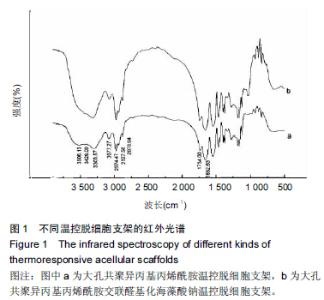
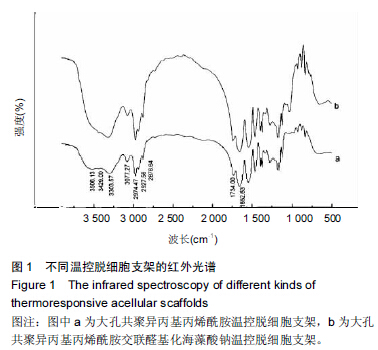
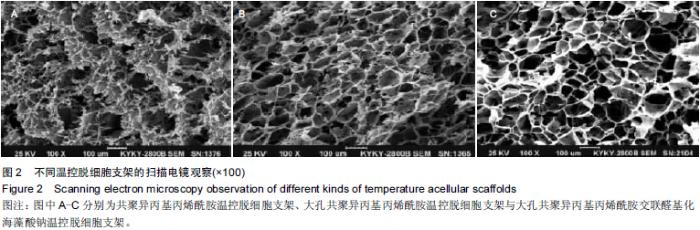
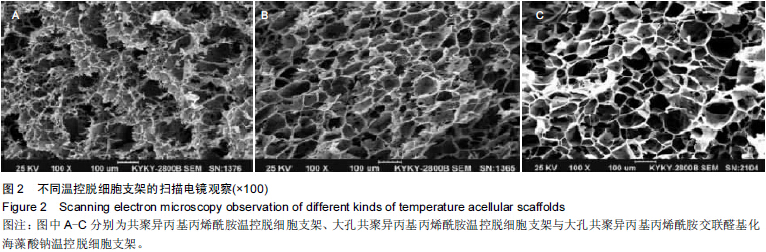
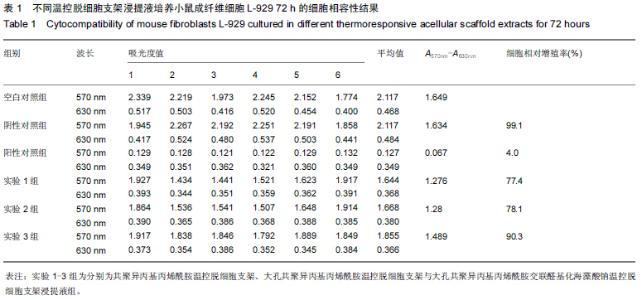
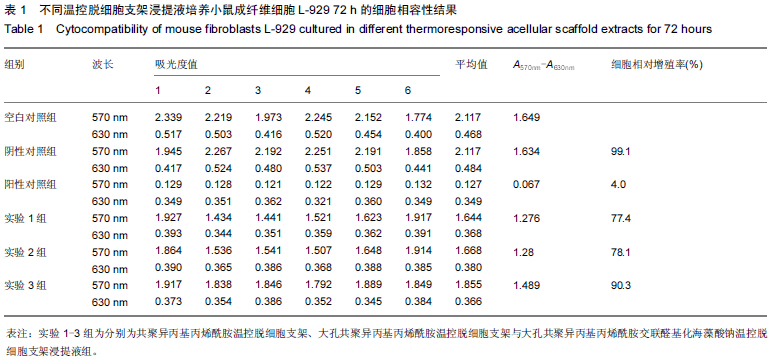
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (43): 7004-7009.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.43.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and performance of three kinds of thermoresponsive acellular carriers
An Shuai-xing1, Yu Mei-li2, Guo Hong-yue2, Li Tan2, Li Yang2
- 1Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Key Laboratory of Artificial Cells, Tianjin Third Central Hospital, Tianjin 300170, China
-
Received:2015-09-11Online:2015-10-15Published:2015-10-15 -
Contact:Yu Mei-li, Key Laboratory of Artificial Cells, Tianjin Third Central Hospital, Tianjin 300170, China -
About author:An Shuai-xing, Studying for master’s degree, Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:the Key Research Project of Tianjin Health Industry, China, No. 13KG110, 14KG109; a Project Funded by Tianjin Science and Technology, China; the Science and Technology Program of Tianjin, China, No. 11JCYBJC27700
Cite this article
An Shuai-xing, Yu Mei-li, Guo Hong-yue, Li Tan, Li Yang. Preparation and performance of three kinds of thermoresponsive acellular carriers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(43): 7004-7009.
share this article
|
[1] 邓洁.对人工肝安全有效性研究相关问题探讨[J].中国血液净化, 2011,10(8):458-460.
[2] Rafael B,Maria C,Javier V.Liver support systems:will theyever reach primetime. Curr Gastroenterol Rep.2013;15(3):1-7.
[3] 王英杰.人工肝在肝衰竭中的应用与评价[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2013,16(1):20-21.
[4] Ryska O,Pantoflicek T,Laszikova E,et al.Artificial liver supportsystem reduces intracranial pressure more sffectively than bioartificial system:an experimental study.Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(7):503-510.
[5] Rademacher S,Oppert M,Jörres A.Artificial extracorporeal liber support therapy inpatients with severe liver failure.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.2011;5(5):591-599.
[6] 郭予斌,李爱民,刘思德.生物人工肝细胞材料的研究进展[J].现代消化及介入诊疗,2013,18(1):53-55.
[7] 刘赛兰,章瀚文,潘天慧,等.猪内源性逆转录病毒与异种移植及生物人工肝安全性问题[J].肝脏,2013,18(2):125-129.
[8] Yamanakas T.Induction of pluripotent stem cell from mouse embiyonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell.2006;126(4):663-676.
[9] Lu LL,Liu YJ,Yang SG,et al.Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica.2006;91:1017-1026.
[10] Karahuseyinoglu S,Cinar O,Kilic E,et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells.2007;25(2):319-331.
[11] Weiss ML,Medicetty S,Bledsoe AR,et al.Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: p reliminary characterization and effect oftransp lantation in a rodent model of Parkinsonps disease. Stem Cells.2006;24:781-792.
[12] Sudo K,Kanno M,Miharada K,et al.Mesenchymal progenitors able to differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic, and/or adipogenic cells in vitro are present in most primary fibroblast-like cell populations.Stem Cells.2007;25:1610-1617.
[13] Hardy SA,Maltman DJ,Przyborski SA.Mesenchymal stem cells as mediators of neural differentiation.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2008;3:43-52.
[14] Titorencu I,Jinga VV,Constantinescu E,et al.Proliferation, differentiation and characterization of osteoblasts from human BM mesenchymal cells. Cytotherapy.2007;9:682-696.
[15] Troyer DL,Weiss ML.Wharton's jelly-derived cells are a primitive stromal cell population.Stem Cells.2008;26(3): 591-599.
[16] Kasuya J,Sudo R,Tamogami R,et al.Reconstruction of 3D stacked hepatocyte tissues use degradable, microporouspoly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)membranes.Biomaterials. 2012;33(9): 2693-2700.
[17] Moran EC,Baptista PM,Evans DW,et al.Evaluation of parenchymal fluid pressure in native and decellularized liver tissue.Biomed Sci Instrum.2012;4(8):303-309.
[18] Kasoju N,Bora U.Silk fibroin based biomimetic artificial extracellular matrix for hepatic tissue engineering applications. Biomed Mater.2012;7(4):1045-1055.
[19] Ducatti DR,Massi A,Noseda MD,et al.Production of carbohydrate building blocks from red seaweed polysaccharides. Efficient conversion of galactans into C-glycosyl aldehydes.Org Biomol Chem.2009;7(3):576-588.
[20] Gao C,Liu M,Chen J,et al.Interactions between bovine serum albumin and oxidized sodium alginate in solution.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2011;22(12):1639-1650.
[21] Okano T,Yamada N,Sakai H,et al.A novel recovery system for cultured cells using plasma-treated polystyrene dishes grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide).J Biomed Mater Res.1993; 27(10):1243-1251.
[22] Miyoshi H,Ehashi T,Kawai H,et al.Three-dimensional perfusion cultures of mouse and pig fetal liver cells in a packed-bed reactor:effect of medium flow rate on cell numbers and hepatic functions.J Biotechnol. 2010;148(4): 226-322.
[23] 于美丽,杜智,韩涛,等.醛基化海藻多糖复合材料作为人工肝载体的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(25):4660-4667
[24] Behbahan IS,Duan Y,Lam A,et al.New approaches in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells toward hepatocytes.Stem Cell Rev.2011; 7(3):748-759.
[25] Yi F,Liu GH,Izpisua Belmonte JC.Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived hepatocytes: rising promise for disease modeling, drug development and cell therapy. Protein Cell. 2012;3(4):246-250.
[26] Mohsin S,Shams S,Ali Nasir G,et al.Enhanced hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells after pretreatment with injured liver tissue.Differentiation.2011;81(1):42-48.
[27] Takahashi K,Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures bydefined factors.Cel1.2006;126(4):663-676.
[28] Moeller HC,Mian MK,Shrivastava S,et al.A microwell array system for stem cell culture. Biomaterials.2008;29(6): 752-763.
[29] Vierbuchen T,Ostermeier A,Pang ZP,et al.Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors.Nature. 2010;463(7284):1035-1041.
[30] Ieda M,Fu JD,Delgado-Olguin P,et al.Direct Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Functional Cardiomyocytes by Defined Factors.Cell.2010;142(3):375-386.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||