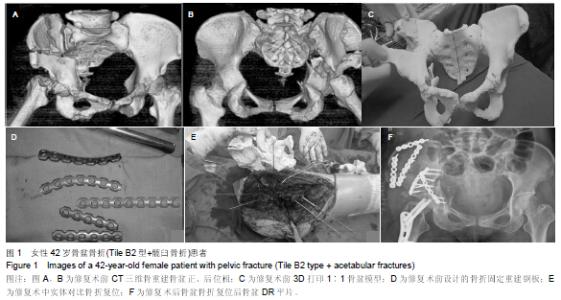
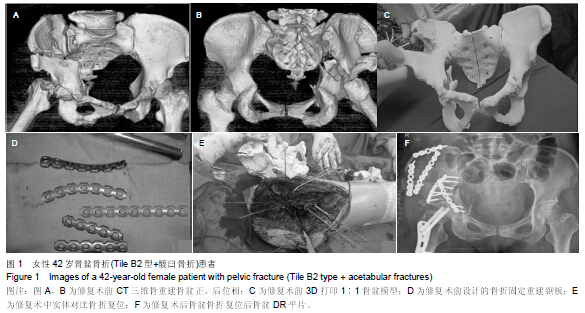
[2] 卢世璧.坎贝尔骨科手术学[M].9版.济南:山东科学技术出版社,2001: 2083.
[3] Gansslen A,Frink M,Hildebrand F,et al.Both column fractures of the acetabulum: epidemiology, operative management and long term results. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012; 79(2):107-113.
[4] 黄美贤,罗吉伟,胡罢生,等.三维螺旋 CT 重建股骨远端旋转力线的测量[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2008,26(1):62-64.
[5] Lu S, Xu YQ, Chen GP, et al. Efficacy and accuracy of a novel rapid prototyping drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(5):240-248.
[6] Fu M, Lin L, Kong X, et al. Construction and accuracy assessment of patient -specific biocompatible drill template for cervical anterior transpedicular screw (ATPS) insertion: An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53580.
[7] Briffa N,Pearce R,Hill AM,et al.Outcomes of acetabular fracture fix ation with ten years'follow- up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):229-236.
[8] 宋军,梅益彰,吴增城,等.复杂髋臼骨折复位及内固定的数字技术模拟研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013,31(4):393-396.
[9] 马立敏,张余,周烨,等.3D打印技术在股骨远端骨肿瘤的应用[J]. 中国数字医学2013, 8(8):70-72.
[10] Silva DN, Gerhardt de Oliveira M, Meurer E, et al. Dimensional error in selective laser sintering and 3D-printing of models for craniomaxillary anatomy reconstruction. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2008;36(8):443-449.
[11] James LG. Acetabular fractures. In:Canale ST.ed.Campbell’s operative orthopaedics.9th ed. ST.Louis:Mosby,1998: 2234-2252.
[12] Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R,等.骨科内固定[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1998.
[13] 邱贵兴.骨盆与髋臼骨折[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2006: 452-455, 498-510.
[14] Doornberg JN, Rademakers MV, van den Bekerom MP, et al. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional computed tomography for the classification and characteri -sation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2011;42(12):1416-1425.
[15] 章莹,夏远军,万磊,等.计算机三维仿真技术与常规手术治疗胫骨平台骨折的疗效对比分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010, 25(8):686-688.