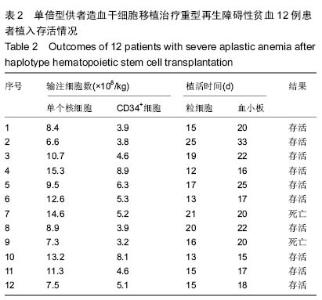
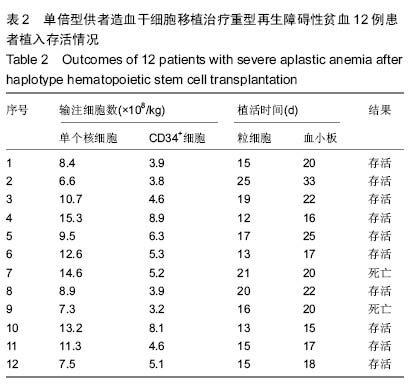
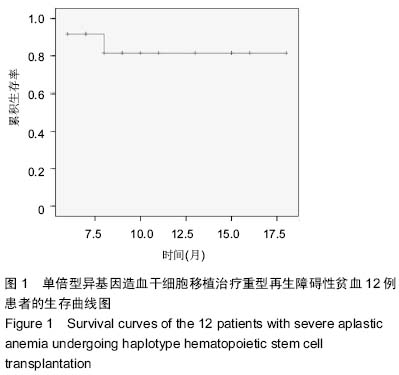
| [1] Yoshida N, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, et al. First-line treatment for severe aplastic anemia in children: bone marrow transplantation from a matched family donor versus immunosuppressive therapy. Haematologica. 2014;99(12): 1784-1791.
[2] Peinemann F, Bartel C, Grouven U. First-line allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation of HLA-matched sibling donors compared with first-line ciclosporin and/or antithymocyte or antilymphocyte globulin for acquired severe aplastic anemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7: CD006407.
[3] 郭智,陈惠仁,何学鹏,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植治疗儿童难治性或复发白血病30例[J].中华器官移植杂志,2013,34(1): 33-36.
[4] 郭智,陈惠仁,刘晓东,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植治疗儿童重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2014,29(15): 1145-1148.
[5] Lee YH, Kim JY, Choi BO, et al. Total lymphoid irradiation based conditioning for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Radiat Oncol J. 2012;30(4): 165-172.
[6] 陈惠仁.单倍型造血干细胞移植的新进展及其临床结果[J].中国组织工程研究,2008,12(34): 6735-6738.
[7] Ciurea SO, Mulanovich V, Saliba RM, et al. Improved early outcomes using a T cell replete graft compared with T cell depleted haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(12): 1835-1844.
[8] 闫洪敏,王志东,朱玲,等.多种来源造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10): 1884-1888.
[9] 孙璨,林遐,黄宇贤,等.采用含氟达拉滨的增强预处理异基因造血干细胞移植治疗22例重型再生障碍性贫血患者的临床研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2014,35(3):221-224.
[10] 陆婧媛,鹿全意,林进宗,等.单倍体相合造血干细胞移植治疗儿童重型再生障碍性贫血[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23):3768- 3772.
[11] Chun C, Fang JP, Xue HM, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for childhood aplastic anemia: prospective trial in China. Transfus Apher Sci. 2011;44(1):41-47.
[12] Sun ZM, Liu HL, Geng LQ, et al. HLA-matched sibling transplantation with G-CSF mobilized PBSCs and BM decreases GVHD in adult patients with severe aplastic anemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2010;3:51.
[13] 陈惠仁,楼金星,张媛,等.非血缘HLA相合供者造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的临床分析[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2012, 20(4): 959-964.
[14] 韩伟,黄晓军,刘开彦,等.配型不合造血干细胞移植治疗重型再生障碍性贫血的疗效及安全性[J].中华内科杂志,2011,50(4): 287-290.
[15] Esteves I, Bonfim C, Pasquini R, et al. Haploidentical BMT and post-transplant Cy for severe aplastic anemia: a multicenter retrospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50(5):685-689.
[16] 陈晓霞,王智明,罗贤生,等.改良BU/CY预处理方案在外周血造血干细胞移植中的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(14): 2638-2642.
[17] Hutspardol S, Sirachainan N, Anurathapan U, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96 Suppl 1: S18-24.
[18] Aversa F, Terenzi A, Tabilio A, et al. Full haplotype-mismatched hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase II study in patients with acute leukemia at high risk of relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(15): 3447-3454.
[19] Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, et al. A novel protocol for haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion in the treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47(12):1507-1512.
[20] Im HJ, Koh KN, Suh JK, et al. Refinement of treatment strategies in ex vivo T-cell-depleted haploidentical SCT for pediatric patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50(2): 225-231.
Gao L, Li Y, Zhang Y, et al. Long-term outcome of HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion for adult severe aplastic anemia after modified conditioning and supportive therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(4):519-524. |