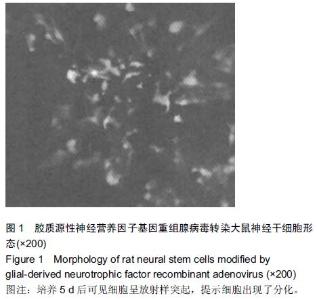
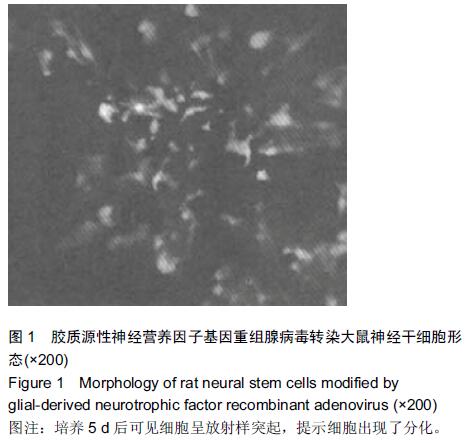
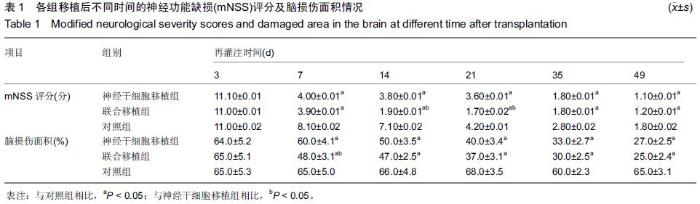
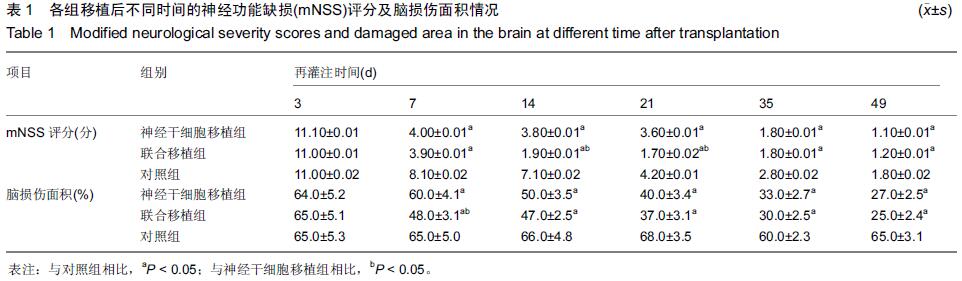
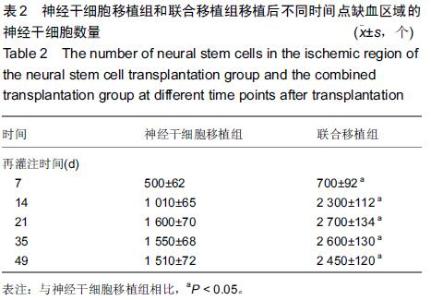
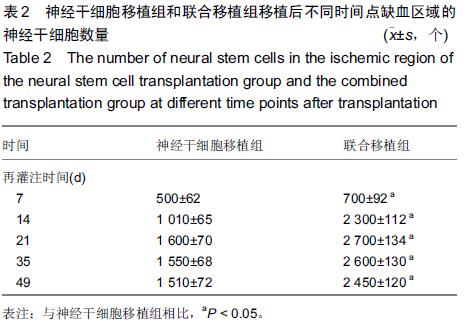
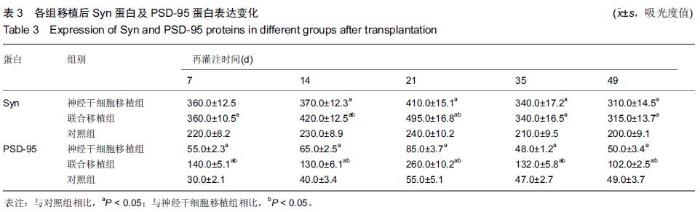
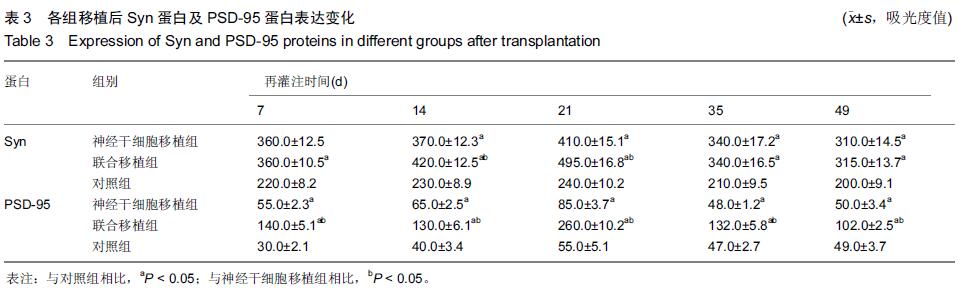
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (45): 7331-7336.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.45.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuroprotective effect of neural stem cells modified by glial-derived neurotrophic factor on cerebral apoplexy
Wu Zhong-hua
- Tongzhou District People’s Hospital, Nantong 226399, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-26Online:2015-11-05Published:2015-11-05 -
Contact:Wu Zhong-hua, Tongzhou District People’s Hospital, Nantong 226399, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wu Zhong-hua, Master, Attending physician, Tongzhou District People’s Hospital, Nantong 226399, Jiangsu Province, China
Cite this article
Wu Zhong-hua. Neuroprotective effect of neural stem cells modified by glial-derived neurotrophic factor on cerebral apoplexy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(45): 7331-7336.
share this article
| [1] 陈波,高小青,杨朝鲜,等.移植GDNF基因修饰的神经干细胞对大鼠脑卒中的神经保护作用[J].解剖学杂志,2009,32(3):286-290, 312. [2] 陈贵军,高小青,杨朝鲜,等.GDNF基因修饰的神经干细胞抑制脑卒中后大鼠的Caspase-3表达[J].四川医学,2012,33(9): 1538-1541.
[3] 陈岚,李玫.神经干细胞移植在脑损伤治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27):5112-5114.
[4] Lin S, Wang Y, Zhang C, et al. Modification of the neurotrophin-3 gene promotes cholinergic neuronal differentiation and survival of neural stem cells derived from rat embryonic spinal cord in vitro and in vivo. J Int Med Res. 2012;40(4):1449-1458.
[5] 邓兴力,王应莉,杨智勇,等.SPIO、EGFP双标GDNF基因修饰中脑神经干细胞移植治疗帕金森病[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2010, 27(2):109-113.
[6] 谭雪锋,金国华,田美玲,等.白介素-1α及与白介素-11、白血病抑制因子和胶质细胞源性神经生长因子联合诱导人神经干细胞向多巴胺神经元的分化[J].解剖学报,2005,36(4):351-355.
[7] 先雄斌,高小青,杨朝鲜,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰神经干细胞移植短暂性脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(49): 9677-9680.
[8] 樊志刚,师瑞红.低氧诱导因子1α基因修饰脐血间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,(10): 1592-1596.
[9] 吴成吉,晋学飞,王璇等.Noggin基因修饰神经干细胞移植对局灶性脑缺血的研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2015,(4):540-542.
[10] 李金艳,王亮.促红细胞生成素基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,(23):3664- 3669.
[11] 刘如恩,Deng XL,郭京,等.超顺磁氧化铁、绿色荧光蛋白双标胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰中脑神经前体细胞的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(8):964-966.
[12] 高明勇,肖建德,李振宇,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子联合转化生长因子β1体外诱导大鼠脊髓源性神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(24):4856-4860.
[13] Kim E, Lee S, Hong S, et al. Sticky "delivering-from" strategies using viral vectors for efficient human neural stem cell infection by bioinspired catecholamines. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(11):8388-8394.
[14] Brito C, Simão D, Costa I, et al. Generation and genetic modification of 3D cultures of human dopaminergic neurons derived from neural progenitor cells. Methods. 2012;56(3): 452-460.
[15] 王旭辉,李世亭.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子与脑缺血损伤[J].卒中与神经疾病,2004,11(4):253-255.
[16] Casalino L, Magnani D, De Falco S, et al. An automated high throughput screening-compatible assay to identify regulators of stem cell neural differentiation. Mol Biotechnol. 2012;50(3): 171-180.
[17] 欧雅莉,杨天伦,方立,等.GDNF基因真核表达载体的构建及其在脐血CD34+干细胞的表达[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2008,25(6): 651-654.
[18] 黄成,杨建东,冯新民,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰后间充质干细胞的生长与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,(45): 7932-7938.
[19] 郁时兵,肖建德,刘尚礼,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和肿瘤坏死因子可溶性受体基因修饰的神经干细胞联合移植治疗脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(12): 1148-1152.
[20] 刘争,张洁元,段朝霞,等.表皮神经嵴干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤后GDNF表达的影响及意义[J].中华器官移植杂志,2014,35(4): 243-246.
[21] 王勇,赵伟,冯健洲,等.神经生长因子修饰脂肪干细胞移植促进损伤脊髓的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,(14):2224-2229.
[22] 刘凯,阴晓峰,相恒伟等.Artemin基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞对多巴胺能神经元的保护作用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2015, 14(2):125-130.
[23] 丁继固,丁文杰,李光,等.胶质源性神经营养因子体外诱导小鼠胚胎中脑神经干细胞分化的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2008, 23(4): 341-343,插2.
[24] 王淑艳,任萍,谢淑,等.含GDNF基因的慢病毒载体的构建和其在人胚胎神经干细胞中的表达[J].生物工程学报,2008,24(12): 2061-2067.
[25] 邓莉,梅志强,常能彬,等.GDNF基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞对脑出血大鼠脑源性神经营养因子及其受体的影响[J].泸州医学院学报,2012,35(5):451-454.
[26] 熊敏,曾云,刘志刚,等.经脑源性神经营养因子基因修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞对大鼠急性脊髓损伤的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2013,30(5):1032-1034.
[27] 刘晓刚,邓宇斌,蔡辉,等.控释GDNF联合MSCs源神经元样细胞移植对猴脊髓损伤后前角运动神经元及bcl-2/bax表达的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2008,25(4):428-430.
[28] 陈立,杜娟,陈丽,等.GDNF及dbcAMP对神经干细胞诱导分化为多巴胺能神经元作用的实验研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2014, 31(7):580-584.
[29] 程赛宇,阮怀珍,杨忠,等.GDNF基因逆转录病毒表达载体的构建及转染神经干细胞的研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2008, 25(3): 642-646.
[30] 杜杰,高小青,陈波,等.GDNF基因修饰的神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠局灶性脑缺血的实验研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2010, 35(3): 346-349.
[31] 晋光荣,李云涛,韩群颖,等.GDNF和NO对局灶性脑缺血大鼠皮质和尾壳核神经干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2007,24(1):8-11.
[32] 邓莉,涂江义,郭侃,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰的骨髓基质干细胞移植抑制大鼠脑出血后神经细胞的凋亡[J].解剖学报,2011,42(6):731-736.
[33] 钟慧霖,陈文明,李翠莹,等.移植BDNF和GDNF基因修饰的hMSCs对大鼠大脑中动脉阻塞的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2014,30(1):102-109.
[34] 姜宇,曾水林,鲁佑瑜,等.GDNF促进帕金森病大鼠模型脑内移植的中脑源神经干细胞表达Pitx3、Nurr1和TH[J].神经解剖学杂志,2011,27(1):92-97.
[35] 罗特坚,丁继固,李光,等.白细胞介素-1β和胶质源性神经营养因子体外诱导鼠胚中脑神经干细胞向酪氨酸羟化酶阳性神经元分化[J].解剖学杂志,2011,34(1):41-44.
[36] 贺月秋,陈惠金,钱龙华,等.经脑室神经干细胞移植治疗脑室周围白质软化新生大鼠电镜下脑病理评估[J].实用儿科临床杂志, 2008,23(20):1610-1612, 1629.
[37] 贺月秋,陈惠金,钱龙华,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子联合神经干细胞移植治疗脑室周围白质软化新生大鼠的疗效观察[J].临床儿科杂志,2009,27(10):963-970.
[38] 周玲,邓莉,涂江义,等.GDNF基因修饰的BMSCs在脑出血大鼠脑内存活与分化的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(1): 48-51.
[39] 庞源广,高小青,陈波,等.GDNF基因修饰的神经干细胞移植对大鼠局灶性脑缺血后GFAP表达的影响[J].四川医学,2013,34(8): 1099-1101.
[40] Médoc M, Dhilly M, Matesic L, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of Radiofluorinated Caspase-3/7 Inhibitors as Radiotracers for Apoptosis Imaging and Comparison with [18F]ML-10 in a Stroke Model in the Rat. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015.
[41] Lv H, Wang L, Shen J, et al. Salvianolic acid B attenuates apoptosis and inflammation via SIRT1 activation in experimental stroke rats. Brain Res Bull. 2015;115:30-36.
[42] Kang YH, Park MG, Noh KH, et al. Low serum TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) levels are associated with acute ischemic stroke severity. Atherosclerosis. 2015;240(1): 228-233.
[43] Liu B, Zhang YH, Jiang Y, et al. Gadd45b is a novel mediator of neuronal apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Int J Biol Sci. 2015; 11(3):353-360.
[44] Wu X, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Inhibition of thioredoxin-1 with siRNA exacerbates apoptosis by activating the ASK1-JNK/p38 pathway in brain of a stroke model rats. Brain Res. 2015;1599:20-31.
[45] Hafeez A, Elmadhoun O, Peng C, et al. Reduced Apoptosis by Ethanol and Its Association with PKC-δ and Akt Signaling in Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2014;5(6):366-372.
[46] Raghavan A, Shah ZA. Withania somnifera Improves Ischemic Stroke Outcomes by Attenuating PARP1-AIF-Mediated Caspase-Independent Apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(3):1093-1105.
[47] Mishiro K, Imai T, Sugitani S, et al. Diabetes mellitus aggravates hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke via mitochondrial defects leading to endothelial apoptosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103818.
[48] Calió ML, Marinho DS, Ko GM, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decreases oxidative stress, apoptosis, and hippocampal damage in brain of a spontaneous stroke model. Free Radic Biol Med. 201;70: 141-154.
[49] Ansar S, Chatzikonstantinou E, Thiagarajah R, et al. Pro-inflammatory mediators and apoptosis correlate to rt-PA response in a novel mouse model of thromboembolic stroke. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e85849.
|
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||