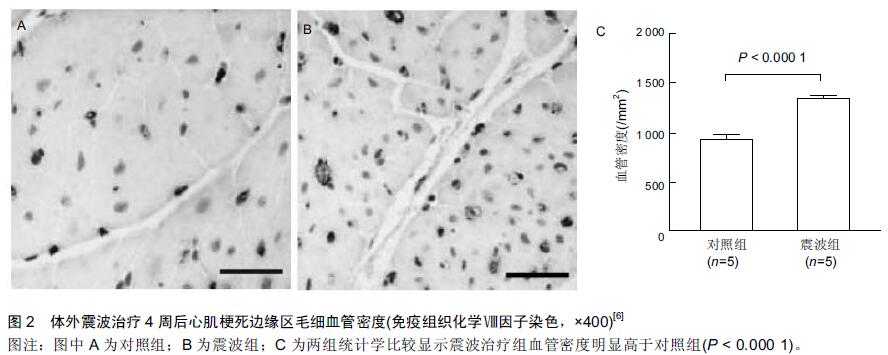
[8] 陶四明,郭涛,王钰,等.低能量体外心脏震波对急性心肌梗死后心肌基质金属蛋白酶系统及缺血心肌毛细血管密度的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(37):6979-6984.
[9] Jackson KA, Majka SM, Wang H, et al. Regeneration of ischemic cardiac muscle and vascular endothelium by adult stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(11):1395-1402.
[10] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature. 2001;410(6829): 701-705.
[11] Bel A, Messas E, Agbulut O, et al. Transplantation of autologous fresh bone marrow into infarcted myocardium: a word of caution. Circulation. 2003;108 Suppl 1:II247-252.
[12] Yip HK, Chang LT, Sun CK, et al. Shock wave therapy applied to rat bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells enhances formation of cells stained positive for CD31 and vascular endothelial growth factor. Circ J. 2008;72(1): 150-156.
[13] Silva GV, Litovsky S, Assad JA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into an endothelial phenotype, enhance vascular density, and improve heart function in a canine chronic ischemia model. Circulation. 2005;111(2):150-156.
[14] Abedin M, Tintut Y, Demer LL. Mesenchymal stem cells and the artery wall. Circ Res. 2004;95(7):671-676.
[15] Suhr F, Delhasse Y, Bungartz G, et al. Cell biological effects of mechanical stimulations generated by focused extracorporeal shock wave applications on cultured human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2): 951-964.
[16] Zhao Y, Wang J, Wang M, et al. Activation of bone marrow- derived mesenchymal stromal cells-a new mechanism of defocused low-energy shock wave in regenerative medicine. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(12):1449- 1457.
[17] Zeoli A, Dentelli P, Brizzi MF. Endothelial progenitor cells and their potential clinical implication in cardiovascular disorders. J Endocrinol Invest. 2009;32(4):370-382.
[18] Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997; 275(5302):964-967.
[19] Urbich C, Aicher A, Heeschen C, et al. Soluble factors released by endothelial progenitor cells promote migration of endothelial cells and cardiac resident progenitor cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;39(5):733-742.
[20] 蔡红雁,王钰,李琳,等.体外心脏震波治疗前后外周血内皮祖细胞数量的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(49): 9249-9252.
[21] 蔡红雁,王钰,郭涛,等.体外心脏震波冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病患者血循环中内皮祖细胞及血管内皮生长因子的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(36):6755-6758.
[22] Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):669-676.
[23] Kamihata H, Matsubara H, Nishiue T, et al. Implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells into ischemic myocardium enhances collateral perfusion and regional function via side supply of angioblasts, angiogenic ligands, and cytokines. Circulation. 2001;104(9):1046-1052.
[24] Lee SH, Wolf PL, Escudero R, et al. Early expression of angiogenesis factors in acute myocardial ischemia and infarction. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(9):626-633.
[25] Grunewald M, Avraham I, Dor Y, et al. VEGF-induced adult neovascularization: recruitment, retention, and role of accessory cells. Cell. 2006;124(1):175-189.
[26] Asahara T, Takahashi T, Masuda H, et al. VEGF contributes to postnatal neovascularization by mobilizing bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. EMBO J. 1999;18(14):3964-3972.
[27] Ito K, Fukumoto Y, Shimokawa H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a new and non-invasive angiogenic strategy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009;219(1):1-9.
[28] Ito K, Fukumoto Y, Shimokawa H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for ischemic cardiovascular disorders. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2011;11(5):295-302.
[29] Schumacher B, Pecher P, von Specht BU, et al. Induction of neoangiogenesis in ischemic myocardium by human growth factors: first clinical results of a new treatment of coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1998;97(7):645-650.
[30] 孙帅, 郭涛. 体外心脏震波治疗对猪急性心肌梗死后内皮型一氧化氮合酶及碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达的影响[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2010, 26(9):769-772.
[31] Yamaguchi J, Kusano KF, Masuo O, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation. 2003;107(9):1322-1328.
[32] De Falco E, Porcelli D, Torella AR, et al. SDF-1 involvement in endothelial phenotype and ischemia-induced recruitment of bone marrow progenitor cells. Blood. 2004;104(12): 3472-3482.
[33] Aicher A, Heeschen C, Sasaki K, et al. Low-energy shock wave for enhancing recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells: a new modality to increase efficacy of cell therapy in chronic hind limb ischemia. Circulation. 2006;114(25):2823-2830.
[34] Fu M, Sun CK, Lin YC, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy reverses ischemia-related left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling: molecular-cellular and functional assessment. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24342.
[35] Cooke GE, Doshi A, Binkley PF. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene: prospects for treatment of heart disease. Pharmacogenomics. 2007;8(12):1723-1734.
[36] Paulus WJ. The role of nitric oxide in the failing heart. Heart Fail Rev. 2001;6(2):105-118.
[37] Yetik-Anacak G, Catravas JD. Nitric oxide and the endothelium: history and impact on cardiovascular disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006;45(5):268-276.
[38] Smith RS Jr, Agata J, Xia CF, et al. Human endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene delivery protects against cardiac remodeling and reduces oxidative stress after myocardial infarction. Life Sci. 2005;76(21):2457-2471.
[39] Gotte G, Amelio E, Russo S, et al. Short-time non-enzymatic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine and hydrogen peroxide induced by shock waves treatment. FEBS Lett. 2002;520(1-3): 153-155.
[40] Mariotto S, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves: from lithotripsy to anti-inflammatory action by NO production. Nitric Oxide. 2005;12(2):89-96.
[41] Mariotto S, de Prati AC, Cavalieri E, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(19):2366-2372.
[42] Ciampa AR, de Prati AC, Amelio E, et al. Nitric oxide mediates anti-inflammatory action of extracorporeal shock waves. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(30):6839-6845.
[43] Sheu JJ, Sun CK, Chang LT, et al. Shock wave-pretreated bone marrow cells further improve left ventricular function after myocardial infarction in rabbits. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010; 24(6):809-821.
[44] Thomas CV, Coker ML, Zellner JL, et al. Increased matrix metalloproteinase activity and selective upregulation in LV myocardium from patients with end-stage dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1998;97(17):1708-1715.
[45] Neve A, Cantatore FP, Maruotti N, et al. Extracellular matrix modulates angiogenesis in physiological and pathological conditions. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:756078.
[46] Rundhaug JE. Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(2):267-285.
[47] Pepper MS. Extracellular proteolysis and angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(1):346-355.
[48] 陶四明,郭涛,王钰,等.低能量体外心脏震波对急性心肌梗死后心肌基质金属蛋白酶系统及缺血心肌毛细血管密度的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(37):6979-6984.
[49] Schmid JP, Capoferri M, Wahl A, et al. Cardiac shock wave therapy for chronic refractory angina pectoris. A prospective placebo-controlled randomized trial. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013; 31(3):e1-6.
[50] Kikuchi Y, Ito K, Ito Y, et al. Double-blind and placebo-controlled study of the effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy for severe angina pectoris. Circ J. 2010;74(3):589-591.
[51] Assmus B, Walter DH, Seeger FH, et al. Effect of shock wave-facilitated intracoronary cell therapy on LVEF in patients with chronic heart failure: the CELLWAVE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;309(15):1622-1631.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||