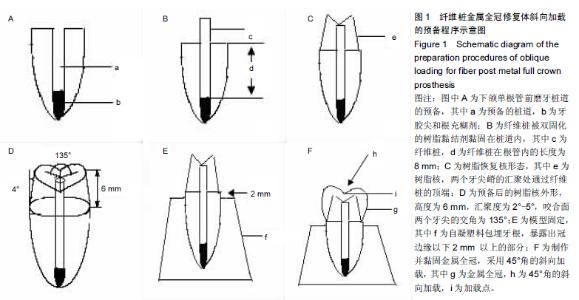
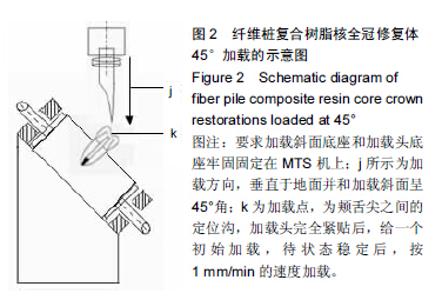
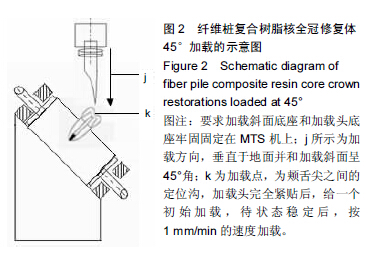
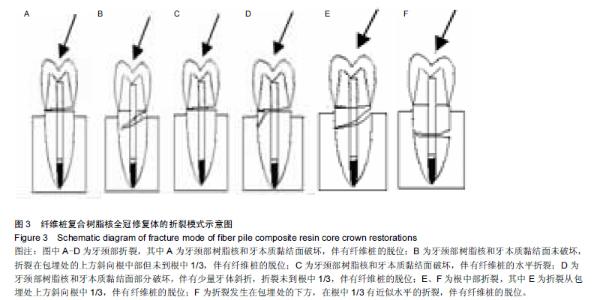
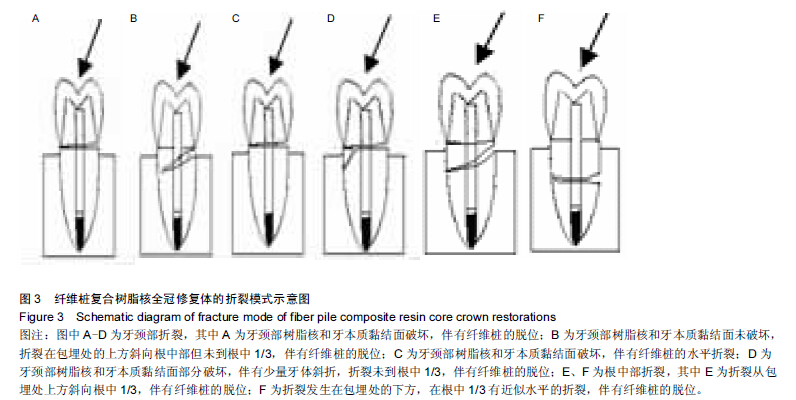
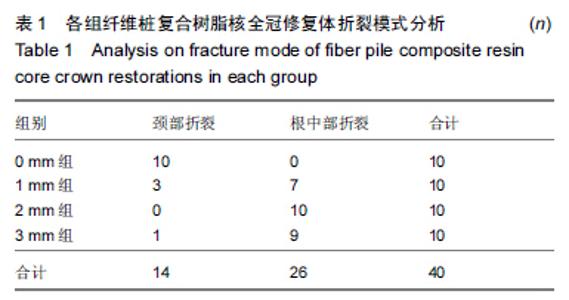
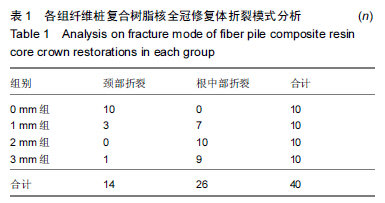
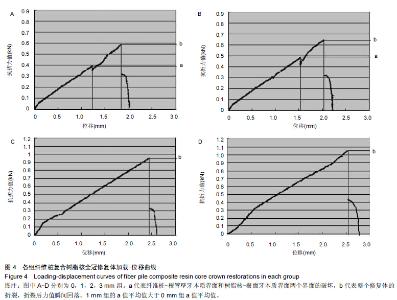
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (43): 6971-6976.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.43.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of the remaining amount of tooth on the fracture mode of fiber post-core full crown restoration
Nie Er-min1, Lu Jie2, Jiang Rui1, Zhang Chun-yuan1, Zeng Jin-di1, Tan Ji-zhou1
- 1Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Stomatology, the Second Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-07-29Online:2015-10-15Published:2015-10-15 -
Contact:Zhang Chun-yuan, Master, Professor, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Nie Er-min, Master, Attending physician, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Social Development Project of Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Department of China, No. 2011B080701010, 2012B061700066
Cite this article
Nie Er-min, Lu Jie, Jiang Rui, Zhang Chun-yuan, Zeng Jin-di, Tan Ji-zhou. Effects of the remaining amount of tooth on the fracture mode of fiber post-core full crown restoration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(43): 6971-6976.
share this article
|
[1] Mangold JT,Kern M.Influence of glass-fiber posts on the fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated premolars with varying substance loss: an in vitro study.J Prosthet Dent.2011;105(6):387-393.
[2] Santini MF,Wandscher V,Amaral M,et al.Mechanical fatigue cycling on teeth restored with fiber posts: impact of coronal grooves and diameter of glass fiber post on fracture resistance.Minerva Stomatol.2010;60(10):485-493.
[3] Hu C,Wang F,Yang H,et al.Preparation and characterisation of poly p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole fibre-reinforced resin matrix composite for endodontic post material: A preliminary study.J Dent.2014;42(12):1560-1568.
[4] Zogheib LV,Pereira JR,do Valle AL,et al. Fracture resistance of weakened roots restored with composite resin and glass fiber post. Braz Dent J.2008;19(4):329-333.
[5] Pereira JR,Valle AL,Shiratori FK,et al.Influence of intraradicular post and crown ferrule on the fracture strength of endodontically-treated teeth.Braz Dent J.2009;20(4): 297-302.
[6] Mangold JT,Kern M.Influence of glass-fiber posts on the fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated premolars with varying substance loss: an in vitro study.J Prosthet Dent.2011;105(6):387-393.
[7] Franco EB,Lins do Valle A,Pompéia Fraga de Almeida AL,et al.Fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth restored with glass fiber posts of different lengths.J Prosthet Dent.2014; 111(1):30-34.
[8] Santos-Filho PC,Veríssimo C,Raposo LH,et al.Influence of ferrule, post system, and length on stress distribution of weakened root-filled teeth.J Endod.2014;40(11):1874-1878.
[9] Ona M,Wakabayashi N,Yamazaki T,et al.The influence of elastic modulus mismatch between tooth and post and core restorations on root fracture.Int Endod J.2013;46(1):47-52.
[10] Chang JW,Soo I,Cheung GS.Evaluation of fiber post-supported restorations under simulated occlusal loading.J Prosthet Dent.2012;108(3):158-164.
[11] Ba?aran EG,Ayna E,Halifeo?lu M.Microleakage of endodontically treated teeth restored with 3 different adhesive systems and 4 different fiber-reinforced posts.J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107(4):239-251.
[12] Valdivia AD,Raposo LH,Simamoto-Júnior PC,et al.The effect of fiber post presence and restorative technique on the biomechanical behavior of endodontically treated maxillary incisors: an in vitro study.J Prosthet Dent.2012;108(3): 147-157.
[13] do Valle AL,Pereira JR,Shiratori FK,et al.Comparison of the fracture resistance of endodontically-treated teeth restored with prefabricated post and composite resin core with different post lengths.J Appl Oral Sci.2007;15(1):29-32.
[14] Farina AP,Weber AL,Severo Bde P,et al.Effect of length post and remaining root tissue on fracture resistance of fibre posts relined with resin composite.J Oral Rehabil.2015;42(3): 202-208.
[15] 鲁洁,聂二民,刘克瑾,等.机械力学评价不同长度石英纤维桩的抗折强度[J].中国组织工程研究,2013.17(3):483-488.
[16] 亓莉莉,聂二民,陈霞云,等.石英纤维桩复合树脂核全冠修复无髓牙的疲劳抗性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(12): 2167-2170.
[17] Nie EM,Chen XY,Zhang CY,et al.Influence of masticatory fatigue on the fracture resistance of the pulpless teeth restored with quartz-fiber post-core and crown.2012;4(4): 218-220.
[18] Zhou L,Wang Q.Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Cast Posts and Fiber Posts: A Meta-analysis of Literature.J Endod.2013;39(1):11-15.
[19] Ni CW,Chang CH,Chen TY,et al.A multiparametric evaluation of post-restored teeth with simulated bone loss.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2011;4(3):322-330.
[20] Sarkis-Onofre R, Jacinto Rde C, Boscato N, et al. Cast metal vs. glass fibre posts: A randomized controlled trial with up to 3 years of follow up. J Dent. 2014;42(5):582-587.
[21] Pereira JR,Valle AL,Ghizoni JS,et al.Evaluation of push-out bond strength of four luting agents and SEM observation of the dentine/fibreglass bond interface.Int Endod J.2013;46(10): 982-992.
[22] Nova V,Karygianni L,Altenburger MJ,et al.Pull-out bond strength of a fibre-reinforced composite post system luted with self-adhesive resin cements.J Dent.2013;41(11): 1020-1026.
[23] Santos-Filho PC,Veríssimo C,Soares PV,et al.Influence of Ferrule, Post System, and Length on Biomechanical Behavior of Endodontically Treated Anterior Teeth.J Endod.2014;40(1): 119-123.
[24] Juloski J,Apicella D,Ferrari M.The effect of ferrule height on stress distribution within a tooth restored with fibre posts and ceramic crown: A finite element analysis. Dent Mater.2014; 30(12):1304-1315.
[25] Juloski J,Radovic I,Goracci C,et al.Ferrule effect: a literature review. J Endod.2012;38(1):11-19.
[26] Schmitter M,Lippenberger S,Rues S,et al.Fracture resistance of incisor teeth restored using fibre-reinforced posts and threaded metal posts: effect of post length, location, pretreatment and cementation of the final restoration. Int Endod J.2010;43(5):436-442.
[27] Balkenhol M,Rupf S,Laufersweiler I,et al.Failure analysis and survival rate of post and core restorations under cyclic loading. Int Endod J.2011;44(10):926-937.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||