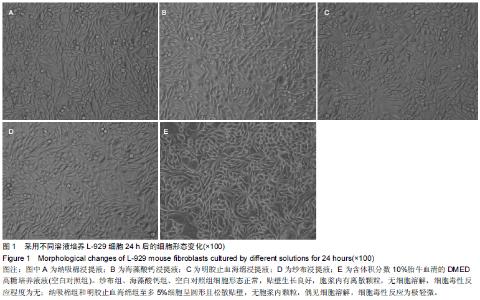
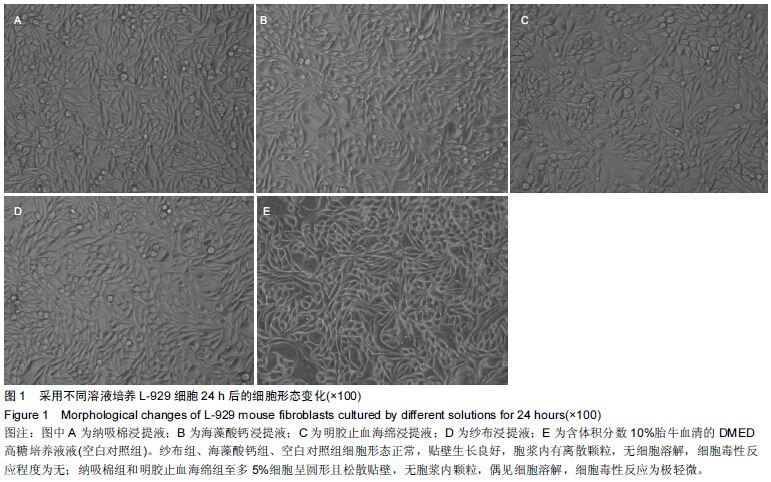
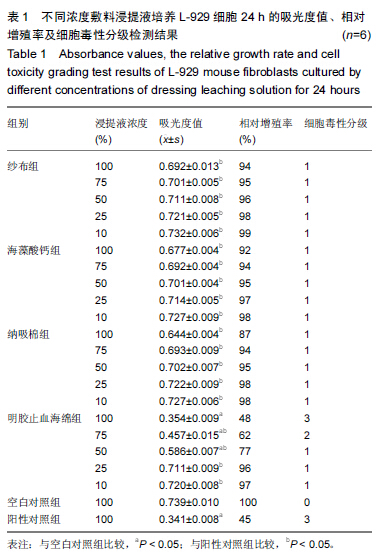
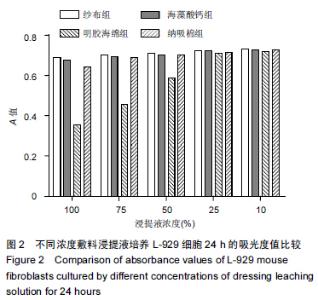
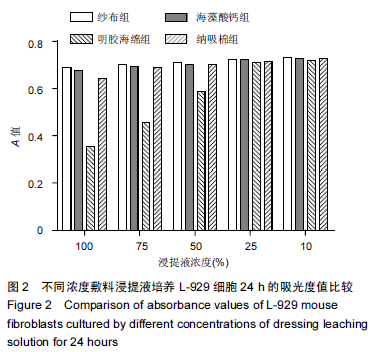
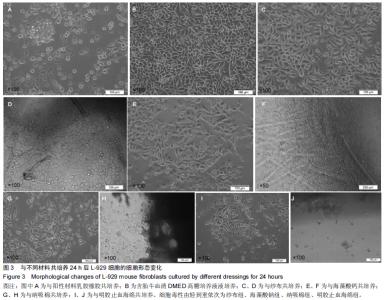
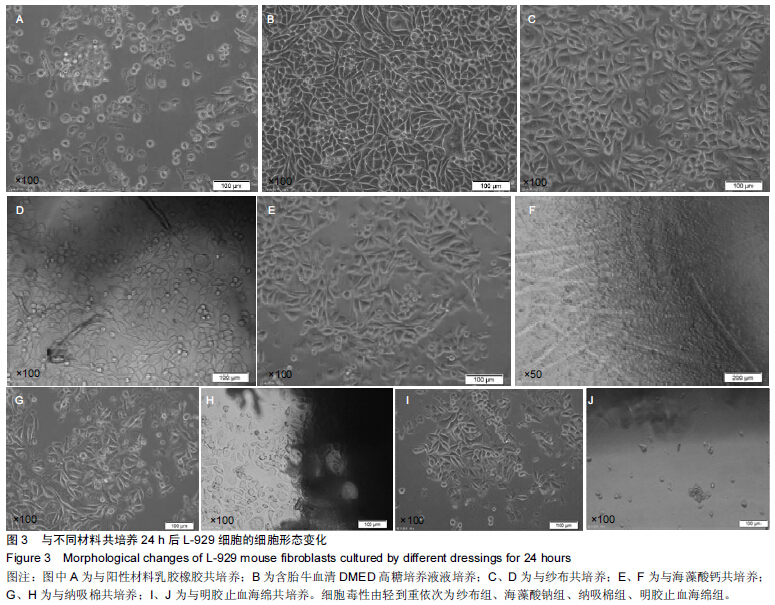
|
[1] 孙玉玲,刘杰.医用敷料用海藻纤维研究进展[J].科技信息,2010, 27(32):134-135.
[2] 黄若昆.可注射性骨组织工程载体研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(9):681-683.
[3] Jayakumar R,Prabaharan M,Sudheesh Kumar PT,et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications.Biotechnol Adv.2011;29(3):322-337.
[4] Lee KY, Mooney DJ. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Progr Polym Sci.2012;37(1):106-126.
[5] 汪涛,赵珺,张震,等.海藻酸钙敷料的细胞毒性体外测试结果分析[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2014,17(9):692-696.
[6] Kasseroller RG,Benner E.A prospective randomised study of algina tedrenched low stretch bandages as an alternative to conventional lymphologic compression bandaging. Support Care Cancer.2010;18(3):343-350.
[7] 秦益民.海藻酸纤维在医用敷料中的应用[J].合成纤维,2004, 32(4): 11-16.
[8] 张林朴,王冠华,连小丽,等.海藻酸钠/壳聚糖复合凝胶的制备与细胞毒性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3310-3315.
[9] 贾文英,史弘道.细胞毒性试验评价医用装置生物相容性的研究概况[J].实用美容整形外科杂志,2001,12(5):255-256.
[10] ISO,International Organization for Standardization.Biological evaluation of medical devices-Part 5:Test for in vitro cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization, 2009.
[11] 刘茜,兰华林,顾铭,等.贻贝粘蛋白创面修复敷料体外细胞毒性的检测方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(38):6785-6790.
[12] Gomes ME,Reis RL,Cunha AM,et al.Cytocompatibility and response of osteblastic-like cells to starch-based polymers: Effect of several additives and processing conditions. Biomaterials.2001;22(13):1911-1917.
[13] 奚延雯.组织工程医疗产品安全性评估[J].现代康复,2001,5(6): 13-15.
[14] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T16886.5 医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验,2003.
[15] Royal College of Nursing. The Management of Pressure Ulcers in Primary and Secondary Care: a Clinical Practice, Guideline. London: Royal College of Nursing, UK.2005.
[16] 林晓华,黎志超,俞金龙,等.新型复合生物抗菌敷料的抗菌强度、吸湿能力及细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16): 2905-2912.
[17] Pielesz A,Katarzyna B,Klimczak M.Physico-chemical properties of commercial active alginate dressings.Polirn Med.2008;38(4):3-17.
[18] 杨建德,韦元强,莫海龙,等.复合皮片移植治疗烧伤后功能部位瘢痕20例[J].中国组织工程研究与工临床康复,2007,11(8): 1544-1545.
[19] 李丽,周建平,胡宇驰.细胞浓度和作用时间对细胞毒性检查法影响的探讨[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(14):101-104.
|