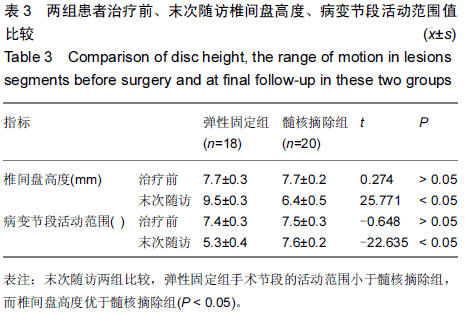
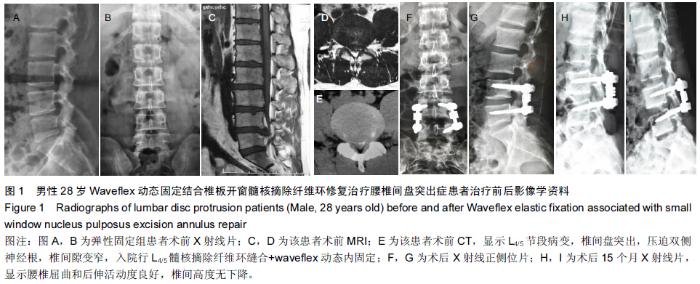
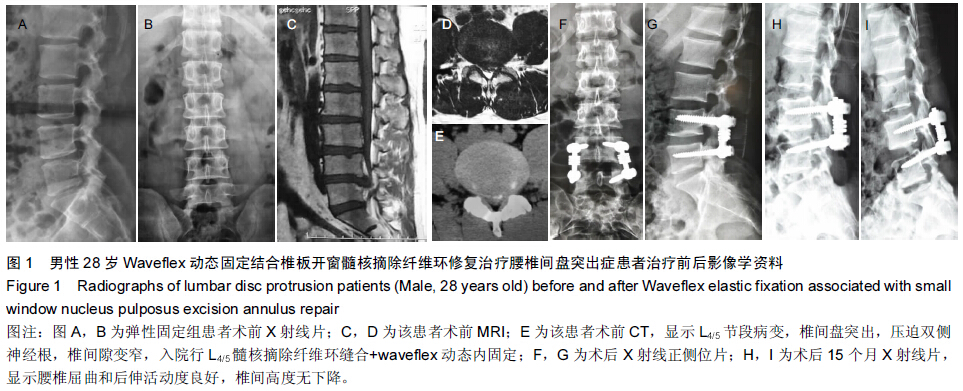
|
[1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012.
[2] Mixter WJ, Barr JS. Ruputure of the intervertebral disc with involvement of the spinal canal. New Eng Med. 1934.
[3] 贾连顺. 脊柱外科学[M].上海:第二军医大学出社,2009: n220-230.
[4] Sengupta DK. Dynamic stabilization devices in the treatmentof low back pain. Neurol India. 2005; 53(4):466-474.
[5] Carlsson AM. Assessment of chronic pain. Aspects of the reliability and validity ofthe visual analogue scale. Pain. 1983; 16:87-101.
[6] Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine. 2000;(25):2940-2952.
[7] Niu G. MR Imaging Assessment of Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Degeneration andAge-Related Changes:Apparent Diffusion Coefficient versus T2 Quantitation AJNR Am J Neuroradio. 2011 Oct;32(9):1617-1623.
[8] 李杰,刘传见,司佳亚.椎间盘镜系统治疗腰椎间盘突出症550 例[J] .中国微创外科杂志, 2005, 5(5):379-380.
[9] 薛朝辉,杨凯,蒋现永.27例青少年腰椎间盘突出症的临床分析[J].中外医疗,2011,11(25):48.
[10] 崇步伟, 周永春.青年腰椎间盘突出症的发病及其诊治[J] .中医正骨杂志,1996,8(6):7-8.
[11] 官建中,周建生,肖玉周,等.青少年腰椎间盘突出症的临床分析[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2011,3(10):1067-1068,1070.
[12] Maigen JY, Pime B, Deligen B.Computed tomographic follow-up studyof forty-eight cases of non-operatively treated lumbar intervertebral discherniaton. Spine. 1992;17:1071- 1074.
[13] 周英杰.腰椎融合与非融合在腰椎间盘突出症手术中的合理选择[J].中医正骨,2014,26(10):3-6.
[14] 张银刚.退变性椎间盘疾病的规范化治疗[J]. 中医正骨,2012, 24(6): 3-8.
[15] 章明,任伟峰.“四防理念”开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症219例[J]. 中医正骨,2011,23(6);64-65.
[16] Suk KS, Lee HM, Moon SH, et al.Recurrent lumbar disc herniation: results of operative management.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(6):672-676.
[17] Erbayraktar S, Acar F, Tekinsoy B,et al. Outcome analysis of reoperations after lumbar discectomies: a report of 22 patients. Kobe J Med Sci. 2002;48(1-2):33-41.
[18] Yong Hang K,Willis WH. The three-joint complex.ln: Weinstein JN, Wiesel SW, eds.The lumbar spine.1st ed.Philadephia: WB sounders company, 1990:80-87.
[19] 关凯,孙天胜,李放,等.动态固定及其在腰椎退行性疾病中的应用现状[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(9):709-711
[20] Sénégas J,Vital JM,Pointillart V, et al. Long-term actuarial survivorship analysis ofan interspinous stabilization system. Eur Spine J. 2007;16: 1279-1287.
[21] Xu HZ,Wang XY, Chi YL, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a dynamic Pedicle screw fixation device. ClinBiomech(Bristol) Avon. 2006;21(4): 330-336.
[22] Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, et al. Surgical vs nonoperativetreatment forlumbar disk herniation: the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT)observational cohort. JAMA. 2006;296(20):2451–2459.
[23] Ambrossi GL, McGirt MJ, Sciubba DM, et al. Recurrentlumbar disc herniation after single-level lumbar discectomy:Incidence and health care cost analysis. Neurosurgery. 2009;65: 574-578 .
[24] Carragee EJ, Spinnickie AO, Alamin TF, et al. A prospectivecontrolled study of limited versus subtotal posteriordiscectomy: short-term outcomes in patients with herniatedlumbar intervertebral discs and large posterior anular defect.Spine. 2006;31:653-657.
[25] Barth M, Diepers M , Weiss C. Two-year outcome afterlumbar microdiscectomy versus microscopic sequestrectomy.Part 2: radiographic evaluation and correlation with clinicaloutcome. Spine. 2008;33:273-279.
[26] Barth M, Weiss C, Thomé C. Two-year outcome after lumbarmicrodiscectomyversus microscopic sequestrectomy: part 1: evaluation of clinical outcome. Spine. 2008;33: 265-272.
[27] Jerosch J, Castro WH. “Long-term results in revision surgery following lumbar disknucleotomy”. Z OrthopIhreGrenzgeb. 1996;134(1):89-96. |